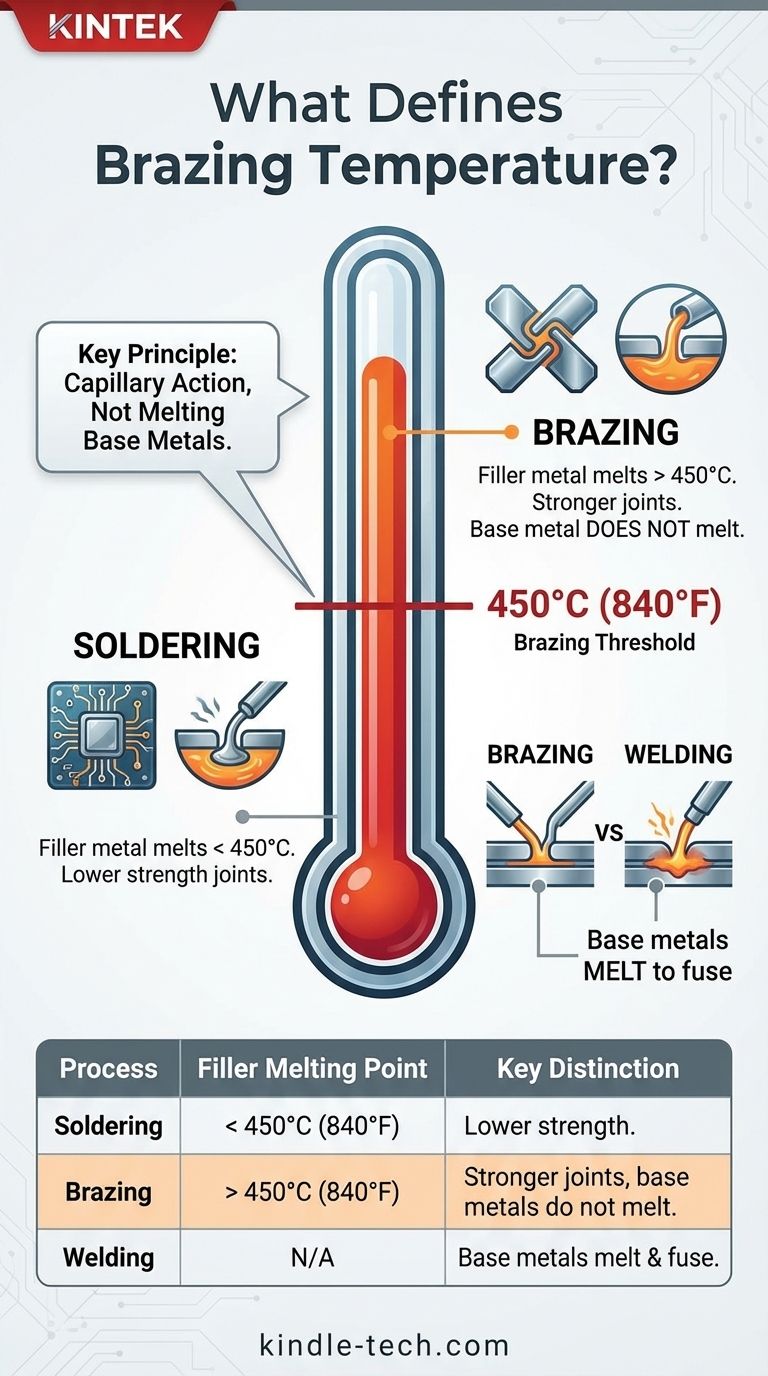
Brazing is defined by a specific temperature threshold. According to the American Welding Society (AWS) and international standards, a metal-joining process is considered brazing when it uses a filler metal that melts at a temperature above 450°C (840°F). Crucially, this process heats the base metals but never melts them, ensuring their fundamental structure remains intact.
The 450°C (840°F) mark is the industry-standard dividing line between brazing and soldering. The true principle of brazing, however, is not a specific temperature but the act of joining metals using a molten filler metal without melting the base materials themselves.

Brazing vs. Soldering: The Critical Temperature Divide
The distinction between brazing and soldering is not arbitrary. It is a classification based on the capabilities and characteristics of the filler metals and the resulting joints.
The 450°C (840°F) Convention
This temperature is the universally accepted threshold that separates soldering from brazing. If the filler metal has a liquidus (the temperature at which it is fully molten) below this point, the process is soldering. If the liquidus is above this point, the process is brazing.
Why This Temperature Matters
This distinction is directly related to the strength of the joint. Filler metals used in brazing are metallurgically different from solders, creating joints that are substantially stronger and more suitable for high-stress or high-temperature applications. Soldered joints, while useful, offer significantly lower mechanical strength.
Beyond the Threshold: What Defines the Actual Brazing Temperature?
While 450°C is the minimum threshold, most brazing operations occur at much higher temperatures. The exact temperature is dictated entirely by the materials involved.
The Role of the Filler Metal
The specific brazing temperature is determined by the melting point of the filler metal alloy. Different alloys are chosen based on the base metals being joined and the desired properties of the final joint.
For example, common silver-based brazing alloys melt between 620°C and 845°C (1150°F and 1550°F). Copper brazing of steel is often performed in a furnace at around 1120°C (2050°F).
The Importance of Capillary Action
Brazing works by capillary action, where the molten filler metal is drawn into the tight gap between the base metals. The assembly must be heated to a temperature that is slightly above the filler's melting point to ensure it flows completely and forms a strong, continuous bond.
How Brazing Differs from Welding
It is vital not to confuse brazing with welding. Welding works by melting the base metals themselves, causing them to fuse together, often with the addition of a filler material. Brazing never melts the base metals, making it a less thermally aggressive process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a brazing temperature is not just about meeting a definition; it's about balancing technical requirements and potential drawbacks.
Heat Input and Distortion
Higher brazing temperatures introduce more thermal energy into the assembly. This can alter the properties of the base metals (e.g., undoing a prior heat treatment) or cause warping and distortion, which is a critical concern for precision components.
Filler Metal Selection and Cost
The choice of filler metal dictates the temperature, which in turn affects cost and performance. Lower-temperature silver brazing alloys are often more expensive than high-temperature copper fillers, but they reduce the risk of thermal damage to the base parts.
Joint Strength and Service Temperature
The brazing temperature is linked to the final joint's performance. High-temperature brazing alloys (like nickel-based fillers) are typically used to create joints that must operate reliably in high-temperature environments, such as in a jet engine.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Use the temperature threshold as a guide to select the correct process for your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is joining heat-sensitive components or minimizing distortion: Explore soldering or low-temperature brazing alloys that operate just above the 450°C threshold.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum joint strength for structural applications: You will need high-temperature brazing alloys, such as copper or nickel-based fillers, which require furnace control at temperatures well over 1000°C.
- If your primary focus is simply differentiating between processes: Remember the rule—if the filler melts below 450°C it's soldering; if it melts above 450°C without melting the base metal, it's brazing.
Understanding this core principle allows you to select the right joining process based on material properties and performance requirements.
Summary Table:
| Process | Filler Metal Melting Point | Key Distinction |
|---|---|---|
| Soldering | Below 450°C (840°F) | Lower strength joints for less demanding applications. |
| Brazing | Above 450°C (840°F) | Stronger joints; base metals are heated but NOT melted. |
| Welding | N/A (Base metals melt) | Base metals are melted to fuse together. |
Ready to achieve perfect, high-strength brazed joints? The precise temperature control of a KINTEK laboratory furnace is essential for successful brazing, ensuring your filler metal flows correctly without damaging your base materials. Whether you're working with sensitive components or high-temperature alloys, our experts can help you select the ideal equipment for your project. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific metal-joining challenges and discover how our lab solutions can enhance your results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What are the advantages of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature Uniformity and Control
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning



















