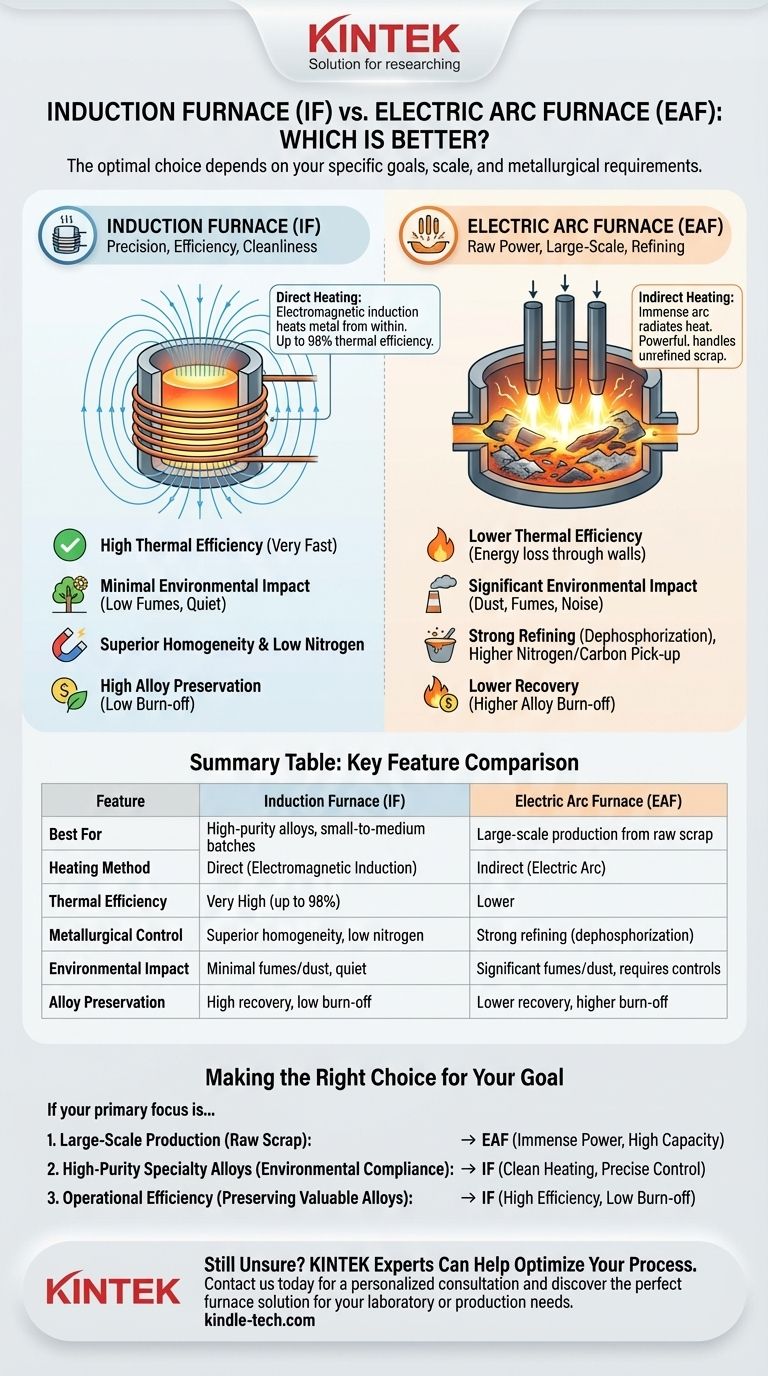
To be direct, neither the induction furnace (IF) nor the electric arc furnace (EAF) is universally "better." The optimal choice is entirely dependent on your specific operational goals, particularly concerning production scale, the type of raw material you use, and the final metallurgical quality required. An EAF is built for raw power and large-scale refining, while an IF excels at precision, efficiency, and cleanliness.
The core difference comes down to this: an Electric Arc Furnace is a high-volume refining tool best suited for melting large quantities of raw scrap, whereas an Induction Furnace is a high-precision melting instrument ideal for producing clean, specific alloys with maximum efficiency.
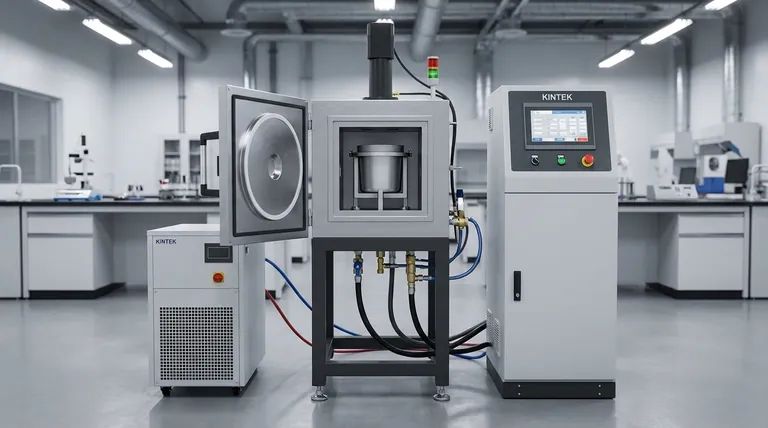

The Fundamental Difference in Heating Method
The choice between an EAF and an IF begins with understanding how each one generates heat. This core mechanism dictates nearly all of their respective strengths and weaknesses.
Electric Arc Furnace (EAF): The Brute Force Approach
An EAF melts metal using indirect heat. It creates an immense electrical arc between graphite electrodes and the metal charge inside.
This arc, reaching thousands of degrees, radiates intense heat that melts the scrap and the surrounding slag. This method is incredibly powerful and effective at handling large, unrefined materials like shredded scrap steel.
Induction Furnace (IF): The Precision Approach
An IF uses the principle of electromagnetic induction for direct heating. An electric coil generates a powerful, alternating magnetic field around the crucible containing the metal.
This magnetic field induces electrical currents directly within the metal itself, causing it to heat rapidly and efficiently from the inside out. This process is inherently cleaner and more controlled.
Comparing Core Performance Metrics
With the heating mechanism in mind, we can objectively compare the two technologies across the metrics that matter most in a foundry or steelmaking operation.
Speed and Thermal Efficiency
The IF is the clear winner here. Because heat is generated directly inside the metal, the process is extremely fast and has a much higher thermal efficiency—up to 98% in some designs.
The EAF is less efficient. It relies on transferring heat from the arc to the metal, losing significant energy through the furnace walls and cover.
Metallurgical Control and Quality
This area is more nuanced, with distinct advantages for each furnace.
The EAF's aggressive, high-temperature environment makes it highly effective at dephosphorization and refining raw, often impure, scrap metal. However, it introduces higher levels of nitrogen and risks carbon pick-up from the graphite electrodes.
The IF provides superior control. The electromagnetic stirring action ensures a perfectly homogeneous molten bath, critical for high-quality alloys. It avoids carbon pick-up entirely and produces steel with lower nitrogen, though it can result in higher oxygen content if not managed properly.
Environmental Impact
The induction furnace is significantly more environmentally friendly. It produces minimal exhaust gas, waste residue, and noise.
In contrast, the EAF process is known for generating considerable dust, fumes, and loud noise, requiring extensive environmental control systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Applications
The right choice becomes clear when you weigh the practical trade-offs against your specific application.
Operational Scale and Feedstock
The EAF is the undisputed leader for large-scale production. Its ability to melt hundreds of tons of raw, lower-cost scrap steel at a time makes it the backbone of modern "mini-mill" steelmaking.
The IF is better suited for small-to-medium batch sizes. It operates most efficiently with cleaner, pre-sorted scrap or known alloys, as its refining capabilities are more limited compared to an EAF.
Metal Recovery and Alloy Costs
The IF's gentle melting process results in a higher metal recovery rate and a much lower burn-off of expensive alloy elements. This can lead to significant cost savings when producing high-value alloys.
The EAF's violent process can cause a greater loss of valuable metals and alloys through oxidation and slag.
Operational Flexibility
EAFs are robust and generally well-suited for demanding, stop-and-start cycles.
Certain types of induction furnaces, particularly core-type designs, are most efficient when run continuously and are rarely allowed to cool, making them less flexible for operations with frequent alloy changes or intermittent schedules.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should not be based on which furnace is "better" in a vacuum, but which is the correct tool for your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is large-scale production from raw scrap: The EAF is the superior choice for its immense power, high capacity, and robust refining capabilities.
- If your primary focus is high-purity specialty alloys and environmental compliance: The IF is the clear winner due to its clean heating, precise temperature control, and minimal emissions.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency and preserving valuable alloys: The IF's high thermal efficiency and low element burn-off make it the more cost-effective instrument for creating high-quality final products.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace is a strategic decision that aligns the technology's inherent strengths with your business's core production requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Induction Furnace (IF) | Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | High-purity alloys, small-to-medium batches | Large-scale production from raw scrap |
| Heating Method | Direct (electromagnetic induction) | Indirect (electric arc) |
| Thermal Efficiency | Very High (up to 98%) | Lower |
| Metallurgical Control | Superior homogeneity, low nitrogen | Strong refining (dephosphorization) |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal fumes/dust, quiet | Significant fumes/dust, requires controls |
| Alloy Preservation | High recovery, low burn-off | Lower recovery, higher burn-off |
Still Unsure Which Furnace is Right for Your Lab or Production Line?
Choosing between an induction furnace and an electric arc furnace is a critical decision that impacts your product quality, efficiency, and bottom line. KINTEK, a trusted specialist in lab equipment and consumables, can help you navigate this complex choice.
We provide expert guidance and high-performance furnaces tailored to your specific operational goals—whether you're focused on producing high-purity specialty alloys or require robust, large-scale melting capabilities.
Let our experts help you optimize your process. Contact KINTEL today for a personalized consultation and discover the perfect furnace solution for your laboratory or production needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM



















