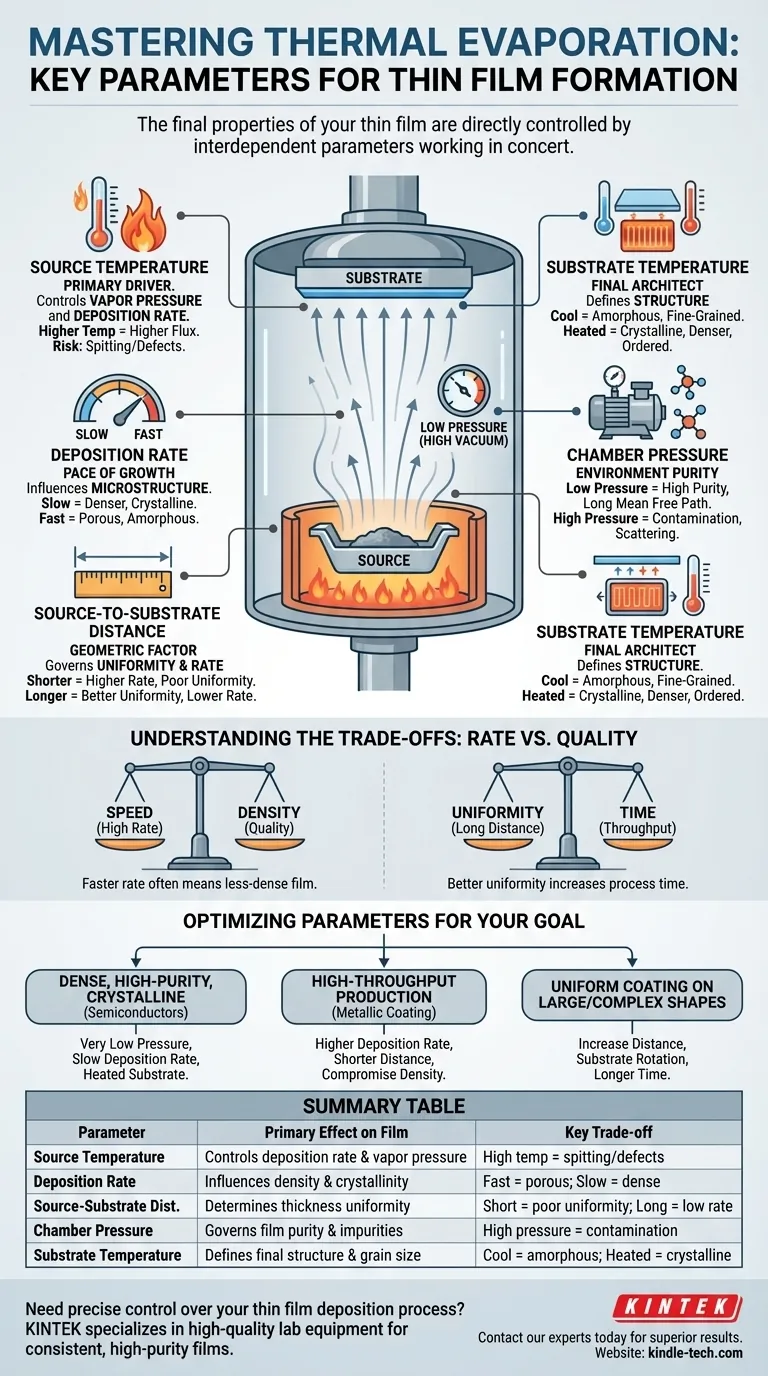
In thermal evaporation, the final properties of your thin film are directly controlled by three primary factors: the temperature of the material source, the resulting deposition rate, and the physical distance between the source and the substrate. These parameters work in concert with the vacuum environment and substrate conditions to dictate everything from film thickness and uniformity to its fundamental microstructure.
The central challenge in thermal evaporation isn't merely depositing material, but precisely balancing interdependent parameters. Your control over source temperature, chamber pressure, and system geometry is what determines whether you produce a high-quality, functional film or an unusable, contaminated layer.

The Key Parameters Dictating Film Formation
Thermal evaporation is fundamentally a process of boiling a material in a vacuum and allowing its vapor to condense onto a cooler surface (the substrate). Each step of this journey—from atom leaving the source to atom arriving at the substrate—is a control point.
Source Temperature: The Engine of Evaporation
The temperature of the evaporation source (e.g., a tungsten boat or an electron-beam-heated crucible) is the primary driver of the entire process.
Increasing the source temperature exponentially increases the material's vapor pressure. This results in a higher flux of atoms leaving the source.
This parameter is the main lever you pull to adjust the deposition rate. However, excessively high temperatures can damage the source material or cause spitting, where small solid chunks are ejected, creating defects in your film.
Deposition Rate: The Pace of Growth
While set by temperature, the deposition rate is often the parameter you measure and control directly, typically with a quartz crystal microbalance. It is a critical factor influencing the film's microstructure.
A slow deposition rate gives arriving atoms more time to move around on the substrate surface and find low-energy sites. This promotes the growth of a denser, more uniform, and often more crystalline film.
A fast deposition rate can "bury" atoms before they have time to settle, often resulting in a more porous, less dense, and potentially amorphous or fine-grained film structure.
Source-to-Substrate Distance: The Geometric Factor
The distance between the source and the substrate governs both the deposition rate and the film's uniformity. The vapor cloud expands from the source, meaning its density decreases with distance.
A shorter distance results in a higher deposition rate but can lead to poor thickness uniformity, with the film being thickest directly above the source.
A longer distance allows the vapor flux to become more uniform before it reaches the substrate, improving coating evenness over a larger area. However, this comes at the cost of a significantly lower deposition rate and a higher chance of atoms colliding with residual gas molecules.
Chamber Pressure: The Purity of the Environment
The quality of the vacuum is not a minor detail; it is essential. The base pressure and working pressure of your chamber determine the purity of your film.
A low pressure (high vacuum) minimizes the number of residual gas molecules (like oxygen or water). This ensures the evaporated atoms have a clear, collision-free path to the substrate, a long mean free path.
A high pressure (poor vacuum) leads to collisions that scatter the evaporated atoms, reducing deposition rate and energy. More importantly, it allows residual gases to become trapped in the growing film, creating impurities that degrade its electrical, optical, and mechanical properties.
Substrate Temperature: The Final Architect of Structure
The temperature of the substrate itself plays a decisive role in the final structure of the film.
A cool substrate reduces the surface mobility of arriving atoms, "freezing" them in place quickly. This tends to produce amorphous or very fine-grained films.
A heated substrate provides thermal energy to the arriving atoms, allowing them to diffuse across the surface. This facilitates the formation of larger crystal grains and a denser, more ordered film structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Rate vs. Quality
Optimizing thermal evaporation is an exercise in managing competing priorities. The choices you make inherently involve trade-offs that impact your final result.
The Speed vs. Density Compromise
The most common trade-off is between deposition speed and film quality. Increasing the source temperature to achieve a faster deposition rate often leads to a less-dense, more disordered film structure. For high-quality optical or electronic films, a slow, controlled growth is almost always superior.
The Uniformity vs. Time Compromise
Achieving high uniformity over a large substrate area requires increasing the source-to-substrate distance. This, however, dramatically reduces the deposition rate, leading to much longer process times. For industrial applications, this trade-off directly impacts throughput and cost.
Optimizing Parameters for Your Goal
The "correct" settings depend entirely on the desired outcome for your thin film. Use the following as a guide to balance the parameters for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is a dense, high-purity, crystalline film (e.g., for semiconductors): Prioritize a very low chamber pressure, a slow deposition rate, and consider heating the substrate to promote organized growth.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput production (e.g., for a simple metallic coating): You can use a higher deposition rate and a shorter source-to-substrate distance, accepting a potential compromise on film density and uniformity.
- If your primary focus is coating a large, complex shape uniformly: Increase the source-to-substrate distance and consider implementing substrate rotation, but be prepared for significantly longer deposition times.
Mastering these interconnected parameters is the key to transforming thermal evaporation from an art into a repeatable and precise manufacturing science.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Primary Effect on Film | Key Trade-off |
|---|---|---|
| Source Temperature | Controls deposition rate and vapor pressure. | High temp can cause spitting/defects. |
| Deposition Rate | Influences density and crystallinity. | Fast rate = porous film; slow rate = dense film. |
| Source-Substrate Distance | Determines thickness uniformity. | Short distance = poor uniformity; long distance = low rate. |
| Chamber Pressure | Governs film purity and impurity levels. | High pressure = contamination; low pressure = high purity. |
| Substrate Temperature | Defines final film structure and grain size. | Cool substrate = amorphous; heated substrate = crystalline. |
Need precise control over your thin film deposition process? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for thermal evaporation and other vacuum coating techniques. Our expertise helps laboratories achieve consistent, high-purity films for applications in semiconductors, optics, and materials research. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can optimize your setup for superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the most commonly used metals in a vacuum furnace's hot zone? Discover the Key to High-Purity Processing
- Can an arc happen in a vacuum? Yes, and here's how to prevent it in your high-voltage design.
- How hot does a furnace heat exchanger get? Understand Safe Operating Temperatures to Prevent Hazards
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space
- What are the safety precautions in a heat treatment process? A Guide to Engineering, Administrative, and PPE Controls



















