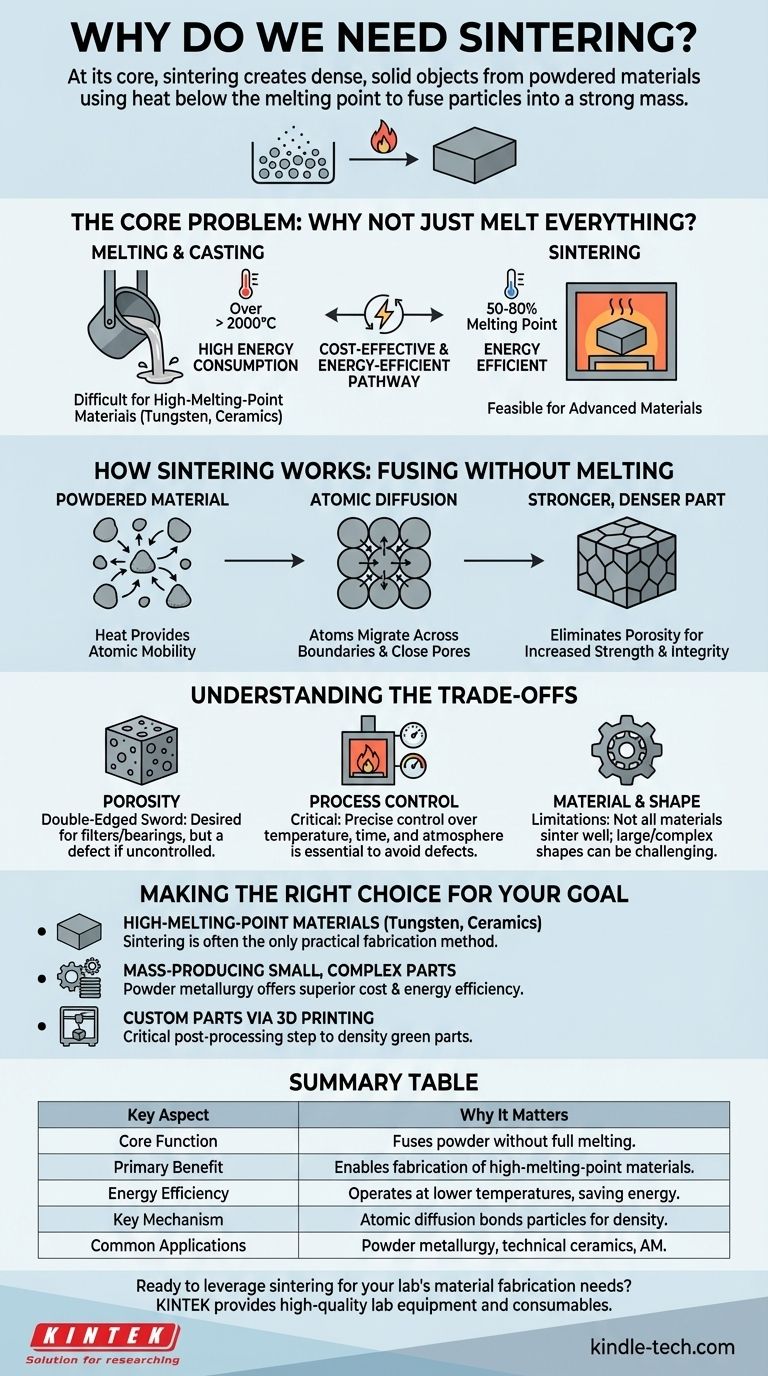
At its core, we need sintering to create dense, solid objects from powdered materials without having to melt them completely. This process uses heat below the material's melting point to fuse individual particles together, transforming a loose powder into a strong, unified mass. It is a foundational technique for working with materials that are difficult or expensive to melt, like high-performance ceramics and certain metals.
The fundamental challenge in materials manufacturing is creating strong, dense parts in a cost-effective and energy-efficient way. Sintering solves this by providing a pathway to consolidate materials that avoids the extreme energy demands and complexities of full melting, making it indispensable for a vast range of industrial applications.

The Core Problem: Why Not Just Melt Everything?
While melting and casting is a common manufacturing method, it isn't always practical or desirable. Sintering provides a critical alternative when facing specific material and economic constraints.
The Challenge of High-Melting-Point Materials
Many advanced materials, such as tungsten, molybdenum, and technical ceramics, have exceptionally high melting points. Reaching these temperatures (often well over 2000°C) requires specialized, expensive equipment and consumes enormous amounts of energy.
Sintering bypasses this issue entirely. By operating at temperatures typically 50-80% of the melting point, it makes the fabrication of parts from these high-performance materials economically and technically feasible.
The Drive for Energy and Cost Efficiency
Melting is an energy-intensive process. Sintering, by avoiding the liquid phase, significantly reduces the total energy required to produce a part.
This efficiency translates directly into lower manufacturing costs, especially for mass production. This is why sintering is the backbone of the powder metallurgy industry, used to create billions of parts like gears, bearings, and sprockets every year.
How Sintering Works: Fusing Without Melting
Sintering is not a simple heating process; it's a phenomenon driven by atomic-level mechanics that fundamentally alters the material's structure.
The Role of Heat and Pressure
Heat provides the critical ingredient: atomic mobility. When a powdered material is heated, its atoms gain enough energy to move around without the entire structure melting.
In some processes, pressure is also applied to force the particles into closer contact, accelerating the bonding process and helping to achieve higher final density.
Atomic Diffusion: The Key Mechanism
The true magic of sintering is atomic diffusion. As particles touch, atoms migrate across the boundaries from one particle to another, effectively closing the gaps and pores between them.
This process slowly eliminates the individual surfaces of the powder particles, merging them into a continuous, solid crystalline structure.
The Result: A Stronger, Denser Part
The primary goal of sintering is to reduce or eliminate porosity—the empty space between the powder particles.
As these voids disappear, the material becomes denser, which directly enhances its mechanical strength, integrity, and thermal and electrical conductivity. For some ceramics, this increased density can even improve optical properties like translucency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sintering is a complex process with specific considerations that are crucial for success. It is not a universal solution for all manufacturing challenges.
Porosity Is a Double-Edged Sword
While sintering is used to reduce porosity, sometimes a controlled amount of residual porosity is desired. This is used to create self-lubricating bearings (where oil is held in the pores) or filters. However, unintended or uneven porosity acts as a defect, weakening the final part.
Process Control is Critical
Sintering requires precise control over temperature, time, and furnace atmosphere. Improper conditions can lead to incomplete densification or unwanted chemical reactions. For instance, carbon-containing gases in the furnace can deposit soot, contaminating the product and damaging equipment.
Material and Shape Limitations
Not all materials sinter well. The process relies on the specific diffusion characteristics of a material. Furthermore, creating very large or geometrically complex parts can be challenging, as ensuring uniform heating and densification throughout the entire volume can be difficult.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting sintering depends entirely on your material, desired properties, and production goals.
- If your primary focus is working with high-melting-point materials (like tungsten or ceramics): Sintering is often the only practical and economical fabrication method available.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing small, complex metal parts cost-effectively: Powder metallurgy using sintering is an industry standard that offers superior cost and energy efficiency over casting or machining.
- If your primary focus is creating custom metal parts via 3D printing: Sintering is a critical post-processing step for methods like binder jetting, used to transform a fragile "green" part into a fully dense and functional metal component.
Ultimately, sintering is an indispensable tool that empowers engineers to create high-performance materials that would otherwise be impossible or prohibitively expensive to manufacture.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Fuses powder particles without full melting. |
| Primary Benefit | Enables fabrication of high-melting-point materials. |
| Energy Efficiency | Operates at lower temperatures than melting, saving energy. |
| Key Mechanism | Atomic diffusion bonds particles, increasing density and strength. |
| Common Applications | Powder metallurgy parts, technical ceramics, additive manufacturing. |
Ready to leverage sintering for your lab's material fabrication needs?
KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables essential for precise sintering processes. Whether you are working with advanced ceramics, metals for powder metallurgy, or post-processing 3D-printed parts, our solutions help you achieve the desired density, strength, and performance in your materials.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's sintering applications and enhance your research and production outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a programmable high-temperature furnace required for Silicalite-1 calcination at 0.2°C/min?
- How does a benchtop drying oven contribute to pectin-based films? Achieve Uniform Curing and Flexibility
- What equipment is used to determine ash content? The Essential Muffle Furnace Guide
- What is the necessity of high-temperature sintering in ODC preparation? Critical Steps for Electrode Performance
- What is ashing a food sample? A Guide to Measuring Mineral Content for Quality Control
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and a drying oven? Choose the Right Thermal Tool
- Does sintering increase strength? Unlock Maximum Material Performance with Proper Sintering
- How to maintain a muffle furnace? Ensure Long-Term Reliability and Safety



















