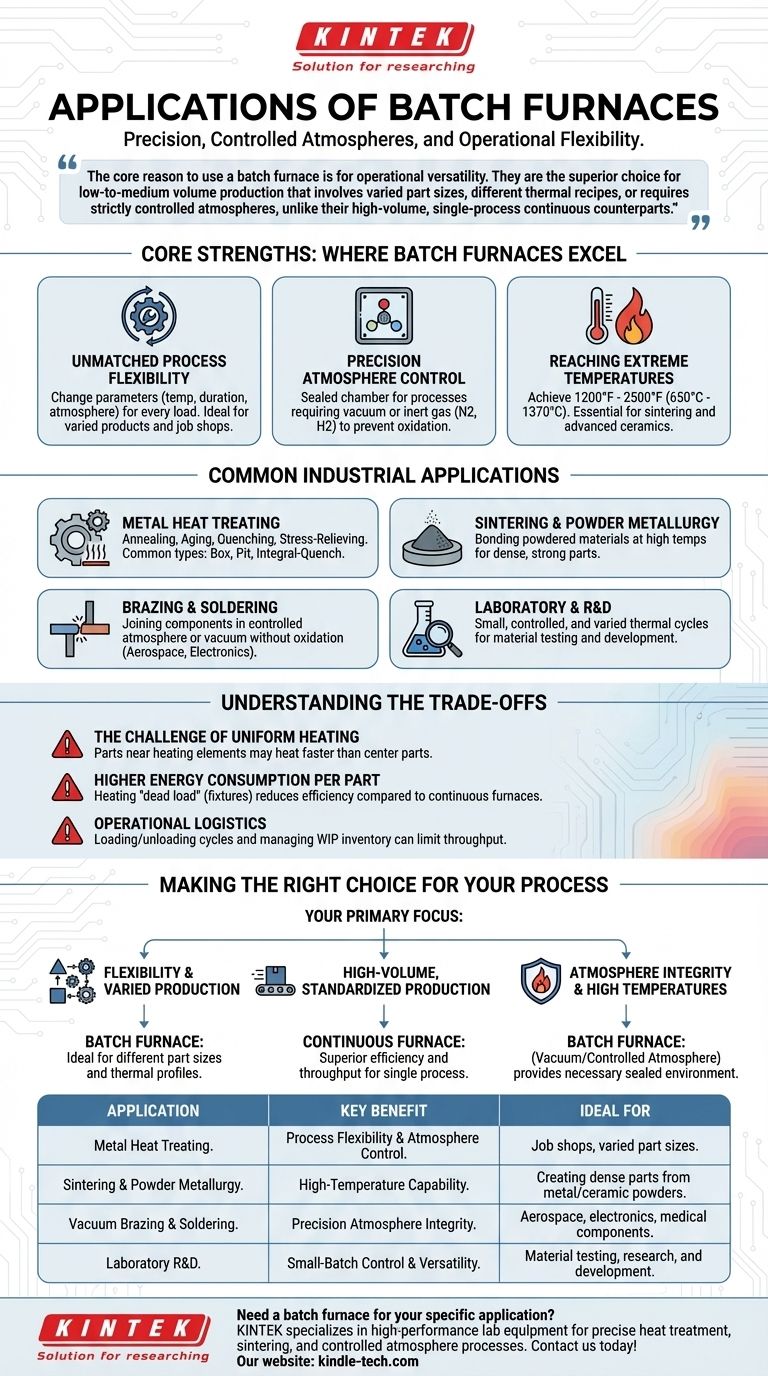
Batch furnaces are primarily applied in processes requiring high precision, controlled atmospheres, and operational flexibility. This includes a wide range of metal heat treatments like annealing and stress-relieving, high-temperature sintering for ceramics and powder metallurgy, and specialized vacuum or inert gas processes common in the aerospace, medical, and electronics industries.
The core reason to use a batch furnace is for operational versatility. They are the superior choice for low-to-medium volume production that involves varied part sizes, different thermal recipes, or requires strictly controlled atmospheres, unlike their high-volume, single-process continuous counterparts.

Core Strengths: Where Batch Furnaces Excel
Batch furnaces are defined by their ability to process materials one distinct group, or "batch," at a time. This fundamental design gives them several key advantages that make them indispensable for specific applications.
Unmatched Process Flexibility
Because each batch is a separate run, operators can change the process parameters—such as temperature, duration, and atmosphere—for every new load.
This makes them ideal for job shops or manufacturing environments that handle a variety of products with different processing requirements. They easily accommodate parts of various sizes and shapes.
Precision Atmosphere Control
Batch furnaces are closed-process machines, meaning the chamber is sealed during operation. This makes them exceptionally well-suited for processes that cannot tolerate oxygen.
Applications requiring a vacuum or a protective inert atmosphere (like nitrogen or hydrogen) almost always use batch furnaces to guarantee process integrity. This is critical for preventing oxidation in sensitive materials during brazing or heat treatment.
Reaching Extreme Temperatures
The design of many batch furnaces allows them to achieve very high temperatures, often between 1200℉ and 2500℉ (approx. 650°C to 1370°C).
This capability is essential for demanding applications like the sintering of powdered metals, firing advanced ceramics, and specialized glass melting processes.
Common Industrial Applications in Detail
The flexibility and control offered by batch furnaces make them a foundational tool in many critical industries.
Metal Heat Treating
This is one of the most common uses for batch furnaces. Processes include:
- Annealing: Softening metals to improve ductility.
- Aging: Hardening materials through controlled precipitation.
- Quenching: Rapidly cooling a part in a liquid to lock in specific material properties.
- Stress-Relieving: Reducing internal stresses caused by machining or welding.
Common furnace types for these tasks include box furnaces, pit furnaces, and integral-quench furnaces.
Sintering and Powder Metallurgy
Sintering involves heating compacted powder material to just below its melting point to bond the particles together.
Batch furnaces provide the high temperatures and controlled atmospheres necessary to create dense, strong parts from powdered metals or ceramics.
Brazing and Soldering
In controlled-atmosphere or vacuum batch furnaces, components can be joined using a filler metal without oxidizing or compromising the base materials. This is a crucial process in the aerospace and electronics industries for creating strong, clean joints.
Laboratory and R&D
The ability to run small, highly controlled, and varied thermal cycles makes batch furnaces perfect for research, development, and material testing environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, batch furnaces are not the solution for every heating application. Understanding their limitations is key to making an informed decision.
The Challenge of Uniform Heating
In a large batch, parts closest to the heating elements will heat up faster than those in the center of the load. This can lead to minor variations in material properties across the batch if not managed carefully.
Higher Energy Consumption per Part
Batch processing requires fixtures like baskets, trays, or racks to hold the parts. These fixtures must also be heated and cooled with every cycle.
This "dead load" increases the total energy required to process each part, making it less energy-efficient than a continuous furnace for high-volume production.
Operational Logistics
Batch processing requires grouping parts and managing work-in-process (WIP) inventory. Loading and unloading cycles create downtime between runs, which can limit overall throughput compared to a continuous flow.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision to use a batch furnace should be based on your specific production goals and process requirements.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility and varied production: A batch furnace is the ideal choice for its ability to handle different part sizes and thermal profiles on a run-by-run basis.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, standardized production: You should investigate continuous furnaces, which offer superior efficiency and throughput for a single, repeatable process.
- If your primary focus is atmosphere integrity and high temperatures: Batch furnaces, particularly vacuum and controlled atmosphere models, provide the necessary sealed environment for critical applications.
Ultimately, selecting a batch furnace is a strategic decision for operations that prioritize precision and adaptability over sheer production speed.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Metal Heat Treating (Annealing, Aging) | Process Flexibility & Atmosphere Control | Job shops, varied part sizes |
| Sintering & Powder Metallurgy | High-Temperature Capability | Creating dense parts from metal/ceramic powders |
| Vacuum Brazing & Soldering | Precision Atmosphere Integrity | Aerospace, electronics, medical components |
| Laboratory R&D | Small-Batch Control & Versatility | Material testing, research, and development |
Need a batch furnace for your specific application? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including batch furnaces for precise heat treatment, sintering, and controlled atmosphere processes. Our experts can help you select the right furnace to enhance your operational flexibility and material outcomes. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of using a high-temperature sintering furnace for PRP? Optimize Preform Structural Engineering
- How do induction heating systems with graphite hot zones function during mechanical testing? Achieve Ultra-High 2573 K
- What is the role of vacuum in deposition methods? Master Purity and Control for Superior Thin Films
- What is the purpose of using a vacuum furnace for diamond composites? Achieve High-Density Material Consolidation
- What is the temperature of a vacuum brazing furnace? Key metrics for precision joining
- What are three heat sources used to braze? Compare Torch, Furnace & Induction Methods
- What is the purpose of using vacuum-sealed ampoules with a furnace for Li6PS5Cl? Ensure Chemical Purity and Conductivity
- What is the role of a laboratory vacuum arc remelting furnace? Mastering High-Entropy Alloy Synthesis



















