Introduction to Rotary Tube Furnaces
Rotary tube furnaces stand as pivotal assets in both industrial and laboratory spheres, orchestrating precision and efficiency in thermal processing. Their cylindrical design, coupled with longitudinal rotation, offers a dynamic approach to heating loose materials. In this exploration, we delve into the foundational aspects and multifaceted functionalities of rotary tube furnaces. Unveiling their structural intricacies and operational prowess, we uncover how these furnaces facilitate meticulous temperature control and streamlined heating processes. Embark on a journey to grasp the essence of these indispensable apparatuses shaping contemporary industrial and laboratory landscapes.
Types of Rotary Tube Furnaces
Rotary tube furnaces are versatile thermal processing systems that offer various configurations to accommodate different applications. They are designed with split furnace capabilities, allowing for multi-zone options along with rotation and tilt angulation features.
The configuration of the tilt angle, multi-zone availability, and stable temperature working lengths make rotary tube furnaces suitable for a wide range of processes. These furnaces are commonly utilized for both continuous processing and batch operations due to their capability to uniformly transport samples from one end to the other of the working tube.
The ability to open up the furnaces enables operators to use different tubes, reactors, or inline heating materials with ease. Additionally, the galvanized coating covered epoxy painted structure enhances durability and aesthetics, ensuring a longer lifetime for the equipment.
Customization is a key aspect of rotary tube furnaces, allowing for adjustments in factors such as the size and shape of the work tube, heating elements and controls, and the material of construction. This customization enables the creation of tailored solutions to meet specific application requirements, whether in laboratory, pilot plant, or industrial settings.
I've focused on the key points from the provided context, emphasizing the versatility and customization options of rotary tube furnaces. Let me know if you need further elaboration or if there's anything specific you'd like to add!
Key Features and Customization Options
Rotary tube furnaces are highly customizable equipment used in various applications, offering flexibility to tailor the furnace according to specific requirements. Here's an overview of the key features and customization options available:
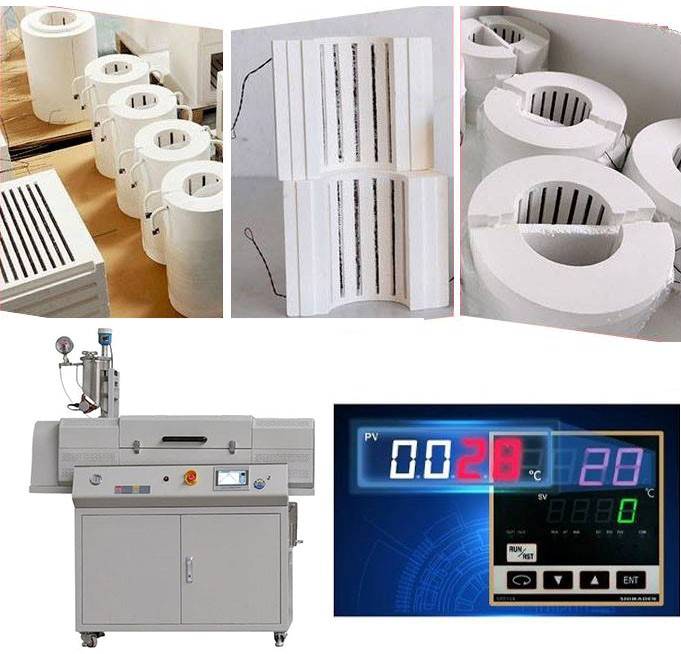

Material of Construction
Rotary tube furnaces are typically constructed using double-walled stainless steel, ensuring durability and resistance to high temperatures. This construction material provides excellent thermal insulation, maintaining uniform heating throughout the furnace.
Size and Shape of Work Tube
These furnaces come in various sizes and shapes to accommodate different processing needs. The work tube diameter typically ranges from 0.9 meters to 1.8 meters, with lengths ranging from 9.1 meters to 18.3 meters. The cylindrical shape of the furnace allows for efficient heat transfer and uniform processing of materials.
Heating Elements and Controls
Rotary tube furnaces are equipped with advanced heating elements and precise temperature controls for accurate thermal management. Multiple heat zones enable precise temperature gradients, ensuring optimal processing conditions for various materials. Heating can be achieved through indirect methods, such as hot gas discharge or direct firing into the tube, offering versatility in heating options.
Customization for Specific Applications
One of the key advantages of rotary tube furnaces is their customizability to meet specific application requirements. Whether used in laboratory research, pilot plant testing, or industrial production, these furnaces can be tailored to accommodate unique processing needs. Custom-designed features, such as variable speed rotation, atmosphere control, and cooling systems, enhance the versatility and efficiency of the furnace.
Advantages of Rotary Tube Furnaces
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of materials and processes.
- Uniform Heating: Ensures consistent temperature distribution for uniform processing.
- Continuous Operation: Ideal for continuous production processes.
- Energy Efficiency: Efficient heat transfer and recovery systems reduce energy consumption.
- Process Control: Precise temperature control and automation enhance process repeatability and reliability.
In summary, rotary tube furnaces offer a customizable and versatile solution for advanced materials processing, with features tailored to meet specific application needs.
Advantages of Rotary Tube Furnaces
Rotary tube furnaces offer numerous advantages in various physiochemical processing applications. Here's a detailed overview of the benefits they provide:

Precise Temperature Control
Rotary tube furnaces enable precise temperature control, allowing for accurate heating of materials to the desired temperature range. This level of control is essential for many laboratory processes that require specific temperature conditions for optimal results.
Efficient Heating
These furnaces are highly efficient in transferring heat to the materials being processed. The design of rotary tube furnaces facilitates efficient heat transfer, ensuring uniform heating throughout the sample. This efficiency results in reduced processing times and enhanced productivity.
Versatility in Physiochemical Processing
Rotary tube furnaces are versatile tools that can accommodate a wide range of physiochemical processing applications. Whether it's thermal processing, material synthesis, or sample preparation, these furnaces offer flexibility and adaptability to meet diverse laboratory needs.
Ability to Burn Various Forms of Fuel
One of the notable features of rotary tube furnaces is their ability to burn different forms of fuel, including pulverized, solid, gaseous, or liquid fuel. This versatility allows for greater flexibility in fuel selection based on the specific requirements of the process.
Classification Based on Heat-Exchange and Energy Transfer Methods
These furnaces are classified based on their method of heat exchange and energy transfer. Depending on factors such as parallel or opposing gas flow and direct, indirect, or combined energy transfer methods, rotary tube furnaces can be tailored to suit specific processing requirements.
Considerations for Process Suitability
When evaluating the suitability of a rotary tube furnace for a particular process, several factors must be considered:
-
Temperature Control: Rotary tube furnaces offer maximum working temperatures of up to 1700 degrees Celsius, providing the necessary temperature range for various applications.
-
Workspace Size: The size of the furnace workspace determines the capacity for processing materials and accommodating different sample sizes.
-
Dwell Time: The dwell time refers to the duration that materials remain in the furnace for processing. It's essential to consider this parameter to achieve the desired processing outcomes.
-
Tube Rotation Speed and Tilt Angle: The rotation speed and tilt angle of the tube impact mixing and heating efficiency, influencing the overall process performance.
-
Temperature Profile: Maintaining a consistent temperature profile is crucial for achieving uniform heating and reliable results.
-
Atmosphere Flow Rate: Controlling the flow rate of the atmosphere within the furnace allows for precise regulation of the processing environment.
-
Powder Bed Depth and Feed Rate: These factors affect material distribution and processing throughput, influencing the overall efficiency of the furnace.
Conclusion
In conclusion, rotary tube furnaces offer significant advantages for physiochemical processing applications in laboratory settings. From precise temperature control to efficient heating and versatile operation, these furnaces play a crucial role in advancing research and development across various disciplines. By understanding the unique capabilities and considerations associated with rotary tube furnaces, researchers can make informed decisions when selecting equipment for their specific processing needs.
Applications in Industrial and Laboratory Settings
Rotary tube furnaces offer a versatile solution for a variety of applications across industrial and laboratory settings. These furnaces can be customized to meet specific requirements, making them suitable for tasks ranging from laboratory research to large-scale industrial processes.
Advantages of Rotary Tube Furnaces
Rotary tube furnaces present several advantages that make them valuable for various applications:
-
Customization Options: One of the key advantages of rotary tube furnaces is their flexibility in customization. Factors such as the size and shape of the work tube, heating elements, controls, and construction material can be tailored to suit specific application needs.
-
Multi-Fuel Compatibility: Rotary tube furnaces can burn pulverized solid, gaseous, or liquid fuel in their working section. This versatility allows for efficient heating processes across different fuel types, enhancing their applicability in diverse industries.
-
Efficient Heat Transfer: These furnaces feature a metal drum lined with refractory material, mounted at an angle. This design facilitates effective heat transfer to the sample, ensuring uniform heating and optimal processing conditions.
-
Continuous Processing Capability: Rotary tube furnaces are designed for continuous material processing. By heating the sample in multiple thermal control zones, they enable consistent and efficient processing over extended durations.
Applications in Research and Industry
The applications of rotary tube furnaces span various fields, including:
-
Material Science: In research areas such as material science and geology, rotary tube furnaces find extensive use. They are employed in tasks such as the gaseous reduction of ores, analysis of metallurgical slags, and synthesis of catalysts and pigments for paints.
-
Chemical Processing: These furnaces are utilized for physiochemical processing of materials, including calcination of oil slate and doping of ceramics with rare earth metals.
-
Industrial Production: Rotary tube furnaces play a crucial role in industrial production processes. They are instrumental in the manufacturing of materials like alumina, vermiculite, iron ore pellets, and cement clinker.
-
Phase Transitions: Rotary tube furnaces facilitate processes such as oxidation and roasting, which influence phase transitions in materials. These processes are essential for modifying material properties and achieving desired outcomes in various applications.
Conclusion
The diverse capabilities of rotary tube furnaces make them indispensable tools in both laboratory research and industrial operations. With their ability to accommodate a wide range of materials and processing requirements, these furnaces contribute significantly to advancements in material science, chemical processing, and industrial production.
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace

















