Yes, absolutely. Brazing and soldering are not only possible but are often the ideal methods for joining dissimilar materials. The fundamental principle is that a filler metal, with a melting point lower than the base materials, is used to form a metallurgical bond between the two surfaces without melting the components themselves.
The success of joining dissimilar materials with brazing or soldering hinges on one key factor: the filler metal must be able to "wet" and adhere to both surfaces. The most critical challenge in this process is managing the different rates of thermal expansion between the materials during heating and cooling.

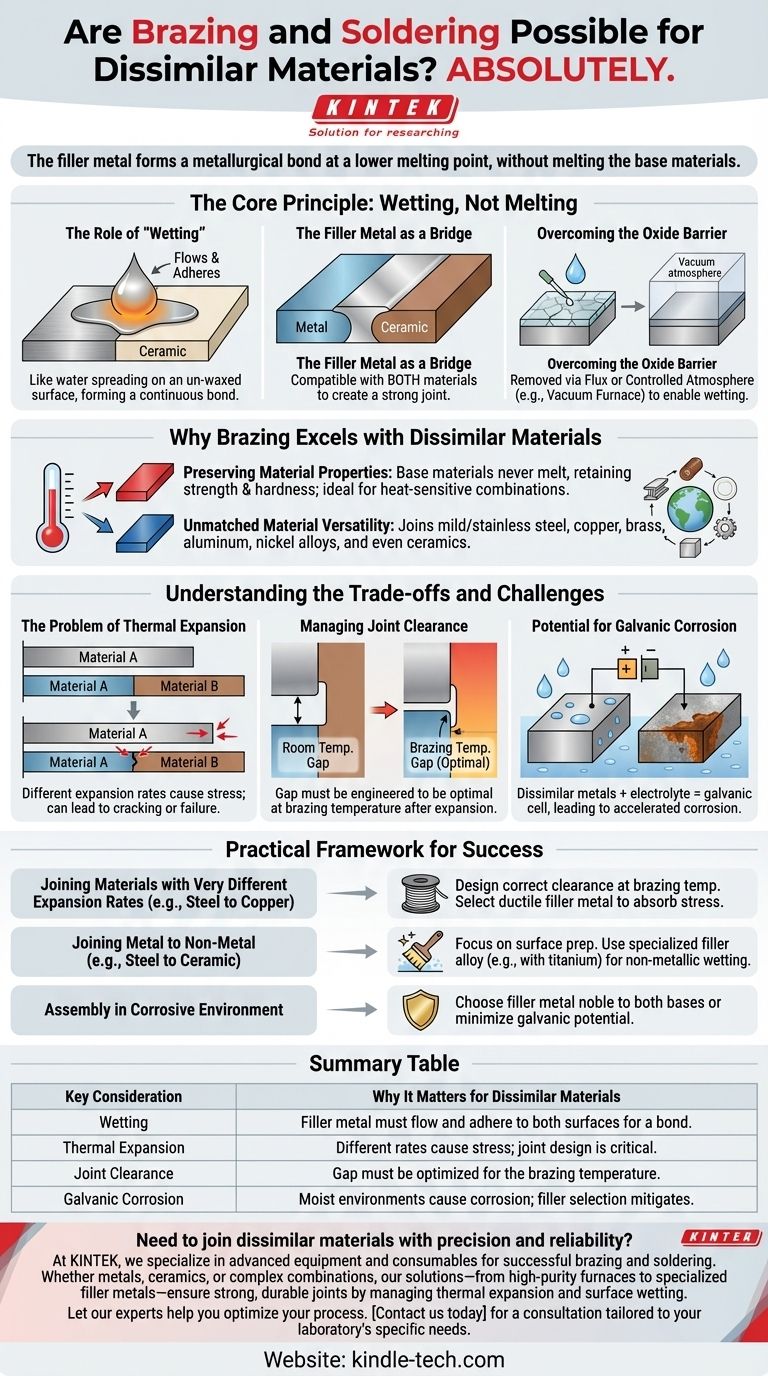
The Core Principle: Wetting, Not Melting
To understand why this process works so well, you must grasp the concept of wetting. It's the foundation of every successful brazed or soldered joint.
The Role of "Wetting"
Wetting describes the ability of the molten filler metal to flow over and adhere to the solid surfaces of the base materials. Think of it like water beading up on a waxed car versus spreading out on an un-waxed surface; proper wetting is the "spreading out" that creates a continuous bond.
The Filler Metal as a Bridge
The filler metal acts as a metallurgical bridge between the two distinct materials. For a strong joint, the chosen filler alloy must be compatible with both base materials, ensuring it can form a strong bond on each side.
Overcoming the Oxide Barrier
Virtually all metals have a thin, invisible layer of oxide on their surface that prevents proper wetting. This barrier must be removed.
This is achieved in two primary ways: by using a chemical flux that cleans the surfaces as it's heated, or by performing the process in a controlled atmosphere (like a vacuum furnace) that prevents oxides from forming in the first place.
Why Brazing Excels with Dissimilar Materials
The low-temperature nature of brazing provides distinct advantages when joining materials with different properties.
Preserving Material Properties
Because the base materials are never melted, their original metallurgical properties, such as strength and hardness, are largely unaffected. This is critical when one material is much more sensitive to heat than the other.
Unmatched Material Versatility
This process is incredibly versatile. It can be used to join a wide range of materials, including mild and stainless steel, copper, brass, aluminum, nickel alloys, and even non-metals like ceramics.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While effective, joining dissimilar materials introduces unique challenges that must be addressed for a reliable joint.
The Problem of Thermal Expansion
This is the single most important factor. Different materials expand and contract at different rates when heated and cooled.
If one material expands significantly more than the other, immense stress can build up in the joint as it cools, potentially leading to cracking or immediate failure.
Managing Joint Clearance
The difference in thermal expansion directly impacts the joint clearance—the gap between the two parts. This gap must be engineered at room temperature so that it becomes the optimal size at the actual brazing temperature, after the materials have expanded.
Potential for Galvanic Corrosion
Joining two different metals can create a galvanic cell, essentially a small battery, in the presence of an electrolyte (like moisture). This can cause one of the metals to corrode at an accelerated rate, compromising the integrity of the assembly over time.
A Practical Framework for Success
To ensure a strong and reliable joint, your approach should be dictated by the specific materials and the final application's service environment.
- If you are joining materials with very different expansion rates (e.g., steel to copper): Prioritize designing a joint with the correct clearance at brazing temperature and select a ductile filler metal capable of absorbing thermal stress.
- If you are joining a metal to a non-metal (e.g., steel to ceramic): Focus heavily on surface preparation and selecting a specialized filler alloy (often containing an active element like titanium) that can properly wet the non-metallic surface.
- If the final assembly will operate in a corrosive environment: Choose a filler metal that is noble to both base materials or one that minimizes the galvanic potential between them.
By understanding these core principles, you can confidently leverage brazing and soldering to create robust, reliable joints between a vast range of dissimilar materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Consideration | Why It Matters for Dissimilar Materials |
|---|---|
| Wetting | The filler metal must flow and adhere to both surfaces to form a bond. |
| Thermal Expansion | Different expansion rates can cause stress; joint design is critical. |
| Joint Clearance | The gap must be engineered to be optimal at the brazing temperature. |
| Galvanic Corrosion | Dissimilar metals in a moist environment can corrode; filler selection mitigates this. |
Need to join dissimilar materials with precision and reliability?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the advanced equipment and consumables required for successful brazing and soldering. Whether you're working with metals, ceramics, or complex combinations, our solutions—from high-purity furnaces to specialized filler metals and fluxes—ensure strong, durable joints by expertly managing thermal expansion and surface wetting.
Let our experts help you optimize your process. Contact us today for a consultation tailored to your laboratory's specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the types of induction melting furnace? Coreless, Channel, and VIM Explained
- What is RF magnetron sputtering? A Guide to Depositing Insulating Thin Films
- What is a magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials
- What is the difference between VAR and VIM? Legacy Vimscript Variables vs. Modern Neovim API



















