The best heat source for brazing is the one that best matches your specific application. There is no single "best" method; the choice depends on factors like the materials being joined, the complexity of the assembly, your required production volume, and your budget. The most common methods include torch, furnace, induction, dip, and resistance brazing, each with distinct advantages.
The central challenge is not finding the "best" heat source, but rather understanding the trade-offs between speed, precision, cost, and scale. The ideal method provides the necessary thermal energy consistently and economically for your specific part and production goals.
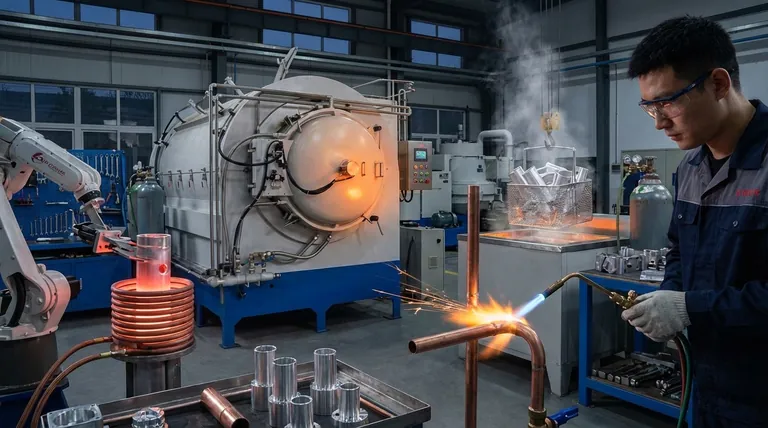
An Overview of Common Brazing Heat Sources
Each brazing method offers a unique profile of capabilities. Understanding how they work is the first step in making an informed decision.
Torch Brazing
How It Works: This is the most common manual or semi-automated method, using a gas flame (like oxy-acetylene or air-propane) to heat the base metals locally. The operator applies the flame to the joint area and introduces the filler metal once the brazing temperature is reached.
Primary Advantages: Torch brazing is valued for its low initial capital cost, portability, and flexibility. It is excellent for one-off repairs, prototyping, and low-volume production where a variety of joint types are encountered.
Ideal Applications: It is widely used in plumbing, HVAC repair, and small-scale fabrication. While it can be automated for higher volumes, it is most often associated with manual operations where operator skill is paramount.
Furnace Brazing
How It Works: Entire assemblies, with brazing filler metal pre-placed at the joints, are loaded into a furnace. The furnace heats the entire assembly to brazing temperature in a controlled atmosphere (like a vacuum or an inert gas) to prevent oxidation.
Primary Advantages: This method produces clean, high-quality joints with minimal distortion and is perfect for high-volume production. It allows for hundreds or thousands of parts—even those with multiple, inaccessible joints—to be brazed simultaneously.
Ideal Applications: Furnace brazing is a dominant process in the automotive and aerospace industries for manufacturing complex components like heat exchangers, fuel rails, and turbine blades.
Induction Brazing
How It Works: An alternating current is passed through a precisely shaped copper coil, creating an electromagnetic field. When the part is placed within or near the coil, this field induces eddy currents within the metal, generating rapid, localized heat exactly where it's needed.
Primary Advantages: Induction offers extremely fast heating cycles, exceptional precision, and high repeatability, making it ideal for automation. The heat is localized to the joint, minimizing the heat-affected zone and protecting the rest of the part.
Ideal Applications: This method excels in high-volume manufacturing of parts like electrical connectors, carbide-tipped cutting tools, and fuel line assemblies where speed and consistency are critical.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Key Selection Criteria
Your decision will ultimately balance four critical factors. Misjudging any of these can lead to poor quality, high costs, or production bottlenecks.
Production Volume and Speed
For low-volume work or repairs, the flexibility and low setup cost of torch brazing are unmatched. For high-volume, automated production lines, the speed and repeatability of induction brazing or the batch processing capability of furnace brazing are far superior.
Material and Part Complexity
If you are joining complex assemblies with multiple or internal joints, furnace brazing is often the only practical solution, as it heats the entire part uniformly. For brazing heat-sensitive components, the pinpoint accuracy of induction brazing allows you to heat the joint without damaging adjacent areas.
Capital Investment vs. Operating Cost
Torch brazing has the lowest barrier to entry, requiring minimal equipment investment. Induction and furnace brazing systems represent a significant capital expense but offer a much lower cost-per-part at high production volumes due to speed, energy efficiency, and reduced labor.
Operator Skill and Process Control
Manual torch brazing is highly dependent on operator skill for quality and consistency. In contrast, furnace and induction brazing are machine-controlled processes that, once set up correctly, deliver highly repeatable results with less need for specialized operator technique during the run.
How to Choose the Right Heat Source
Match the method to your most critical objective.
- If your primary focus is low-volume production or field repair: Torch brazing offers the best combination of low cost, portability, and flexibility.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, consistent manufacturing of complex parts: Furnace brazing provides unparalleled quality and throughput for assemblies with multiple joints.
- If your primary focus is speed and precision in an automated production line: Induction brazing delivers the fastest, most repeatable, and most localized heating available.
- If your primary focus is joining complex aluminum assemblies like heat exchangers: Dip brazing or controlled-atmosphere furnace brazing are the industry standards.
Ultimately, selecting the right heat source is about aligning the process capabilities with the technical and economic demands of your specific job.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Method | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Torch Brazing | Low-volume, repairs, prototyping | Low cost, flexibility, portability |
| Furnace Brazing | High-volume, complex assemblies | Batch processing, uniform heating, high quality |
| Induction Brazing | High-speed, automated production | Fast, precise, localized heat |
Still Unsure Which Brazing Method is Right for Your Lab?
Choosing the correct heat source is critical for achieving strong, reliable joints and maximizing your production efficiency. The experts at KINTEK specialize in lab equipment and consumables, including brazing solutions tailored to your specific materials, volume, and quality requirements.
We can help you:
- Analyze your application to recommend the most efficient and cost-effective brazing method.
- Source the right equipment to ensure consistent, high-quality results for your laboratory or production line.
Let's optimize your brazing process together. Contact our technical team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- What is brazing in heat treatment? Achieve Superior Joint Quality and Efficiency



















