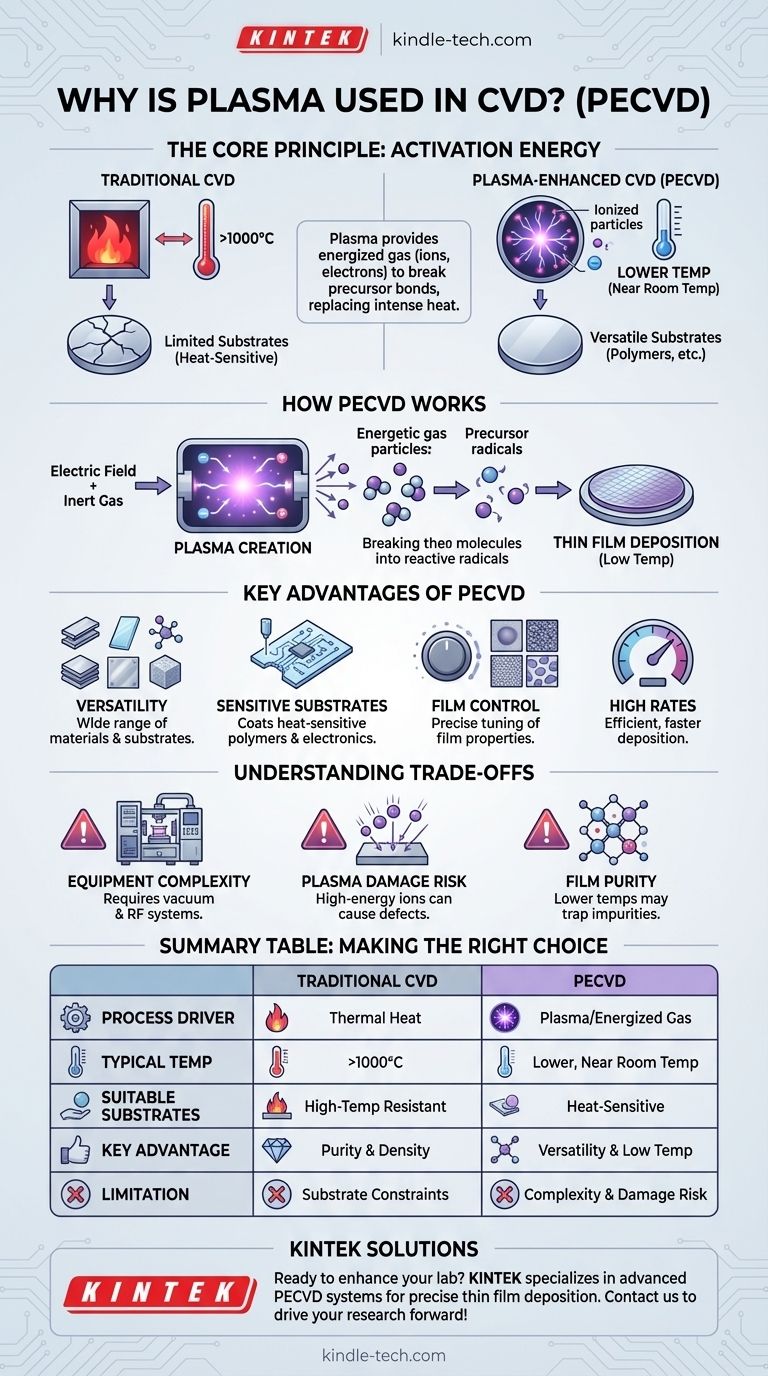
At its core, plasma is used in Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) to activate the necessary chemical reactions at significantly lower temperatures. Instead of relying on intense heat to break down precursor gases, Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) uses an energized gas, or plasma, to provide the energy needed to form a thin film on a substrate.
The fundamental reason for using plasma in CVD is to overcome the high-temperature limitation of traditional thermal processes. This allows for the deposition of high-quality thin films onto temperature-sensitive materials, such as polymers, that would otherwise be damaged or destroyed by the heat.

Understanding Traditional CVD
The Core Principle: Gas-to-Solid
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a process where volatile chemical precursors in a gas phase react or decompose to form a solid, non-volatile film on a substrate surface.
The Role of Extreme Heat
In traditional thermal CVD, this chemical reaction is driven entirely by thermal energy. The substrate is heated to very high temperatures, often over 1000°C, providing the activation energy required to break chemical bonds and initiate deposition.
The High-Temperature Limitation
This reliance on extreme heat is the primary constraint of thermal CVD. It makes the process completely unsuitable for coating materials with low melting points or those that degrade with heat, fundamentally limiting its range of applications.
The Role of Plasma: Overcoming the Heat Barrier
Activating Reactions Without Heat
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) introduces a new energy source into the equation. By applying an electric field to an inert gas, a plasma is created—an ionized state of matter containing highly energetic electrons and ions.
These energetic particles collide with the precursor gas molecules, breaking them apart into reactive radicals. This process effectively provides the activation energy for the deposition reaction without needing to heat the substrate to extreme temperatures.
The Low-Temperature Advantage
Because the plasma, not heat, drives the reaction, PECVD can be performed at much lower temperatures, sometimes even near room temperature. This single change dramatically expands the range of materials that can be coated.
Key Advantages of Plasma-Enhanced CVD
Versatility in Materials
PECVD can be used to deposit a vast array of materials, including elements, alloys, compounds, and even glassy films, on a wide variety of substrates.
Deposition on Sensitive Substrates
The most significant advantage is the ability to coat heat-sensitive materials like polymers, plastics, and certain electronics that would be incompatible with traditional CVD.
Control Over Film Properties
The plasma process offers additional parameters for control, allowing engineers to precisely tune the microstructure of the deposited film, from fully amorphous to polycrystalline.
High Deposition Rates
PECVD often achieves higher deposition rates than low-temperature thermal CVD methods, making it a more efficient process for many industrial applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Equipment Complexity
PECVD systems are inherently more complex than thermal CVD reactors. They require vacuum systems, radio-frequency (RF) power supplies, and sophisticated controls to generate and maintain a stable plasma.
Potential for Plasma Damage
The high-energy ions within the plasma can, if not properly managed, bombard the substrate and cause physical damage or create defects in the growing film.
Film Purity
Because the reactions occur at lower temperatures, precursor gas fragments (like hydrogen) can sometimes become incorporated into the film as impurities, which can affect its optical or electrical properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When deciding between a thermal or plasma-enhanced process, your primary objective is the most important factor.
- If your primary focus is depositing on temperature-sensitive materials like polymers: PECVD is the definitive and often only choice, as its low-temperature nature prevents substrate damage.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible film purity and density: High-temperature thermal CVD may be superior, as the intense heat helps drive off impurities and create dense, crystalline structures.
- If your primary focus is process versatility and speed: PECVD provides more control variables to tune film properties and generally offers higher deposition rates than other low-temperature techniques.
Ultimately, using plasma transforms CVD from a specialized high-temperature process into a remarkably versatile and widely applicable coating technology.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Traditional CVD | Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Driver | Thermal energy (heat) | Plasma (energized gas) |
| Typical Temperature | > 1000°C | Lower, even near room temperature |
| Suitable Substrates | High-temperature resistant materials | Heat-sensitive materials (polymers, plastics) |
| Key Advantage | High film purity and density | Coating versatility and low-temperature operation |
| Limitation | Limited to high-temperature substrates | Potential plasma damage and equipment complexity |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with precise thin film deposition? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including Plasma-Enhanced CVD systems, designed to meet the diverse needs of modern laboratories. Whether you're working with sensitive polymers or require high-purity films, our solutions offer the versatility and control you need. Contact us today to discuss how our CVD technology can drive your research and development forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- Are all lab grown diamonds CVD? Understanding the Two Main Methods
- What are nanotubes drawbacks? The 4 Major Hurdles Limiting Their Real-World Use
- How do nanotubes affect the environment? Balancing Low Carbon Footprint with Ecological Risks
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition



















