In the search for sustainable energy, the question of cost is paramount. As a general rule, most biofuels are currently more expensive to produce than their fossil fuel counterparts like gasoline and diesel. This cost disparity arises from several key factors, including the high price of raw materials (feedstock), the energy-intensive conversion processes, and a lack of the massive, century-old infrastructure that supports the fossil fuel industry.
The economic viability of biofuels is a complex issue. While their raw production cost is typically higher than fossil fuels, njihova konkurentnost na tržištu često ovisi o državnim subvencijama, poreznim poticajima i mandatima za miješanje goriva, a ne o samim troškovima proizvodnje.

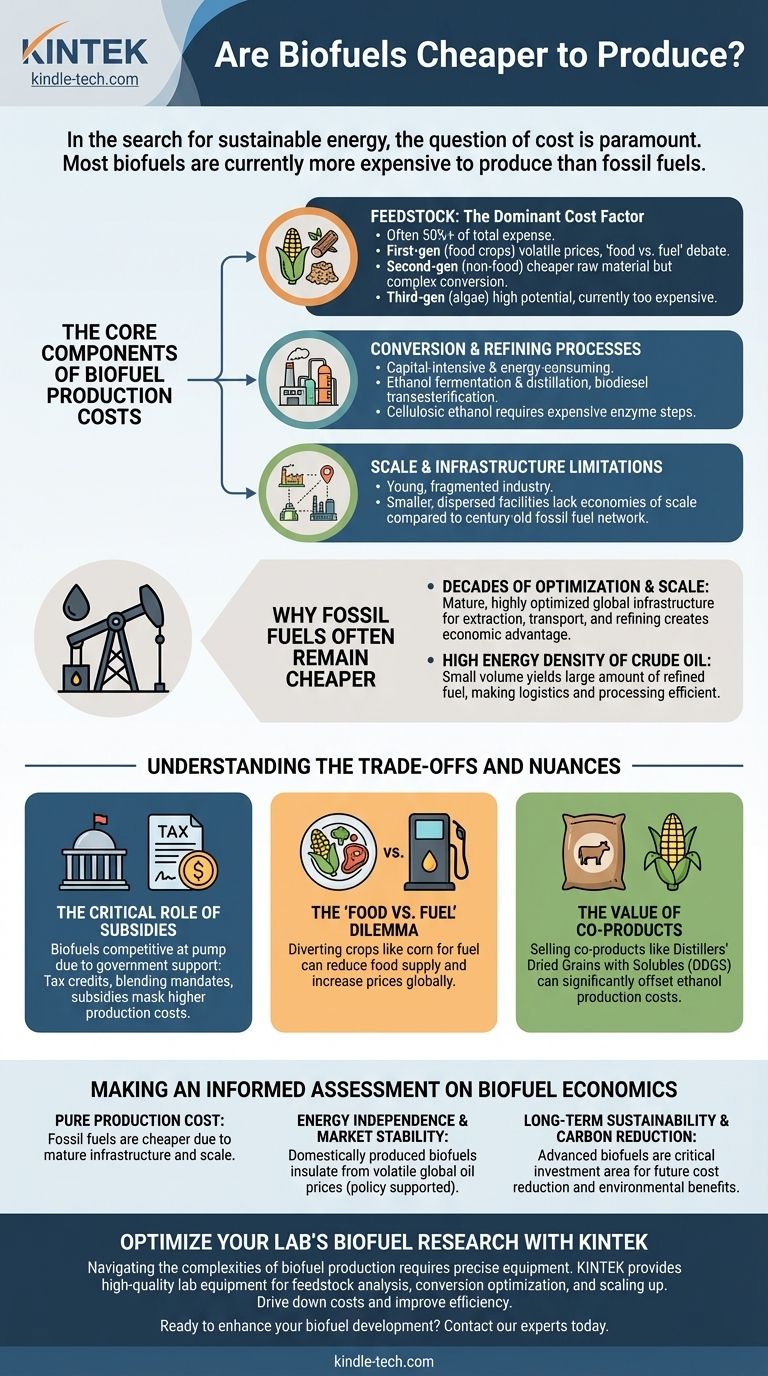
The Core Components of Biofuel Production Costs
To understand why biofuels are often more expensive, we must break down their production chain. The final cost is not a single number but an accumulation of expenses at each stage.
Feedstock: The Dominant Cost Factor
The raw material, or feedstock, is the single largest contributor to the cost of biofuel, often accounting for over 50% of the total expense.
- First-generation biofuels use food crops like corn, sugarcane, and soybeans. Their prices are volatile and directly linked to global agricultural and food markets, creating the "food vs. fuel" debate.
- Second-generation biofuels use non-food sources like switchgrass, wood chips, and agricultural waste. While the feedstock itself can be cheaper, converting it into fuel is technologically complex and expensive.
- Third-generation biofuels, primarily from algae, hold immense promise due to high yields and no competition with agriculture. However, the technology is still in its early stages and is currently far too expensive for commercial-scale production.
Conversion and Refining Processes
Turning biomass into a usable liquid fuel is a capital-intensive and energy-consuming process.
Ethanol production requires fermenting sugars and then distilling the result to separate the alcohol, a process that consumes significant energy. Producing biodiesel involves a chemical reaction called transesterification. Cellulosic ethanol from second-generation feedstocks requires an additional expensive step of using enzymes to break down tough plant fibers.
Scale and Infrastructure Limitations
The fossil fuel industry has benefited from over a century of investment, resulting in a highly optimized global network for extraction, transportation, refining, and distribution.
The biofuel industry, by contrast, is much younger and more fragmented. Production facilities are smaller and more geographically dispersed, preventing them from achieving the same economies of scale.
Why Fossil Fuels Often Remain Cheaper
The cost advantage of fossil fuels is not inherent to the fuel itself, but to the system built around it.
Decades of Optimization and Scale
Every step of the fossil fuel supply chain, from seismic exploration to the gas pump, has been relentlessly optimized for efficiency over many decades. This mature, global infrastructure creates a powerful economic advantage.
High Energy Density of Crude Oil
Crude oil is an incredibly dense source of energy. This means that a relatively small volume of raw material yields a large amount of refined fuel, making the logistics and processing highly efficient compared to bulky biomass.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
A direct comparison of production costs tells only part of the story. The true economic picture is influenced by government policy and external factors.
The Critical Role of Subsidies
In many countries, biofuels are only competitive at the pump because of government intervention. Tax credits, blending mandates (requiring a certain percentage of biofuel to be mixed with fossil fuels), and other subsidies artificially lower the price for consumers. This support is a policy choice to foster energy independence and reduce emissions, but it masks the higher underlying production cost.
The "Food vs. Fuel" Dilemma
For first-generation biofuels, the economic and ethical trade-off is significant. Diverting crops like corn to fuel production can reduce the food supply and increase prices for consumers and livestock producers around the world.
The Value of Co-products
The economics of biofuel production are often improved by selling co-products. For example, the corn ethanol process creates Distillers' Dried Grains with Solubles (DDGS), a high-protein animal feed. The revenue from selling DDGS can significantly offset the cost of ethanol production.
Making an Informed Assessment on Biofuel Economics
Your perspective on the cost-effectiveness of biofuels depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is pure production cost: Fossil fuels are currently the cheaper option due to mature infrastructure and enormous economies of scale.
- If your primary focus is energy independence and market stability: Domestically produced biofuels can insulate an economy from volatile global oil prices, though this stability is often supported by government policy.
- If your primary focus is long-term sustainability and carbon reduction: Advanced second and third-generation biofuels are a critical area of investment, where future technological breakthroughs are expected to drive down costs and improve their environmental footprint.
Ultimately, evaluating fuel costs requires looking beyond the pump price to understand the complex web of production economics, government policy, and long-term strategic goals.
Summary Table:
| Cost Factor | Biofuels | Fossil Fuels |
|---|---|---|
| Feedstock Cost | High (50%+ of total) | Low (well-established extraction) |
| Processing Complexity | Energy-intensive (e.g., fermentation, transesterification) | Highly optimized & efficient |
| Infrastructure & Scale | Limited, fragmented | Global, century-old network |
| Government Support | Often reliant on subsidies & mandates | Less dependent on subsidies |
| Co-product Revenue | Can offset costs (e.g., animal feed from DDGS) | Minimal co-product impact |
Optimize Your Lab's Biofuel Research with KINTEK
Navigating the complexities of biofuel production requires precise, reliable equipment. Whether you're analyzing feedstock, optimizing conversion processes, or scaling up sustainable fuel solutions, KINTEK provides the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need. From reactors and analyzers to consumables for accurate testing, our products help researchers and industry professionals drive down costs and improve efficiency.
Ready to enhance your biofuel development? Contact our experts today to find the right tools for your laboratory's unique challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- kbr pellet press 2t
People Also Ask
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas








