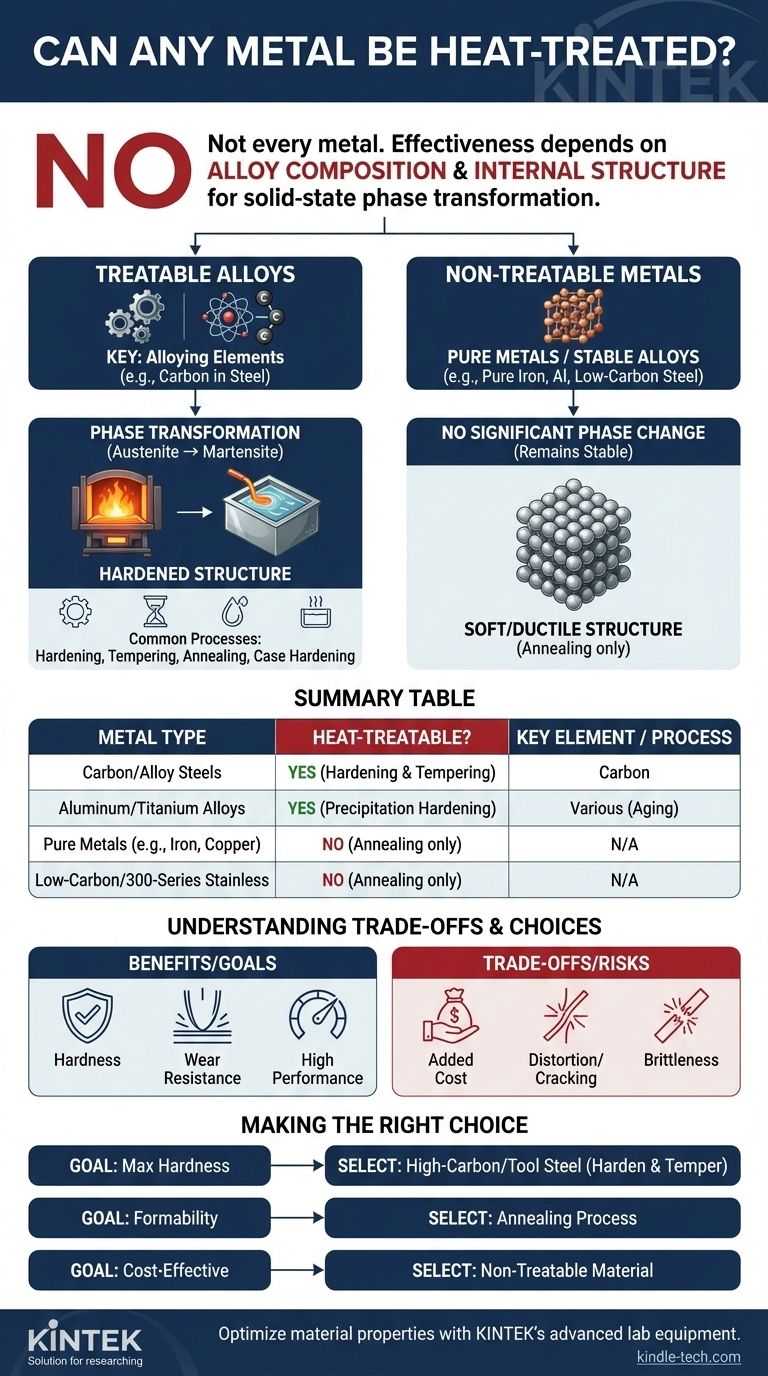
No, not every metal can be meaningfully heat-treated to alter its core mechanical properties like strength and hardness. The ability to be heat-treated is not a universal property of metals but is dependent on the alloy's specific chemical composition and internal crystal structure. While processes like annealing can soften almost any metal, transformative treatments that impart significant strength are reserved for a select group of alloys.
The key takeaway is that heat treatment's effectiveness hinges on a metal's ability to undergo a phase transformation in its solid state. It is the specific alloying elements, like carbon in steel, that enable these internal structural changes when subjected to a controlled cycle of heating and cooling.

What Makes a Metal "Heat-Treatable"?
The difference between a metal that can be hardened by heat and one that cannot comes down to its internal atomic structure. Heat treatment is a process of controlled manipulation of this structure.
The Role of Alloying Elements
A pure metal generally has a stable crystal structure that is difficult to change without melting it. Meaningful heat treatment relies on alloying elements—other metals or non-metals intentionally mixed in.
For example, the most critical alloying element in steel is carbon. Even a small amount of carbon completely changes how iron behaves when heated and cooled.
The Concept of Phase Transformation
Heat-treatable alloys are defined by their ability to change their internal crystal arrangement, or phase, at specific temperatures while remaining solid.
In steel, heating it above a critical temperature transforms its structure into a phase called austenite, which can dissolve carbon atoms. Upon rapid cooling (quenching), this structure is trapped in a new, highly-stressed, and very hard phase called martensite. This is the fundamental principle of hardening steel.
Common Heat Treatment Processes
The goal of the treatment dictates the process. Processes mentioned in manufacturing include:
- Hardening & Quenching: To create maximum hardness and strength.
- Tempering: A secondary, lower-temperature heating process done after hardening to reduce brittleness and increase toughness.
- Annealing: A process of heating and slow cooling to make a metal softer, more ductile, and easier to machine.
- Case Hardening (Carburizing): A method that adds carbon to the surface of a low-carbon steel, allowing only the outer "case" to be hardened while the inner "core" remains tough.
Examples of Treatable vs. Non-Treatable Metals
Understanding which metals respond to which treatments is essential for material selection.
Prime Candidates: Carbon and Alloy Steels
Medium and high-carbon steels are the most common heat-treatable metals. Their iron-carbon composition is perfectly suited for the austenite-to-martensite phase transformation, allowing for a dramatic increase in hardness and strength.
Other Treatable Alloys
Certain alloys of other metals can also be heat-treated, often through a different mechanism called precipitation hardening or age hardening.
In this process, alloying elements are first dissolved into the base metal at high temperature and then allowed to "precipitate" out as extremely small, strength-imparting particles during a lower-temperature "aging" treatment. This applies to many high-performance aluminum, titanium, and copper alloys.
Metals That Don't Respond to Hardening
Pure metals like pure iron, copper, or aluminum cannot be hardened by heat treatment because they lack the alloying elements necessary for phase transformations or precipitation.
Likewise, many common alloys like low-carbon steel or 300-series stainless steels do not respond to this type of hardening because their composition does not support the necessary structural change. They may be annealed to soften them, but they cannot be significantly hardened by quenching.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Heat treatment is a powerful tool, but it is not a solution for every application. It introduces complexity, cost, and risk that must be justified by the performance requirements.
Added Cost and Production Time
Heat treatment is an additional manufacturing step that requires specialized equipment (furnaces, quench tanks), energy, and time. For many components, using a metal "as-cast" or "as-rolled" is far more economical if its inherent properties are sufficient for the application.
Risk of Distortion and Cracking
The rapid cooling involved in quenching creates significant internal stresses within a metal part. This stress can cause the part to warp, distort, or even crack, especially if the geometry is complex or the process is not carefully controlled.
Property Compromises
You cannot maximize all properties at once. Hardening a metal almost always makes it more brittle. The secondary process of tempering is a perfect example of this trade-off: it is performed to regain some toughness at the expense of a small amount of hardness.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a heat-treatable metal and process depends entirely on the component's end-use requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance: Select a heat-treatable alloy like a high-carbon steel or tool steel designed for a hardening and tempering process.
- If your primary focus is extreme performance under high heat and stress: You will need specialized alloys and processes, such as the vacuum heat treatment used for aerospace or high-performance automotive parts.
- If your primary focus is formability or machinability: Use an annealing process to soften the workpiece before manufacturing, even if it is a heat-treatable alloy that will be hardened later.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for a low-stress application: Choose a material that meets the design requirements without heat treatment to avoid unnecessary cost and complexity.
Ultimately, effective engineering is about matching the right material and its corresponding processes to the specific demands of the task.
Summary Table:
| Metal Type | Heat-Treatable? | Key Alloying Element | Common Process |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon/Alloy Steels | Yes | Carbon | Hardening & Tempering |
| Aluminum/Titanium Alloys | Yes (Precipitation Hardening) | Various | Aging |
| Pure Metals (e.g., Iron, Copper) | No | N/A | Annealing (softening only) |
| Low-Carbon Steel / 300-Series Stainless | No | N/A | Annealing (softening only) |
Ready to optimize your material properties with precision heat treatment? KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for controlled thermal processes. Whether you're working with high-carbon steels for maximum hardness or precipitation-hardening alloys for aerospace applications, our solutions ensure accurate temperature control and reliable results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific heat treatment challenges and help you achieve superior material performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the process of vacuum quenching? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish
- How does heat treatment process work? Tailor Material Properties for Your Application
- What are the four types of heat treating processes? Master Annealing, Normalizing, Hardening, and Tempering
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering



















