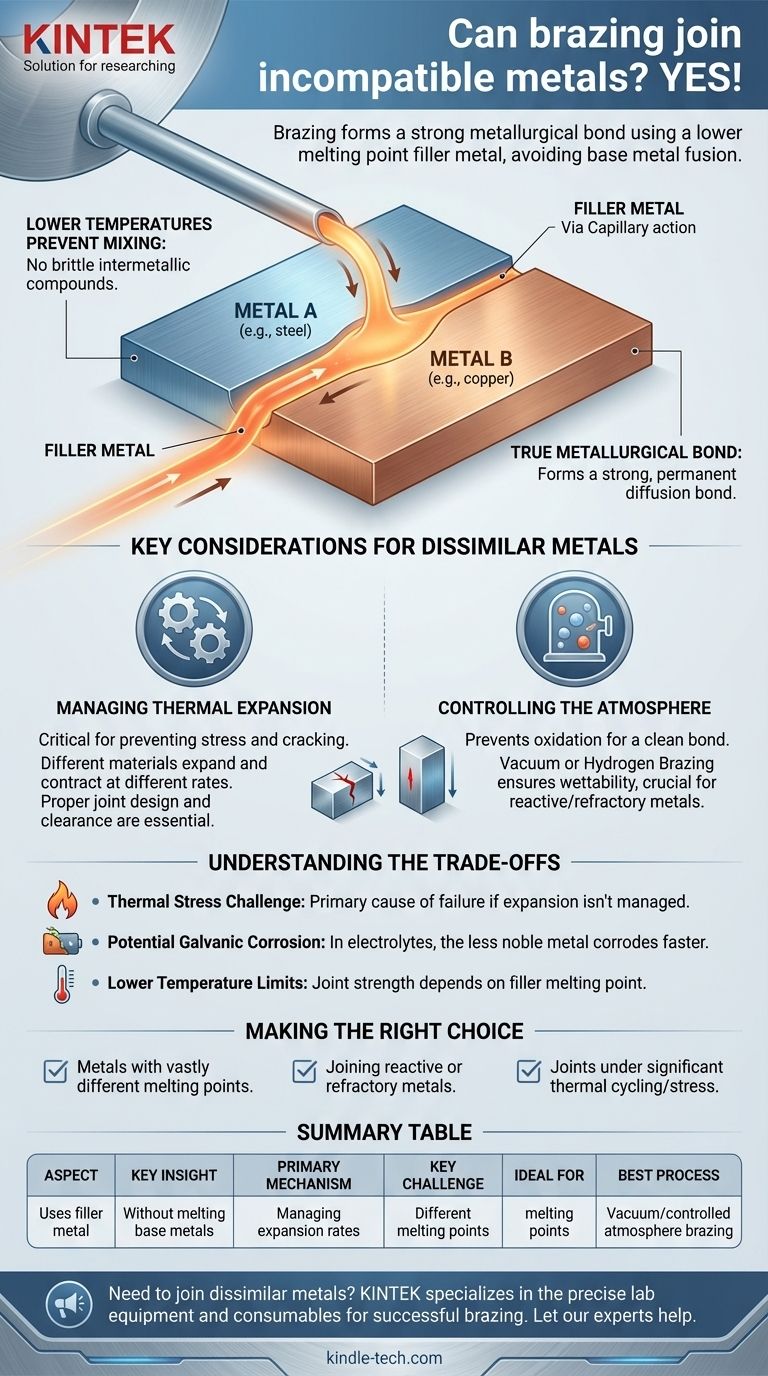
Yes, brazing is one of the most effective and widely used methods for joining incompatible or dissimilar metals. Unlike welding, which melts the base metals together, brazing uses a filler metal with a lower melting point to flow between the parts and form a strong metallurgical bond. This fundamental difference is what allows it to successfully join materials that would be impossible to fuse directly.
Brazing excels at joining dissimilar metals because it avoids the issues caused by melting and mixing incompatible materials. However, success is not automatic; it depends entirely on managing the different rates of thermal expansion between the metals being joined.

Why Brazing Works for Dissimilar Metals
The effectiveness of brazing lies in its process, which sidesteps the primary challenges of joining different metals.
The Role of the Filler Metal
The braze filler metal is the critical intermediary in the joint. This alloy is specifically chosen to have a melting point that is lower than either of the two base metals.
The filler metal is also selected for its ability to "wet" and bond with both materials, acting as a compatible bridge between them.
Lower Temperatures Prevent Common Failures
Welding dissimilar metals often creates brittle intermetallic compounds where the molten materials mix and resolidify, leading to weak and unreliable joints.
Because brazing occurs at a lower temperature without melting the base metals, this harmful mixing is completely avoided, preserving the original properties of the materials.
A True Metallurgical Bond
Brazing is not a simple gluing process. As the filler metal flows into the joint via capillary action, it forms a diffusion bond with the surface of each base metal.
This creates a strong, permanent, and often hermetic seal between the two distinct materials.
Key Considerations for Dissimilar Metal Brazing
While brazing is highly capable, joining dissimilar metals requires careful engineering to manage the physical forces at play.
Managing Thermal Expansion
This is the single most important factor. Almost all materials expand when heated and contract when cooled, but they do so at different rates (coefficients of thermal expansion).
When two dissimilar metals are brazed and then cool, one will shrink more than the other. This differential can create immense stress, potentially cracking the filler metal or one of the base materials.
Proper joint design, such as adjusting the clearance at room temperature, is essential to accommodate this movement and ensure a stress-free joint at the end of the process.
Controlling the Brazing Atmosphere
Many metals, especially reactive ones, form oxides on their surface when heated. These oxide layers prevent the filler metal from wetting the surface and forming a strong bond.
Processes like vacuum brazing or hydrogen brazing use a controlled atmosphere to prevent oxidation, ensuring the joint surfaces remain perfectly clean for bonding. This is critical when joining materials like refractory metals to reactive metals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Brazing offers a powerful solution, but it's essential to recognize its limitations.
Thermal Stress is the Primary Challenge
Again, failure to account for different expansion rates is the most common reason for failure in dissimilar metal brazing. A joint that looks perfect when hot can tear itself apart as it cools if not designed correctly.
Potential for Galvanic Corrosion
Joining two different metals can create a galvanic cell in the presence of an electrolyte (like moisture). This can cause the less noble metal to corrode at an accelerated rate.
The design must consider the service environment and, if necessary, protect the joint from corrosive elements.
Lower Temperature Limits
The strength of a brazed joint is dependent on the filler metal, which inherently has a lower melting point than the base metals. This means brazed components are not suitable for service in temperatures that approach the filler's melting point.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these principles to guide your decision-making when considering brazing for your project.
- If your primary focus is joining metals with vastly different melting points (e.g., copper to steel): Brazing is an ideal solution because it joins the materials without melting the higher-temperature base metal.
- If you are joining reactive or refractory metals: You must use a controlled atmosphere process, such as vacuum brazing, to prevent surface oxides from ruining the joint.
- If the joint will be under significant thermal cycling or stress: You must carefully engineer the joint clearance to accommodate the different thermal expansion rates of the materials.
By managing thermal expansion and selecting the correct process, brazing provides a reliable and powerful method for engineering complex, multi-metal components.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Insight |
|---|---|
| Primary Mechanism | Uses a filler metal to bond materials without melting the base metals. |
| Key Challenge | Managing different thermal expansion rates to prevent joint stress. |
| Ideal For | Joining metals with different melting points (e.g., copper to steel). |
| Best Process | Vacuum or atmosphere-controlled brazing for reactive/refractory metals. |
Need to join dissimilar metals for a demanding application?
Brazing is a sophisticated process that requires the right equipment and expertise to manage thermal expansion and ensure a strong, reliable bond. KINTEK specializes in the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for successful brazing processes, including furnace systems for controlled atmosphere brazing.
Let our experts help you select the right solution for your laboratory's unique material joining challenges. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how we can enhance your capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What is hot press forging? Creating Complex, High-Strength Metal Components
- What is pressure-assisted sintering? Achieve Denser, Stronger Materials Faster
- What is the effect of increasing the pressure during sintering hot press sintering? Optimize Density, Time, and Temperature
- What is the main function of hot press forming? Achieve Superior Strength & Precision in Manufacturing
- What products are made by hot pressing? Achieve Maximum Density and Performance for Your Components



















