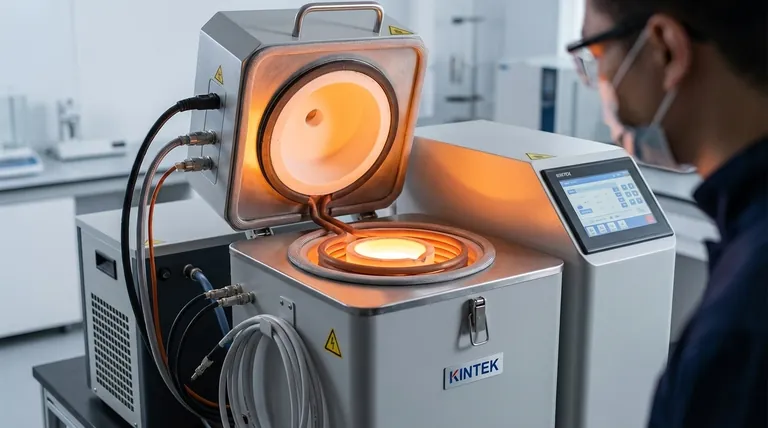
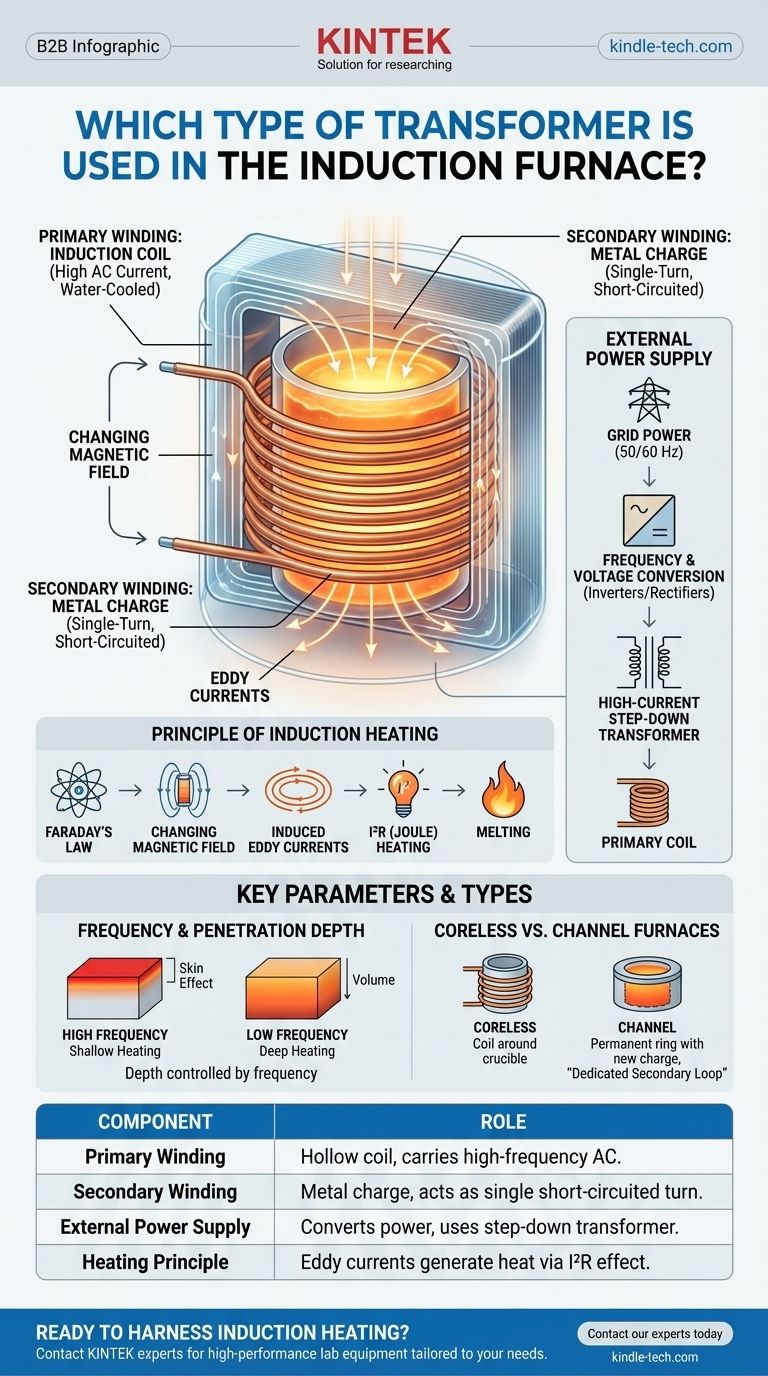
Crucially, an induction furnace does not use a conventional transformer for heating; instead, the furnace itself operates on the core principles of a transformer. The system is designed so that the furnace's primary coil induces a current directly into the metal being heated, which acts as the secondary coil.
The fundamental concept to grasp is that an induction furnace is a transformer where the primary winding is the furnace's induction coil and the secondary winding is the conductive metal charge itself, which is effectively a single, short-circuited turn.

The Induction Furnace as a Transformer System
To understand how this works, it's best to break the system down into its two essential "transformer" components: the primary and the secondary. This relationship is the basis for all induction heating.
The Primary Winding: The Induction Coil
The primary side of this system is a hollow copper coil. A powerful alternating current (AC), often at a medium or high frequency, is passed through this coil.
Because the coil carries a very high current, it generates significant heat. To prevent it from melting, it is continuously cooled, typically with circulating water.
The Secondary Winding: The Metal Charge
The secondary side is the metal to be heated or melted, known as the charge. This conductive material is placed inside the crucible, which is surrounded by the primary induction coil.
The metal charge acts as a single-turn secondary winding that is, by its very nature, short-circuited.
The Principle of Induction Heating
When AC flows through the primary coil, it generates a strong, rapidly changing magnetic field around it.
According to Faraday's Law of Induction, this changing magnetic field cuts through the metal charge (the secondary) and induces powerful circulating currents within it. These are known as eddy currents.
The metal has natural electrical resistance. As these massive eddy currents flow against this resistance, they generate immense heat due to the I²R effect (Joule heating), causing the metal to heat up and eventually melt.
The Role of the External Power Supply
While the furnace itself acts as the transformer for heating, the entire system relies on a sophisticated external power supply. This unit often contains its own transformers, but their role is to condition the power, not to perform the heating itself.
Frequency and Voltage Conversion
Standard grid power (50/60 Hz) is often not suitable for efficient induction heating. A dedicated power supply is used to convert the incoming power to the desired frequency and voltage.
This power unit uses components like inverters and rectifiers to achieve the correct frequency.
The Furnace Transformer
The power supply also includes a specialized, high-current, step-down transformer. Its job is to take the higher voltage from the power source and convert it to a lower voltage with a very high current.
This high current is what's needed to flow through the primary induction coil to create a magnetic field strong enough for efficient heating.
Understanding the Key Parameters
The efficiency and effectiveness of an induction furnace are not accidental. They depend on a careful balance of electrical principles, most notably the choice of operating frequency.
Frequency and Penetration Depth
The frequency of the AC power is a critical parameter that dictates how the metal heats. This is governed by a principle called the skin effect.
Higher frequencies cause the induced eddy currents to concentrate near the surface of the metal, resulting in shallow, rapid heating. Lower frequencies allow the magnetic field to penetrate deeper, heating more of the material's volume.
Coreless vs. Channel Furnaces
The system described above primarily refers to a coreless induction furnace, which is the most common type.
There is another type, the channel induction furnace, which functions even more like a traditional transformer. It maintains a permanent ring of molten metal that acts as a dedicated secondary loop, into which new material is added.
How to Apply This to Your Understanding
Your interpretation of the "transformer" in an induction furnace system depends entirely on your frame of reference.
- If your primary focus is the heating principle: View the furnace's coil as the primary and the metal charge as the single-turn, short-circuited secondary of a transformer.
- If your primary focus is the electrical supply: Recognize that a high-current, step-down transformer is a critical component within the power supply unit that feeds the furnace coil.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: Understand that the operating frequency is the key variable that determines the depth and speed of heating.
By understanding that the furnace and its charge form a unique transformer system, you can grasp the fundamental principle that makes induction heating so effective.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in the Induction Furnace System |
|---|---|
| Primary Winding | The hollow, water-cooled copper induction coil carrying high-frequency AC. |
| Secondary Winding | The metal charge itself, acting as a single-turn, short-circuited coil. |
| External Power Supply | Converts grid power and uses a step-down transformer to provide high current to the coil. |
| Heating Principle | Eddy currents induced in the metal generate heat via the I²R (Joule heating) effect. |
Ready to harness the efficiency of induction heating in your lab? The unique transformer-like design of an induction furnace offers rapid, precise, and clean melting for metals and alloys. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment, including induction furnaces tailored to your specific research and production needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and streamline your processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys



















