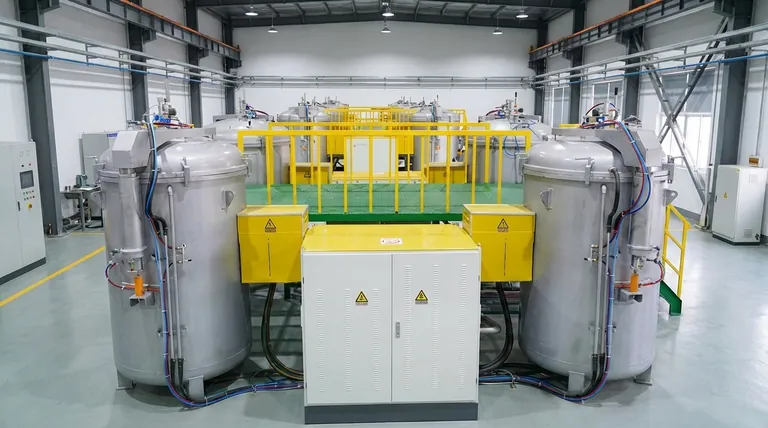
The melting point of graphite is not a single, fixed value. Decades of experiments have produced a wide range of results, generally placing the melting temperature between 4,000 K and 5,000 K (approximately 6,700°F to 8,500°F). This uncertainty exists because, under normal conditions, graphite does not melt at all—it sublimates directly from a solid into a gas.
The core issue is pressure. To force graphite to become a liquid, you need to apply extreme pressure (around 100 times normal atmospheric pressure) while simultaneously heating it to thousands of degrees. The immense technical difficulty of this process is why a single, definitive melting point remains elusive.
Why Graphite Resists Melting
To understand the challenge of melting graphite, we must look beyond temperature and consider the fundamental role of pressure.
The Problem of Sublimation
At standard atmospheric pressure, materials have a clear path from solid to liquid to gas as temperature increases. Graphite is different.
Its atoms are held together by such strong covalent bonds that when heated, they gain enough energy to break free entirely, turning directly into a gas. This process is called sublimation. For graphite, this happens at around 3,900 K (6,560°F).
The Role of Extreme Pressure
To prevent sublimation and force graphite into a liquid state, immense pressure is required. This relationship between temperature, pressure, and state (solid, liquid, gas) is described by a material's phase diagram.
The key feature is the triple point: the specific combination of temperature and pressure where the solid, liquid, and gaseous phases can all exist in equilibrium. For graphite, the triple point is estimated to be around 4,500 K and 10 megapascals (MPa), which is nearly 100 times standard atmospheric pressure.
Only at pressures above this triple point can a distinct liquid carbon phase exist.
The Challenge of Precise Measurement
The extreme conditions required to reach graphite's triple point are the primary reason for the conflicting experimental data.
Technical Hurdles
Accurately maintaining and measuring a stable temperature of over 4,000 K while simultaneously applying over 100 atmospheres of pressure is at the edge of our current technological capabilities.
Different experimental methods, such as laser heating or electrical resistance heating, can produce slight variations in conditions, leading to the wide range of reported melting points.
The Elusive Nature of Liquid Carbon
Even when achieved, liquid carbon is one of the most exotic and difficult-to-study materials in existence. It is highly reactive and exists for only fractions of a second under controlled conditions, making definitive analysis incredibly difficult.
This experimental uncertainty is not new; it is a well-documented scientific challenge that has persisted for over 60 years.
How to Apply This Knowledge
The "right" temperature for graphite's phase change depends entirely on your application. Understanding the context is more important than memorizing a single number.
- If your primary focus is practical engineering (furnaces, rocket nozzles): The sublimation temperature of ~3,900 K at standard pressure is the most critical value. This is the temperature limit for using graphite in most real-world, high-heat applications.
- If your primary focus is materials science or physics research: The triple point of ~4,500 K and 10 MPa is the key benchmark. This represents the minimum conditions under which liquid carbon can be formed and studied.
- If you need a general estimate for the melting curve: Acknowledge the broad range of 4,000 K to 5,000 K, understanding this occurs only under extreme, non-atmospheric pressures.
Ultimately, graphite's remarkable stability at high temperatures comes from its preference to become a gas rather than melt.
Summary Table:
| Key Point | Value / Condition |
|---|---|
| Sublimation Point (at 1 atm) | ~3,900 K (~6,560°F) |
| Estimated Triple Point (Solid, Liquid, Gas) | ~4,500 K at 10 MPa |
| Reported Melting Range (High Pressure) | 4,000 K - 5,000 K |
| Critical Factor | Extreme Pressure (>100 atm) |
Need precise, high-temperature solutions for your lab?
Graphite's behavior under extreme conditions highlights the need for reliable, high-performance equipment. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust lab equipment and consumables designed to meet the demanding needs of modern laboratories.
Whether you are working with high-temperature processes or advanced materials science, our products ensure accuracy, durability, and safety.
Contact us today to discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's high-temperature applications and research goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is graphite used for heat transfer? For Superior In-Plane Thermal Conductivity
- How is synthetic graphite manufactured? A Deep Dive into the High-Temperature Process
- What is the graphite furnace used for? Achieve Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C in a Controlled Environment
- Why is graphite the best conductor of heat? Understanding Its Directional Thermal Superiority
- What are the industrial applications of graphite? From Metallurgy to Semiconductors



















