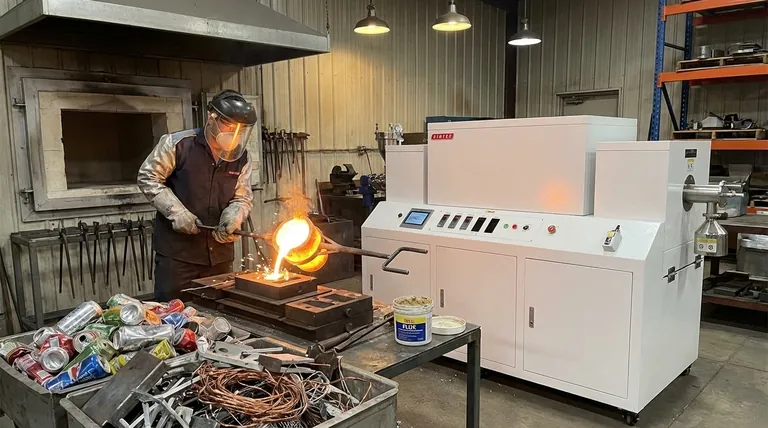
Without a doubt, yes. The ability to be melted and reformed is one of the most fundamental and valuable properties of nearly all metals. This process is a physical transformation, not a chemical one, allowing metals to be recycled, cast into new shapes, and repurposed infinitely without degrading their core metallic nature.
While virtually all metals can be remelted, the quality and properties of the resulting material depend entirely on controlling for contamination, oxidation, and the potential loss of specific alloying elements during the process. It is a process governed by physics, but perfected through chemistry and engineering.

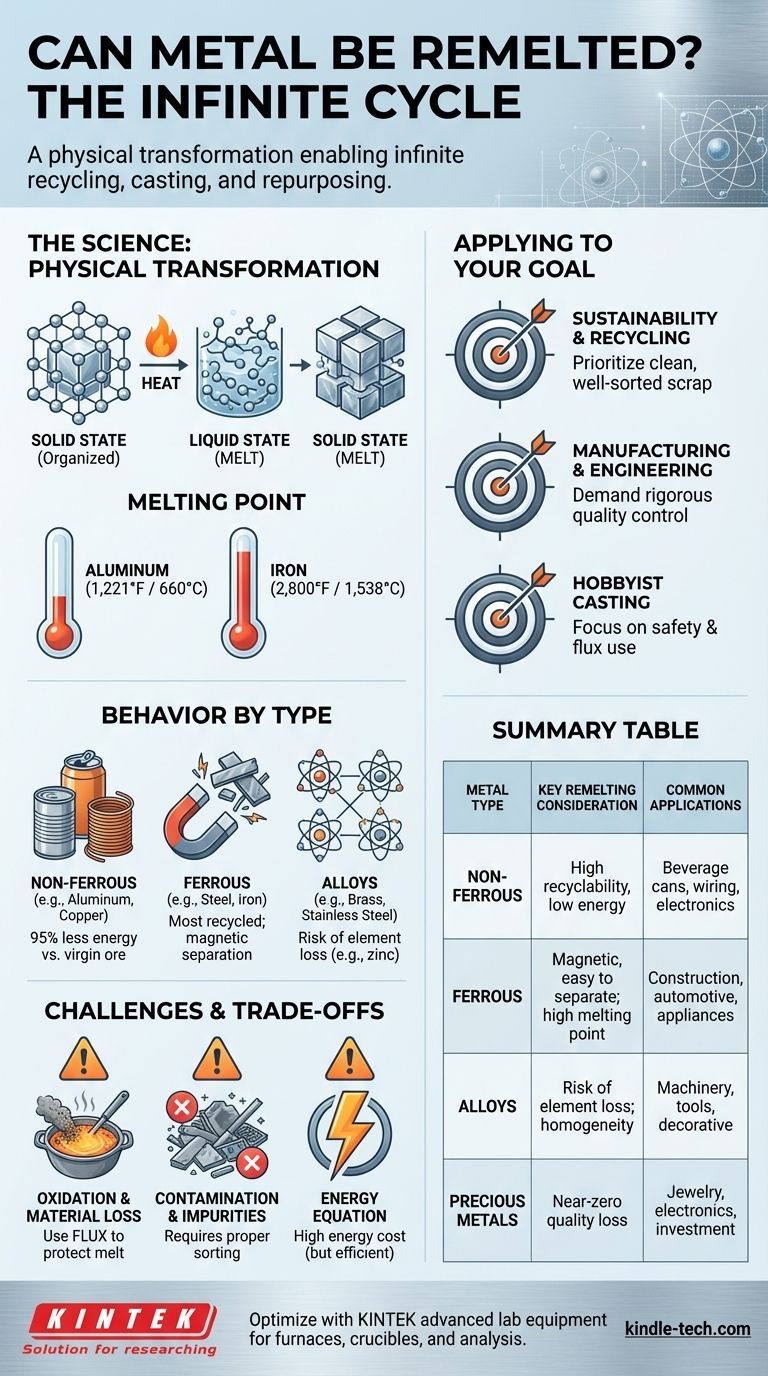
The Science Behind Remelting: A Physical Transformation
The remeltability of metal is rooted in its atomic structure. It is a predictable cycle of phase changes from solid to liquid and back to solid.
Crystalline Structures and Phase Change
Metals in their solid state have a highly organized, crystalline atomic structure. When heated to their melting point, the energy input overcomes the bonds holding this structure together, and the metal becomes a liquid (a melt). Upon cooling, these metallic bonds reform, and the material solidifies again, ready for a new life.
The Role of Melting Point
Different metals become liquid at vastly different temperatures. For example, aluminum melts at a relatively low 1,221°F (660°C), making it accessible for recycling and even hobbyist casting. In contrast, iron melts at 2,800°F (1,538°C), requiring significant industrial furnaces and energy.
How Different Metals Behave in Remelting
While the principle is universal, the practical details vary significantly between different types of metals and their alloys.
Non-Ferrous Metals (Aluminum, Copper, Gold)
Metals that do not contain iron are prized for their recyclability. Aluminum is a prime example; recycling an aluminum can uses about 95% less energy than creating new aluminum from its raw ore (bauxite). Precious metals like gold and silver can be remelted repeatedly with almost no loss of quality, which is why they have been recycled for millennia.
Ferrous Metals (Iron and Steel)
Steel is the most recycled material on Earth. Its magnetic properties make it exceptionally easy to separate from mixed waste streams. Scrap steel is a critical ingredient in modern steelmaking, with electric arc furnaces often using a feed of nearly 100% scrap metal.
The Special Case of Alloys
Alloys are mixtures of a base metal with other elements to achieve specific properties (e.g., steel is iron and carbon, brass is copper and zinc). When remelting alloys, the goal is to melt them কাজাখস্তানি ভাষায় "into a homogenous liquid" before any individual elements can burn off or separate. However, some more volatile elements, like zinc in brass, can be partially lost to oxidation if the process is not carefully controlled.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Remelting metal is not a flawless process. Success requires managing several key challenges that can impact the quality of the final product.
Oxidation and Material Loss
When molten metal is exposed to air, its surface reacts with oxygen to form oxides, which manifest as dross or slag. This represents a direct loss of usable material. Foundries use a substance called flux to cover the melt, which protects it from the atmosphere and helps draw impurities out.
Contamination and Impurities
This is the single biggest challenge in metal recycling. If scrap metal is contaminated with other metals, paint, plastics, or dirt, these impurities get mixed into the melt. This can drastically alter the final metal's properties, making it weaker, more brittle, or less corrosion-resistant. Proper sorting of scrap मटेरियल is therefore essential.
The Energy Equation
Melting metal is an extremely energy-intensive process. While it is almost always more energy-efficient than producing metal from virgin ore, the high energy cost is a significant operational and environmental factor.
The Concept of Downcycling
When contamination cannot be fully removed, the remelted metal may not be suitable for its original, high-performance application. It may be "downcycled" into a product with less stringent requirements. For example, a high-grade aluminum alloy from an aircraft might be remelted and, due to minor impurities, become feedstock for lower-grade castings.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your approach to remelting metal depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is sustainability and recycling: Prioritize clean, well-sorted scrap. This is the key to high-value recycling that saves the maximum amount of energy and natural resources.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing or engineering: Demand rigorous quality control and chemical analysis of remelted feedstock to ensure it meets the precise mechanical and performance specifications for your product.
- If your primary focus is hobbyist metal casting: Focus on safety, proper ventilation, and using clean, identifiable scrap. Learning to use flux correctly will dramatically improve the quality and usability of your castings.
By understanding these core principles, you can effectively leverage metal's infinite recyclability for any purpose.
Summary Table:
| Metal Type | Key Remelting Consideration | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Non-Ferrous (Aluminum, Copper) | High recyclability, low energy use vs. virgin ore | Beverage cans, wiring, electronics |
| Ferrous (Steel, Iron) | Magnetic, easy to separate; high melting point | Construction, automotive, appliances |
| Alloys (Brass, Stainless Steel) | Risk of element loss (e.g., zinc); requires homogeneity | Machinery, tools, decorative items |
| Precious Metals (Gold, Silver) | Near-zero quality loss; ideal for repeated recycling | Jewelry, electronics, investment |
Optimize your metal remelting and recycling processes with KINTEK's advanced lab equipment. Whether you're in manufacturing, recycling, or R&D, controlling contamination, oxidation, and alloy consistency is critical to maintaining material quality. KINTEK specializes in furnaces, crucibles, and consumables designed for precise thermal processing and analysis. Let our solutions help you achieve higher purity, better efficiency, and sustainable outcomes. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific metal processing needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the main types of biomass conversion processes? Unlock the Best Pathway for Your Energy Needs
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- What is the range of pyrolysis? Master Temperature Control for Optimal Bio-Product Yields
- What are the equipment requirements for loading platinum (Pt) onto composite supports? Precise Stirring for High Dispersion
- What temperature is needed for pyrolysis waste? A Guide to Optimizing Your Waste-to-Value Process



















