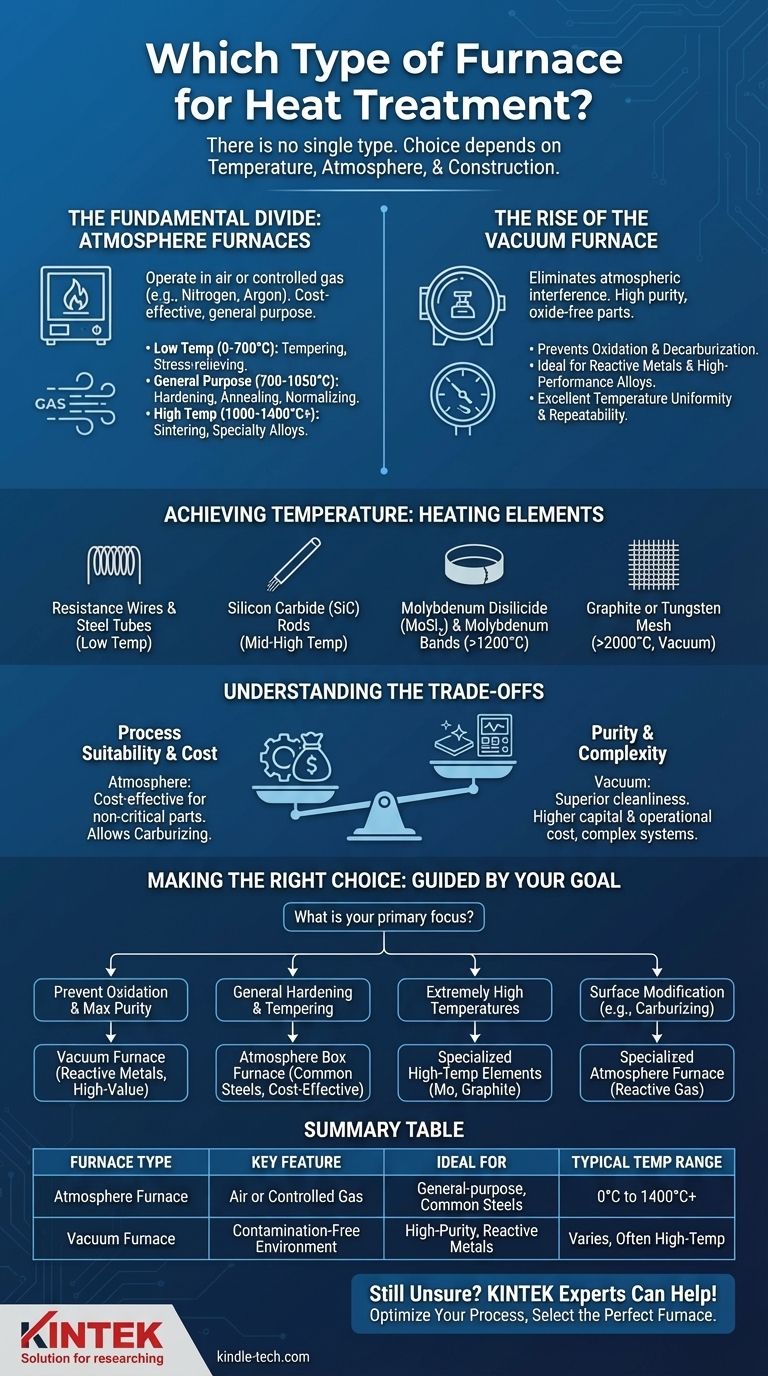
There is no single type of furnace for heat treatment. Instead, furnaces are categorized by their operating temperature, the atmosphere they use, and their physical construction. The most fundamental distinction is between conventional atmosphere furnaces, which operate in air or a controlled gas, and vacuum furnaces, which provide a highly controlled, contamination-free environment.
The critical decision is not about finding one "heat treatment furnace," but about matching the furnace's capabilities—specifically its atmosphere control and temperature range—to the precise requirements of your material and desired metallurgical outcome.

The Fundamental Divide: Atmosphere vs. Vacuum
The most important choice you will make is the furnace's processing environment. This single factor dictates the quality, purity, and surface finish of the final component.
Conventional Atmosphere Furnaces
A conventional or "atmosphere" furnace is the most common and straightforward type. It often takes the form of a box-type furnace.
These furnaces operate either in ambient air or with a controlled, flowing gas (like nitrogen or argon) to reduce oxidation. They are typically classified by their temperature range, which dictates their application:
- Low Temperature (0 to 700°C): Used for processes like tempering and stress-relieving of steel.
- General Purpose (700 to 1050°C): Suitable for hardening, normalizing, and annealing common alloys.
- High Temperature (1000 to 1400°C+): Required for specialty alloys, sintering, and some brazing operations.
The Rise of the Vacuum Furnace
A vacuum furnace is a more advanced technology where the heat treatment process occurs in a chamber with the air removed. This environment is defined as being below one standard atmosphere.
The primary benefit is the elimination of atmospheric interference. By removing oxygen and other gases, vacuum furnaces prevent oxidation and decarburization, resulting in clean, bright, oxide-free parts.
This precision environment ensures excellent temperature uniformity, process repeatability, and reliability, making it ideal for high-performance applications in aerospace, medical, and electronics.
How Furnaces Achieve Different Temperatures
A furnace's maximum temperature and efficiency are dictated by the type of heating element used within its chamber.
Selecting the Right Heating Element
Different materials are used for heating elements based on their temperature resistance and stability.
- Resistance Wires & Stainless Steel Tubes: Common in lower-temperature furnaces for tempering and annealing.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC) Rods: A versatile choice for general-purpose and mid-to-high temperature furnaces.
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) & Molybdenum Bands: Used for high-temperature applications requiring rapid heating and excellent stability above 1200°C.
- Graphite or Tungsten Mesh: Reserved for very-high-temperature or vacuum applications, capable of exceeding 2000°C.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing process requirements with operational realities. There is no universally superior option.
Process Suitability vs. Purity
While a vacuum furnace offers superior cleanliness, not every process requires it. Simple tempering or annealing of non-critical parts can often be done more cost-effectively in a conventional atmosphere furnace.
Furthermore, some processes like carburizing or carbonitriding are impossible in a vacuum. These treatments fundamentally require a specific, carbon-rich atmosphere to introduce elements into the material's surface.
Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces represent a significantly higher capital investment than atmosphere furnaces. They also involve more complex subsystems, including vacuum pumps, seals, and advanced controls.
This complexity translates to higher operational costs and requires more specialized knowledge for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Material Compatibility
The primary advantage of a vacuum furnace—preventing oxidation—is most critical for reactive metals and high-performance alloys. For many common carbon and low-alloy steels, the benefits may not justify the added cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be guided by your end goal. Match the furnace technology to your specific process requirements.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation and achieving maximum material purity: A vacuum furnace is the definitive choice, especially for reactive metals or high-value components.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose hardening or tempering of common steels: A conventional box-type atmosphere furnace is often the most practical and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is reaching extremely high temperatures for specialty alloys or ceramics: You must select a furnace with the appropriate high-temperature heating elements, such as molybdenum or graphite.
- If your primary focus is a surface modification process like carburizing: You need a specialized atmosphere furnace designed specifically to handle controlled, reactive gas environments.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace is an engineering decision that balances the need for quality against the constraints of cost and complexity.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Key Feature | Ideal For | Typical Temp Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Furnace | Operates in air or controlled gas | General-purpose hardening, tempering, annealing of common steels | 0°C to 1400°C+ |
| Vacuum Furnace | Contamination-free, oxygen-free environment | High-purity applications, reactive metals (aerospace, medical) | Varies, often high-temp |
Still Unsure Which Furnace is Right for Your Heat Treatment Process?
Choosing the correct furnace is critical to achieving your desired material properties and product quality. The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing the ideal lab equipment, including both atmosphere and vacuum furnaces, tailored to your specific material and process requirements.
Let us help you:
- Optimize your heat treatment process for superior results.
- Select the perfect furnace based on your temperature, atmosphere, and material needs.
- Ensure reliability and repeatability in your laboratory operations.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum drying oven required for NCM-811 and LTO? Ensure Stability in Solid-State Battery Assembly
- What is the application of quenching effect? Achieve Superior Hardness and Strength in Materials
- What is the function of the furnace in the laboratory? A Tool for Precise Thermal Transformation
- What materials are used in vacuum chambers? Choose the Right Material for Your Vacuum Level
- What is the sintering process of powder metallurgy? Transform Powder into Durable Metal Parts
- What is the function of a vacuum arc melting furnace? Master Homogeneity for Fe-Co Metallic Glasses
- What could happen if you overheated the brazing joint before adding filler metal? Avoid These Common Brazing Failures
- What is the most important factor influencing the strength of the brazed joint? Master Joint Clearance for Maximum Strength



















