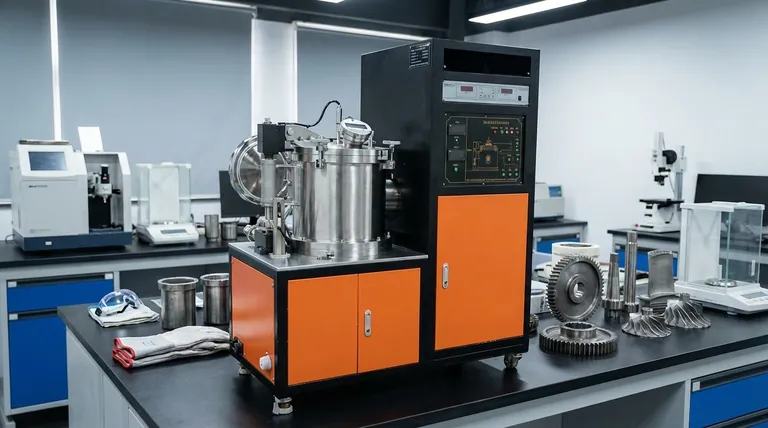
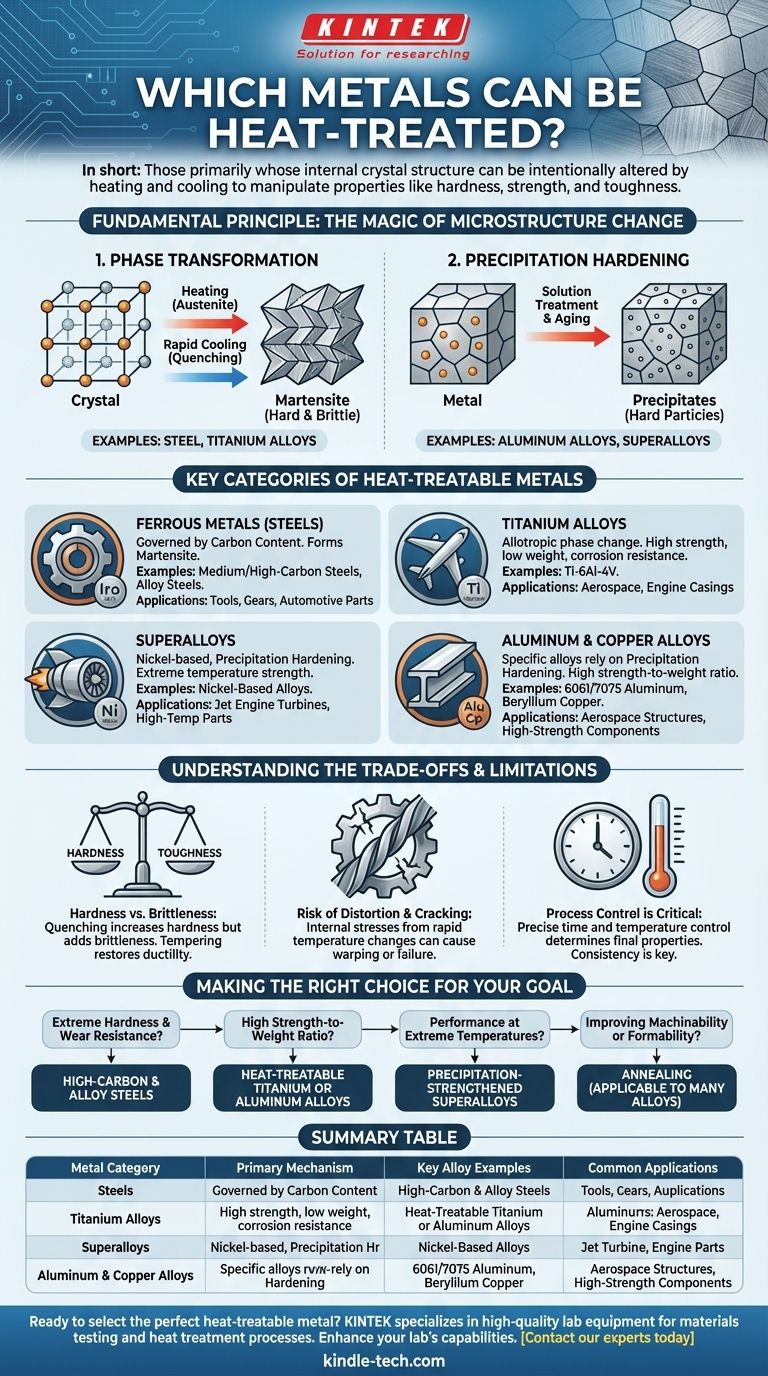
In short, the metals that can be heat-treated are primarily those whose internal crystal structure can be intentionally altered by heating and cooling. This includes most steels, many titanium alloys, nickel-based superalloys, and specific alloys of aluminum and copper. The goal is to manipulate properties like hardness, strength, and toughness to meet specific engineering demands.
The ability to heat-treat a metal is not a property of the base element (like iron or aluminum) but of the specific alloy. It fundamentally depends on the alloy's capacity to undergo a phase transformation or precipitation reaction, which changes its internal microstructure to achieve desired mechanical properties.

The Fundamental Principle: What Makes a Metal Heat-Treatable?
The "magic" of heat treatment happens at a microscopic level. It's about changing the metal's internal grain structure, or microstructure. Two primary mechanisms enable this transformation.
The Role of Phase Transformation
Many critical alloys, like steel and titanium, are allotropic. This means their underlying crystal lattice structure changes at specific temperatures.
For steel, this involves heating it until its structure shifts from a room-temperature phase (ferrite) to a high-temperature phase (austenite). Rapidly cooling or quenching it from the austenite phase traps the atoms in a new, highly strained, and very hard structure called martensite.
The Mechanism of Precipitation Hardening
Other alloys, particularly certain aluminum alloys and superalloys, don't rely on this type of phase shift. Instead, they use a process called precipitation hardening or age hardening.
In this method, the alloy is heated to dissolve certain elements into a solid solution and then cooled. A second, lower-temperature heating cycle (aging) causes tiny, hard particles to precipitate within the metal's grain structure. These particles act as microscopic obstacles, making the material significantly stronger and harder.
Key Categories of Heat-Treatable Metals
While many metals exist, only specific families of alloys are engineered for significant property changes through heat treatment.
Ferrous Metals (Steels)
Steel is the most common heat-treated metal. Its treatability is governed by its carbon content. The carbon atoms are what enable the formation of the hard martensite structure.
Low-carbon steels have limited hardenability, while medium- and high-carbon steels, as well as alloy steels containing elements like chromium or molybdenum, respond dramatically to heat treatment.
Titanium Alloys
Similar to steel, many titanium alloys are allotropic. They can be heat-treated to produce a fine-tuned balance of high strength, low weight, and excellent corrosion resistance. This makes them essential for high-performance applications like the aerospace components mentioned in the references, including engine casings and turbine blades.
Superalloys
Superalloys, typically based on nickel, are designed for extreme environments, especially high temperatures. Their strength comes almost entirely from precipitation hardening. The process creates a highly stable and strong microstructure that resists deformation even when close to its melting point, which is critical for jet engine parts.
Other Notable Alloys
It's important to remember that not all alloys within a family are treatable. Pure aluminum and pure copper cannot be hardened by heat treatment.
However, specific alloys like 6061 and 7075 aluminum or beryllium copper are designed specifically for precipitation hardening, allowing them to achieve strengths far exceeding their non-heat-treatable counterparts.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Heat treatment is a powerful tool, but it is not without its challenges. Understanding the associated compromises is critical for successful application.
Hardness vs. Brittleness
A core trade-off in heat treatment is between hardness and toughness. Quenching steel to make it extremely hard also makes it very brittle. This is why a secondary process called tempering is almost always required to reduce brittleness and restore some ductility, albeit at the cost of some hardness.
Risk of Distortion and Cracking
The rapid heating and cooling cycles inherent to heat treatment create significant internal stresses within a metal part. If not properly controlled, these stresses can cause the part to warp, distort, or even crack, rendering it useless.
Process Control is Critical
The final properties of a heat-treated component depend entirely on precise control over time and temperature. Minor deviations from the specified process can lead to drastically different and undesirable results, making consistent process management essential for quality control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right material and treatment depends entirely on the demands of the application.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness and wear resistance (e.g., tools, gears): High-carbon and alloy steels that can be quenched and tempered are your best choice.
- If your primary focus is high strength-to-weight ratio (e.g., aerospace structures): Heat-treatable titanium alloys or high-strength aluminum alloys are the ideal solution.
- If your primary focus is performance at extreme temperatures (e.g., jet engine turbines): Precipitation-strengthened nickel-based superalloys are specifically designed for this purpose.
- If your primary focus is improving machinability or formability: Annealing, a heat treatment process that softens metal, can be applied to a very wide range of alloys, including those not hardenable by quenching.
Ultimately, choosing a metal for heat treatment is about understanding and leveraging its potential to change its internal structure to achieve your specific engineering goal.
Summary Table:
| Heat-Treatable Metal Category | Primary Mechanism | Key Alloy Examples | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steels | Phase Transformation (Quenching & Tempering) | Medium/High-Carbon Steels, Alloy Steels | Tools, Gears, Automotive Parts |
| Titanium Alloys | Phase Transformation | Ti-6Al-4V | Aerospace Components, Engine Parts |
| Superalloys | Precipitation Hardening | Nickel-Based Alloys | Jet Engine Turbines, High-Temp Parts |
| Aluminum & Copper Alloys | Precipitation Hardening | 6061/7075 Aluminum, Beryllium Copper | Aerospace Structures, High-Strength Components |
Ready to select the perfect heat-treatable metal for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to support your materials testing and heat treatment processes. Whether you're working with advanced steels, titanium alloys, or superalloys, our products help you achieve precise temperature control and reliable results.
Let us help you enhance your lab's capabilities. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can support your success in materials science and engineering.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between firing and sintering? Master the Thermal Process for Stronger Materials
- Why is a program-controlled furnace critical for mixed-phase niobates? Master Precision in Solid-State Synthesis
- What is the difference between solid state sintering and liquid state sintering? Choose the Right Method for Your Materials
- How does heating in a muffle furnace after vacuum sealing study WTaVTiZrx alloys? Enhance High-Temp Material Stability
- How does a high-temperature laboratory furnace control hydrated RuO2 conversion? Achieve Precision Phase Transformation
- What is the application of ashing? A Guide to Mineral Content Analysis
- What are the advantages of sintered materials? Achieve High-Performance, Custom Material Properties
- What are the disadvantages of dry ashing? Key Limitations for Accurate Elemental Analysis



















