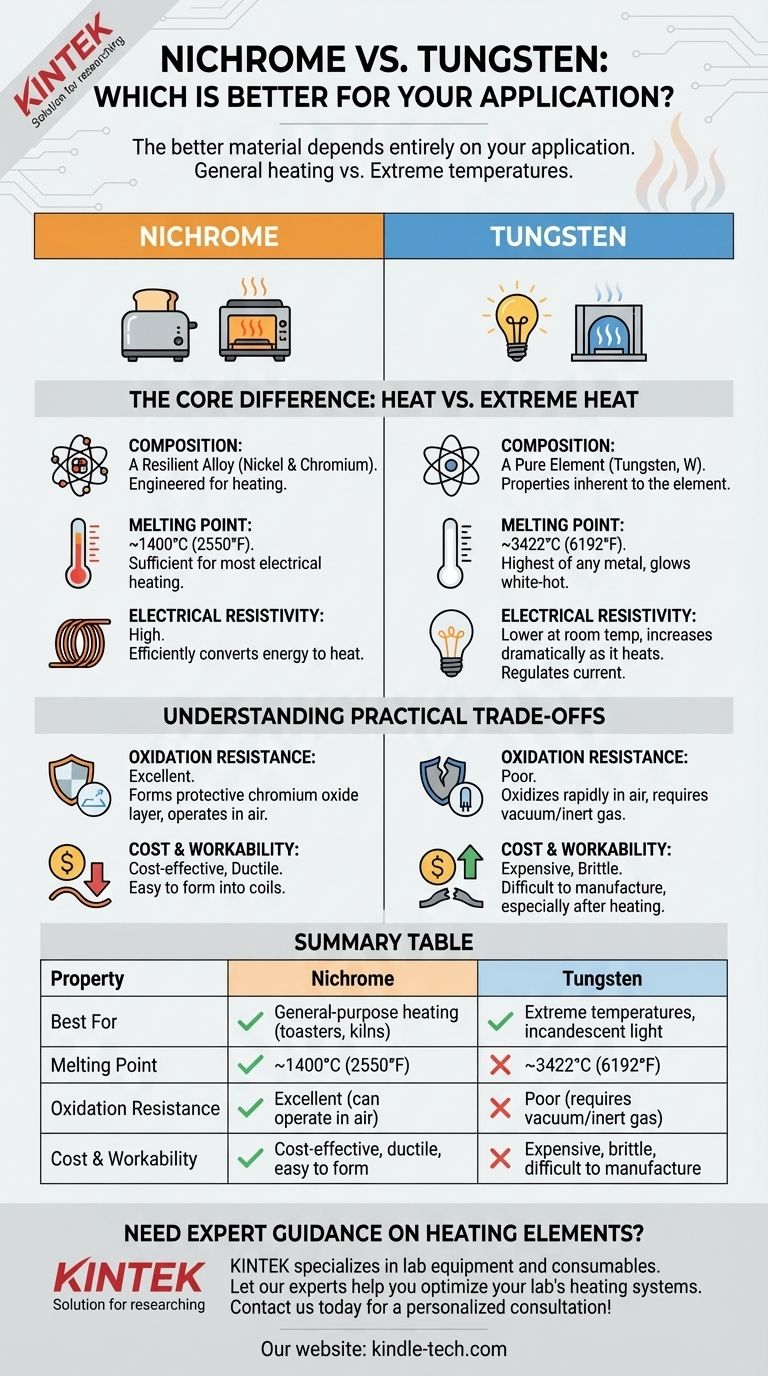
The better material depends entirely on your application. For general-purpose heating elements like those in toasters or kilns, Nichrome is superior due to its excellent oxidation resistance and lower cost. For applications requiring extreme temperatures to the point of incandescence, such as light bulb filaments, Tungsten is the only viable choice due to its exceptionally high melting point.
The choice between Nichrome and Tungsten is a classic engineering trade-off. Nichrome is the reliable, cost-effective workhorse for generating heat in open air, while Tungsten is the specialist for achieving extreme temperatures in a controlled, oxygen-free environment.
The Core Difference: Heat vs. Extreme Heat
The fundamental distinction between these two materials lies in their melting points and how they behave at high temperatures. This dictates their ideal use case.
Composition: A Resilient Alloy vs. a Pure Element
Nichrome is an alloy, typically composed of nickel and chromium. This combination is specifically engineered for its heating properties.
Tungsten is a pure, dense metallic element. Its properties are inherent to the element itself, not the result of a mixture.
Melting Point: The Deciding Factor
Nichrome has a melting point of around 1400°C (2550°F). This is more than sufficient for the vast majority of electrical heating applications.
Tungsten has the highest melting point of any metal at 3422°C (6192°F). This unique property allows it to glow white-hot without melting, which is the principle behind the incandescent light bulb.
Electrical Resistivity: How They Generate Heat
Nichrome possesses a high electrical resistivity. This is a desirable trait for a heating element, as it efficiently converts electrical energy into heat over a relatively short length of wire.
Tungsten has a lower resistivity at room temperature, but its resistance increases dramatically as it heats up. This property is critical for its function in light bulbs, helping to regulate the current as it reaches operating temperature.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
Beyond the core scientific properties, real-world factors like cost, durability, and operating environment are critical to making the right choice.
Oxidation Resistance: The Hidden Weakness of Tungsten
The chromium in Nichrome forms a passive layer of chromium oxide when heated. This protective layer makes it highly resistant to oxidation, allowing it to operate reliably in open air for long periods without degrading.
Tungsten, by contrast, oxidizes very rapidly at high temperatures. A hot tungsten filament exposed to oxygen will burn out almost instantly. This is why it must be enclosed in a vacuum or an inert gas environment, such as in a glass bulb.
Cost and Workability: Ease of Use
Nichrome is relatively inexpensive and ductile. It is easy to form into coils and other shapes needed for heating elements without breaking.
Tungsten is significantly more expensive and brittle, especially after being heated. This makes it more difficult and costly to manufacture into precise components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective determines the correct material. There is no single "better" option, only the right tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is a heating element for an appliance (toaster, kiln, hairdryer): Choose Nichrome for its ideal combination of high resistance, durability in air, and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is generating light or reaching extreme temperatures above 1400°C: Choose Tungsten for its unmatched melting point, but be prepared for its higher cost and the absolute necessity of an oxygen-free environment.
By aligning the material's fundamental properties with your project's requirements, you ensure an efficient, reliable, and cost-effective outcome.
Summary Table:
| Property | Nichrome | Tungsten |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | General-purpose heating (toasters, kilns) | Extreme temperatures, incandescent light |
| Melting Point | ~1400°C (2550°F) | ~3422°C (6192°F) |
| Oxidation Resistance | Excellent (can operate in air) | Poor (requires vacuum/inert gas) |
| Cost & Workability | Cost-effective, ductile, easy to form | Expensive, brittle, difficult to manufacture |
Need Expert Guidance on Heating Elements?
Selecting the right material is critical for your lab equipment's performance, efficiency, and longevity. The wrong choice can lead to premature failure, inconsistent results, and increased costs.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert solutions for all your heating needs. We can help you navigate these material trade-offs to ensure you get a reliable, cost-effective solution tailored to your specific application—whether it's for a furnace, oven, or specialized high-temperature process.
Let our experts help you optimize your lab's heating systems. Contact us today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the properties of molybdenum heating element? Choose the Right Type for Your Furnace Atmosphere
- Which high temperature furnace elements to be used in oxidizing atmosphere? MoSi2 or SiC for Superior Performance
- What is the thermal expansion coefficient of molybdenum disilicide? Understanding its role in high-temperature design
- What function do molybdenum disilicide heating elements perform? Precision Heat for Pulverized Coal Research
- What is the temperature range of a MoSi2 heating element? Unlock 1900°C Performance for Your Lab


















