Introduction to Hydraulic Heated Lab Pellet Presses
Hydraulic heated lab pellet presses are essential tools in material science research, enabling precise and efficient sample preparation. These devices combine hydraulic pressure with controlled heating to create uniform pellets for various analytical techniques. Understanding the basic principles of hydraulic operation and heating mechanisms is crucial for selecting the right press and optimizing laboratory efficiency. This comprehensive guide will delve into the types, features, and applications of hydraulic heated lab pellet presses, providing insights into their setup, operation, and maintenance, ensuring you make informed decisions for your research needs.
Types and Specifications of Hydraulic Heated Lab Pellet Presses
Hydraulic heated lab pellet presses are essential equipment in material science laboratories for tasks such as pressing pellets, lamination, and punching electrodes. These presses are available in various types and specifications, each designed to meet specific laboratory needs. This section provides a detailed description of different types of hydraulic heated lab pellet presses, focusing on their pressing force, heating capabilities, and design features.
Adjustable Features and Safety Measures
All hydraulic lab presses come equipped with several adjustable and safety features to ensure efficient and safe operation. These include an adjustable top pressing surface, which allows for precise control over the pressing process. Additionally, a perspex safety guard is included to protect the operator from potential hazards. The long, easy-to-use handle simplifies the operation, while the accurate pressure gauge provides real-time monitoring of the pressing force. The hardened steel construction ensures durability and longevity, and the all-in-one leak-free design prevents any potential oil leaks, making these presses reliable and easy to maintain.
Varied Pressing Forces and Heating Capacities
Hydraulic lab presses are available in various pressing forces, ranging from 5 tons to 40 tons. The 5-ton press is suitable for lighter applications, while the 40-ton press is designed for heavier tasks. These presses operate on the hydraulic principle, where a relatively low force applied through pumping the handle can deliver high loads into the pellet die or other pressing applications. This design makes them highly efficient and user-friendly.
For laboratories requiring heated presses, models with heating platens are available. These presses can heat up to 300 °C, with a standard stroke of 100 mm. Customizable options allow for an extended stroke up to 200 mm, catering to specific laboratory needs. The heating capability is crucial for applications involving materials that require heat treatment during pressing.
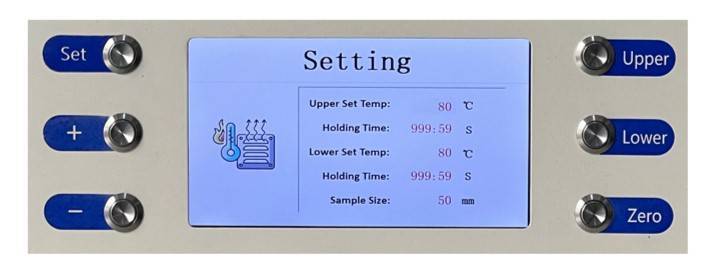
Specific Models and Their Applications
-
Manual Hydraulic Press with FTIR + XRF Pellet Press Features:
- Configurations: Available in 15-ton and 25-ton models.
- Safety Features: Polycarbonate safety guards.
- Adjustability: Adjustable upper bolster and pressure control valve.
- Additional Features: Vacuum ports, pressure release valve, and low-pressure conversion gauges.
- Applications: Ideal for FTIR, KBr, and XRF sample preparation.
-
Standard Laboratory Press Range (LAB PRESS):
- Capacity: Ranges from 20 kN to 200 kN.
- Design: Operator-friendly with low maintenance requirements.
- Heating Capability: Standard press can heat up to 300 °C.
- Customization: Stroke can be adapted up to 200 mm.
-
Hydraulic Lab Presses from Pellet Press Die Sets:
- Pressing Forces: Available in 5-ton, 15-ton, 25-ton, and 40-ton models.
- Design: All-in-one leak-free design for easy use with pellet press die sets or other pressing applications.
Comparison and Selection
When selecting a hydraulic heated lab pellet press, it is crucial to consider the pressing force required for the specific application. Laboratories dealing with heavier materials may opt for higher tonnage presses, while lighter applications can be managed with lower tonnage models. Additionally, the heating capability is a significant factor, especially for materials that require heat treatment during pressing. The availability of adjustable features and safety measures ensures that the selected press meets the operational and safety standards of the laboratory.
In conclusion, hydraulic heated lab pellet presses are versatile and essential tools in material science laboratories. With a range of pressing forces, heating capabilities, and design features, these presses cater to various laboratory needs, ensuring efficient and safe sample preparation.
Key Features to Consider When Choosing a Hydraulic Heated Lab Pellet Press
When selecting a hydraulic heated lab pellet press, it's crucial to consider several key features that align with your specific research needs. These features ensure not only the safety and efficiency of the pressing process but also the quality and reproducibility of the pellets produced. Below, we delve into the essential aspects to consider when making your choice.
Adjustable Pressing Surfaces
One of the primary features to look for in a hydraulic heated lab pellet press is adjustable pressing surfaces. These surfaces allow for the customization of pellet dimensions, accommodating various sample sizes and shapes. Adjustable surfaces are particularly beneficial in research settings where different experiments may require different pellet sizes. For instance, a press with a 250x250 mm chrome-plated steel platen and a thickness of 40 mm provides a robust and versatile pressing area.
Safety Features
Safety is paramount in any laboratory setting, and hydraulic presses are no exception. Look for presses that include safety mechanisms such as protection doors with safety locks and a perspex safety guard. These features protect the operator from potential hazards during the pressing process. Additionally, a press with a CE label ensures that it meets European safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
Ease of Operation
An ideal hydraulic heated lab pellet press should be user-friendly, minimizing the learning curve for new operators. Features such as a long, easy-to-use handle and a user-friendly touch screen display on the PLC controller enhance operational ease. The ability to freely define the molding cycle by setting displacements of the moving platen also contributes to the press's usability.

Maintenance Requirements
Consider the maintenance requirements of the hydraulic press. A press with a mechanical structure featuring four columns (with 60 mm diameter) and sliding platen driven by self-lubricating bushings reduces the need for frequent maintenance. Additionally, a hardened steel construction and an all-in-one leak-free design ensure durability and longevity, minimizing downtime and repair costs.
Hydraulic System Specifications
The hydraulic system's specifications are crucial for effective pressing. A system with a 25-ton closure force provides sufficient pressure for most laboratory applications. Ensure that the press includes an accurate pressure gauge, which is essential for knowing the exact force being applied. This precision is critical for reproducible results and safe operation.
Temperature Control and Distribution
Uniform temperature distribution over the platen surface is vital for consistent pellet quality. Presses equipped with specifically designed flat heating elements ensure this uniformity. This feature is particularly important in research involving temperature-sensitive materials or those requiring precise temperature control during the pressing process.
Versatility and Application
Hydraulic lab presses are indispensable in material science labs for tasks such as pressing pellets, lamination, and punching electrodes. Ensure that the press you choose is compatible with various die sets and can be utilized for multiple processes within the lab. A press with an adjustable top pressing surface and a closed molding area for easy fume aspiration enhances its versatility and applicability.
In conclusion, choosing the right hydraulic heated lab pellet press involves a careful consideration of adjustable pressing surfaces, safety features, ease of operation, maintenance requirements, hydraulic system specifications, temperature control, and versatility. By focusing on these key features, you can select a press that not only meets your current research needs but also ensures the safety and efficiency of your laboratory operations.
Applications of Hydraulic Heated Lab Pellet Presses
Hydraulic heated lab pellet presses are indispensable tools in various laboratory settings, particularly in material science and analytical chemistry. These presses are designed to exert controlled pressure and heat, making them suitable for a wide range of applications such as pressing KBr pellets for Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), creating sample pellets for X-ray Fluorescence (XRF), and numerous other material science experiments.
Pressing KBr Pellets for FTIR
One of the primary applications of hydraulic heated lab pellet presses is in the preparation of KBr pellets for FTIR analysis. FTIR spectroscopy is a powerful technique used to identify and analyze the chemical composition and molecular structure of a sample. To perform FTIR on a powdered sample, it must first be mixed with potassium bromide (KBr) and then pressed into a transparent pellet under high pressure. This process ensures that the sample is uniformly distributed and optically clear, allowing for accurate and reproducible spectral data.
Hydraulic presses are essential for this application due to their ability to apply consistent and high pressures. The press typically includes an adjustable top pressing surface, a perspex safety guard, and an accurate pressure gauge, ensuring that the pressure applied is controlled and safe. The hardened steel construction and leak-free design of these presses further enhance their durability and reliability in the laboratory.

Creating Sample Pellets for XRF
Another significant application of hydraulic heated lab pellet presses is in the preparation of sample pellets for XRF analysis. XRF is a non-destructive analytical technique used to determine the elemental composition of materials. To obtain accurate results, the sample must be compressed into a pellet form, ensuring uniform distribution and adequate density.
Hydraulic presses are ideal for this task as they can apply the necessary pressure to create high-quality pellets. The presses are available in various sizes and configurations, allowing laboratories to select the most suitable model for their specific needs. The full hydraulic operation and integrated pressure gauge facilitate reproducible load application, ensuring consistent pellet quality for quantitative studies.
Other Material Science Experiments
Beyond FTIR and XRF, hydraulic heated lab pellet presses are used in various other material science experiments. These include:
- Testing the strength and durability of materials: Hydraulic presses can apply high pressures to test the mechanical properties of materials, such as their compressive strength and elasticity.
- Investigating the effects of high pressure on different substances: Researchers can use hydraulic presses to study how materials behave under high pressure, which is crucial for understanding their physical and chemical properties.
- Creating pellets for sample analysis: In addition to KBr pellets for FTIR and general sample pellets for XRF, hydraulic presses can be used to prepare pellets for other analytical techniques, such as Raman spectroscopy and particle size analysis.
Conclusion
In summary, hydraulic heated lab pellet presses are versatile and essential tools in laboratory settings. Their ability to apply controlled pressure and heat makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, including pressing KBr pellets for FTIR, creating sample pellets for XRF, and numerous other material science experiments. The durability, reliability, and precision of these presses ensure that laboratories can obtain accurate and reproducible results, making them a fundamental piece of equipment in modern research and testing.
Setting Up and Operating a Hydraulic Heated Lab Pellet Press
Setting up and operating a hydraulic heated lab pellet press involves several critical steps to ensure safety, accuracy, and efficiency in the laboratory. This section provides detailed instructions on how to set up the press, operate it safely, calibrate it for optimal performance, and troubleshoot common issues that may arise during its use.
Setting Up the Hydraulic Heated Lab Pellet Press
-
Assembly and Placement: Begin by ensuring that the hydraulic press is placed on a stable, flat surface. The press should be positioned away from any flammable materials and in a well-ventilated area. Assemble the press according to the manufacturer's instructions, ensuring all components are securely fastened.
-
Connecting Power and Heating Elements: Connect the press to a reliable power source. Ensure that the heating elements are properly connected and functioning. Most hydraulic heated presses come with adjustable temperature controls, allowing you to set the desired temperature for your specific application.
-
Safety Features: Activate and check all safety features, including the Perspex safety guard and the accurate pressure gauge. The safety guard should be in place to prevent accidental contact with the moving parts and high-pressure areas.
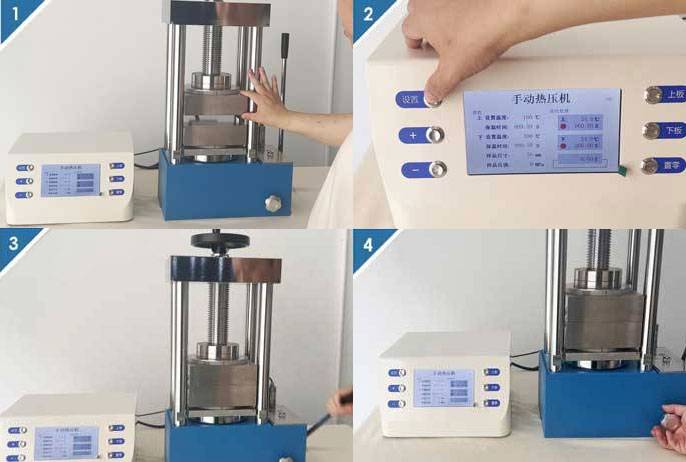

Operating the Hydraulic Heated Lab Pellet Press
-
Loading the Sample: Place your workpiece, such as a pellet die containing the sample material, centrally on the piston. Ensure the sample is evenly distributed to prevent uneven pressure distribution during the pressing process.
-
Applying Pressure: Slowly turn the leadscrew at the top of the press to bring the nose of the leadscrew onto the top of the workpiece. Use the handle to pump hydraulic oil into the piston and start applying a load. Monitor the pressure gauge to achieve the desired load.
-
Maintaining Pressure and Temperature: Once the desired load has been achieved, maintain the pressure and temperature for the required duration. This is crucial for achieving the desired pellet density and consistency.
-
Releasing Pressure: After the pressing process is complete, turn the release valve to release the pressure. Carefully remove the workpiece from the press.
Safety Precautions
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE, including heat-resistant gloves, safety glasses, and protective clothing. This protects against high temperatures and potential flying debris in case of press failure.
- Training and Supervision: Ensure that all users are properly trained in the safe operation of the hydraulic heated lab pellet press. Supervision is essential, especially for new users.
- Regular Maintenance: Conduct regular maintenance checks to ensure all components are functioning correctly. Replace any worn or damaged parts immediately.
Calibration Procedures
- Pressure Calibration: Regularly calibrate the pressure gauge to ensure accurate readings. This involves using a calibrated pressure gauge to verify the readings of the press's gauge.
- Temperature Calibration: Calibrate the temperature controls to ensure the heating elements are maintaining the correct temperature. Use a precision thermometer to verify the temperature readings.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Inconsistent Pellet Quality: This can be caused by uneven sample distribution or inconsistent pressure application. Ensure the sample is evenly spread in the die and that the pressure is applied uniformly.
- Pressure Fluctuations: If the pressure gauge shows inconsistent readings, check for air bubbles in the hydraulic system or a malfunctioning pressure gauge.
- Overheating: If the press overheats, check the heating elements and the temperature control settings. Ensure there is adequate ventilation around the press.
By following these detailed instructions and safety precautions, you can effectively set up and operate a hydraulic heated lab pellet press, ensuring high-quality results and a safe working environment.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Hydraulic Heated Lab Pellet Presses
Hydraulic heated lab pellet presses are essential equipment in material science laboratories, used for tasks such as pressing pellets, lamination, and punching electrodes. These presses operate under high pressure and temperature conditions, making maintenance and troubleshooting crucial for their longevity and optimal performance. This comprehensive guide will cover essential topics such as oil replacement, checking for leaks, and adjusting pressure settings.
Oil Replacement
The hydraulic fluid in lab presses plays a critical role in transmitting power and ensuring smooth operation. Over time, this fluid can degrade due to heat and pressure, leading to reduced efficiency and potential system failures. Regular oil replacement is therefore essential. It is recommended to replace the hydraulic oil every 1,000 hours of operation or annually, whichever comes first. When replacing the oil, ensure that the correct type and viscosity are used, as specified by the manufacturer. This helps in maintaining the press's performance and preventing damage to internal components.
Checking for Leaks
Leaks in hydraulic systems can lead to significant issues, including loss of pressure, contamination of the lab environment, and potential safety hazards. Regular inspection for leaks is crucial. Check all hoses, seals, and connections for signs of oil or fluid leakage. Common areas to inspect include the pressure gauge, handle mechanism, and the base of the press. If any leaks are detected, they should be addressed immediately by tightening connections or replacing damaged parts. Prolonged leaks can lead to more extensive damage and costly repairs.
Adjusting Pressure Settings
Proper pressure settings are vital for the accurate and safe operation of hydraulic presses. These settings should be adjusted according to the specific requirements of the material being processed. The pressure gauge on the press provides a visual indication of the current pressure. To adjust the pressure, use the provided controls, typically located on the side or back of the press. It is important to follow the manufacturer's guidelines for maximum pressure limits to avoid damaging the press or the materials being processed. Regularly verifying and adjusting pressure settings ensures consistent and reliable results.

General Maintenance Tips
In addition to the specific maintenance tasks mentioned above, several general tips can help extend the life of your hydraulic heated lab pellet press:
- Regular Cleaning: Keep the press clean from dirt, dust, and spilled materials. Regular cleaning prevents contamination and ensures that all components function smoothly.
- Lubrication: Ensure that all moving parts are properly lubricated. This reduces friction and wear, contributing to longer operational life.
- Visual Inspections: Conduct regular visual inspections to identify any signs of wear or damage. Early detection of issues can prevent more significant problems down the line.
- Operator Training: Ensure that all operators are properly trained in the safe and correct use of the press. This includes understanding how to operate the controls, adjust settings, and respond to any issues that may arise.
Conclusion
Maintaining and troubleshooting hydraulic heated lab pellet presses is essential for ensuring their longevity and optimal performance. By following regular maintenance practices such as oil replacement, checking for leaks, and adjusting pressure settings, along with general upkeep, you can significantly reduce the risk of system failures and extend the life of your equipment. Regular maintenance not only saves on potential repair costs but also ensures consistent and reliable results in your laboratory operations.
Comparison with Other Types of Lab Presses
Laboratory presses are essential tools in various research contexts, particularly in material science and XRF sample preparation. They come in different types, each with unique features and applications. This section will compare hydraulic heated lab pellet presses with manual and electric lab presses, highlighting their advantages and limitations.
Hydraulic Heated Lab Pellet Presses
Hydraulic heated lab pellet presses are renowned for their robustness and precision. These presses typically feature a hardened steel construction, an adjustable top pressing surface, and a perspex safety guard. They are equipped with an accurate pressure gauge and operate with a long, easy-to-use handle, ensuring a leak-free design.
Advantages:
- Precision and Consistency: Hydraulic presses offer high accuracy and consistency in pressure application, which is crucial for tasks like XRF pellet preparation. The pressure can be precisely controlled, ensuring uniform samples.
- Versatility: These presses are versatile and can be used for various applications beyond pellet pressing, such as lamination and punching electrodes.
- Safety: The inclusion of a perspex safety guard enhances the safety of these presses, protecting operators from potential hazards.
Limitations:
- Cost: Hydraulic presses can be more expensive than their manual or electric counterparts.
- Maintenance: They require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Manual Lab Presses
Manual lab presses are operated by hand, requiring physical effort from the operator. They are simpler in design and operation compared to hydraulic and electric presses.
Advantages:
- Cost-Effective: Manual presses are generally more affordable and can be a suitable option for laboratories with budget constraints.
- Simplicity: Their simple design means fewer parts, reducing the likelihood of mechanical failures.
Limitations:
- Physical Effort: Operating a manual press can be labor-intensive, especially when used frequently.
- Inconsistency: The pressure applied can vary between samples, leading to inconsistencies in the final product.
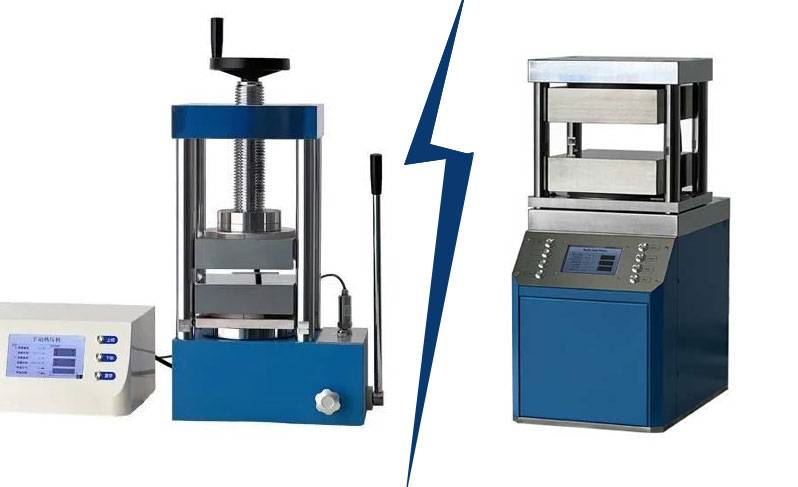

Electric Lab Presses
Electric lab presses use an electric motor to drive the pump and control the pressure. They offer a middle ground between manual and hydraulic presses in terms of automation and precision.
Advantages:
- Automation: Electric presses can be programmed to operate autonomously, improving workflow efficiency in busy laboratories.
- Accuracy: They provide a high level of accuracy and repeatability, similar to hydraulic presses but with less maintenance.
Limitations:
- Intermediate Cost: While more expensive than manual presses, they are generally less costly than hydraulic presses.
- Complexity: Their increased complexity can lead to higher maintenance requirements compared to manual presses.
Comparative Analysis
When choosing a lab press, the specific needs and context of the laboratory should be considered. For high-throughput applications requiring precision and consistency, such as XRF sample preparation, hydraulic heated lab pellet presses are the preferred choice. They offer the highest level of control and safety, albeit at a higher cost and with more maintenance requirements.
Manual presses are ideal for laboratories with infrequent use and budget constraints. They are simple to operate but may lack the precision and consistency needed for critical research applications.
Electric presses provide a balance between cost, automation, and precision. They are suitable for laboratories that require frequent use of presses but do not need the full capabilities of hydraulic presses.
In conclusion, the choice of lab press depends on the specific requirements of the research, the frequency of use, and the budget of the laboratory. Each type of press offers unique advantages and limitations, making them suitable for different research contexts.
Related Products
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates Split Manual Laboratory Hot Press
- 30T 40T Split Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
















