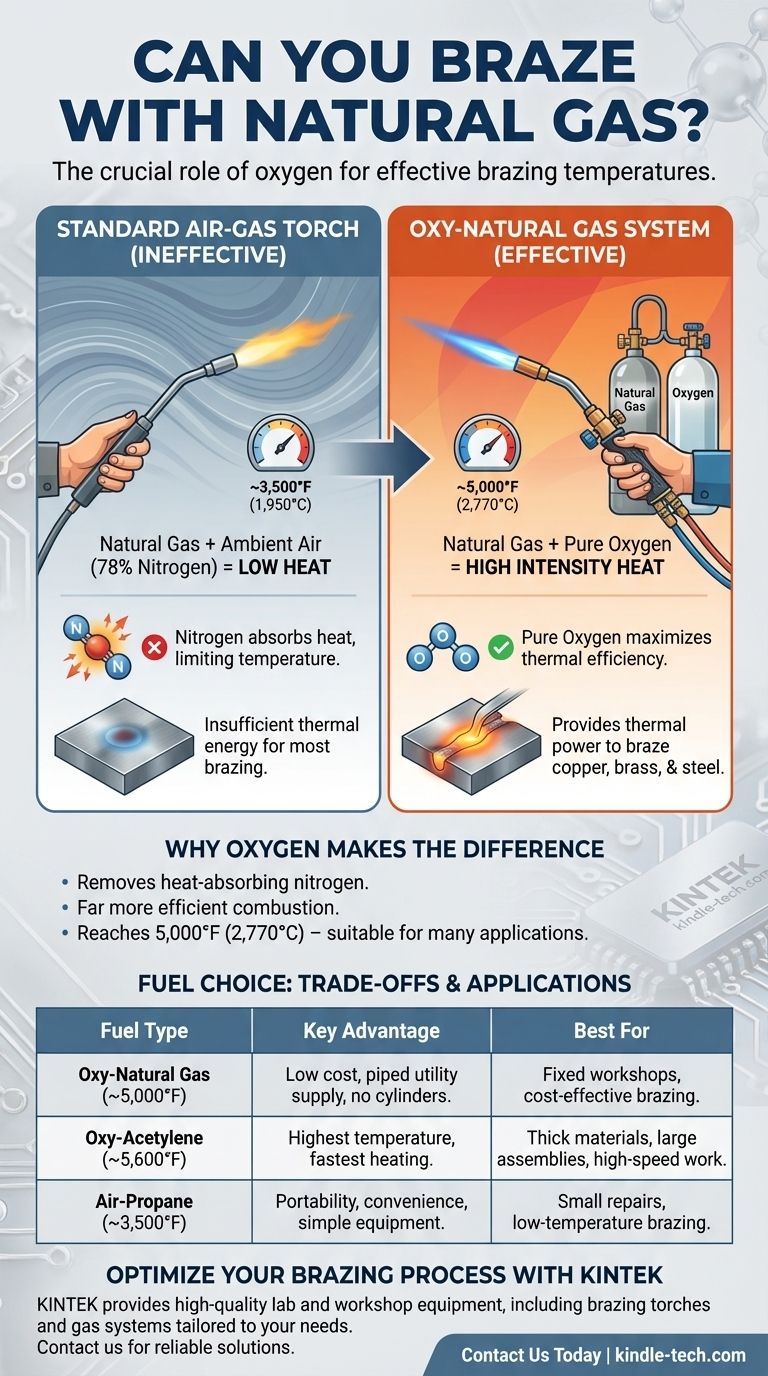
Yes, you can braze with natural gas, but with a critical caveat: it is rarely effective when mixed with ambient air. To reach the high temperatures required for brazing, natural gas must be combined with pure oxygen in an oxy-fuel torch. Using a standard air-gas torch will not provide sufficient heat for a proper brazing bond.
While technically possible, using natural gas with air from a standard torch is ineffective for most brazing applications due to its low flame temperature. The key to successfully brazing with natural gas is upgrading to an oxy-natural gas system, which provides the necessary heat but comes with its own set of trade-offs compared to other common fuel gases.

Why Natural Gas Alone Falls Short for Brazing
Brazing is defined by heating base metals to a temperature above 840°F (450°C) so a filler metal can melt and flow into the joint. The fuel you use must be able to overcome this threshold efficiently.
The Critical Barrier: Flame Temperature
A standard torch mixes fuel with ambient air, which is about 78% nitrogen and only 21% oxygen. This nitrogen absorbs a massive amount of heat, effectively limiting the flame's maximum temperature.
A natural gas and air flame burns at approximately 3,500°F (1,950°C). While this is technically much hotter than the melting point of many braze alloys, it leaves very little thermal "headroom" for heating the actual workpiece, which constantly loses heat to the surrounding environment.
The Problem of Heat Output (BTUs)
Flame temperature is only half the story; total heat output is just as important. Natural gas has a lower heat value (BTUs per cubic foot) than fuels like propane or acetylene.
Think of it like this: a single match is very hot at its tip, but it cannot heat a large iron skillet. A natural gas/air flame lacks the thermal energy density to quickly bring anything but the smallest, thinnest parts up to brazing temperature.
The Solution: Introducing Oxygen (Oxy-Natural Gas)
To make natural gas a viable fuel for brazing, you must replace the air with pure oxygen. This is known as an oxy-natural gas system.
How Oxy-Natural Gas Works
By removing the heat-absorbing nitrogen from the equation, the combustion reaction becomes far more efficient and intense.
An oxy-natural gas flame burns at a much higher temperature, around 5,000°F (2,770°C). This provides the necessary thermal power to heat a wide range of metal thicknesses to brazing temperature quickly and efficiently.
Typical Applications
Oxy-natural gas is a perfectly suitable process for brazing common materials like copper, brass, and mild steel, especially in fabrication shops where natural gas is supplied via utility lines.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a fuel gas is a decision based on performance, cost, and convenience. While functional, oxy-natural gas is not the hottest or most powerful option available.
Heat and Speed: Natural Gas vs. Other Fuels
An oxy-natural gas flame is significantly cooler than an oxy-acetylene flame, which can reach over 5,600°F (3,100°C).
This temperature difference means that oxy-natural gas heats more slowly. For large parts or metals that conduct heat quickly (like thick copper), oxy-acetylene will perform the job much faster. For most common jobs, however, the heating speed of oxy-natural gas is perfectly adequate.
Cost and Convenience
This is the primary advantage of natural gas. It is typically the cheapest fuel gas available and can be piped directly from a utility line, eliminating the need to manage, store, and refill heavy cylinders.
In contrast, acetylene and oxygen both require rented or purchased cylinders that must be transported and handled, adding significant logistical overhead and cost.
Flame Characteristics and Joint Cleanliness
No matter the fuel, a successful braze requires a clean surface, free of oxides that prevent the filler metal from bonding. The torch flame itself plays a role here.
A properly adjusted "neutral" or slightly "reducing" (fuel-rich) flame helps consume oxygen at the joint surface, protecting the metal during heating. This, combined with the use of flux, creates the clean chemical environment necessary for the braze alloy to flow properly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best fuel gas depends entirely on your specific application, budget, and logistical constraints.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for a fixed workshop: Oxy-natural gas is an excellent choice for brazing copper, brass, and steel, offering low operating costs and eliminating cylinder management.
- If your primary focus is performance, speed, and versatility: An oxy-acetylene system provides the highest flame temperature, making it ideal for thick materials, large assemblies, and faster production work.
- If your primary focus is portability and occasional repairs: A simple air-MAPP or air-propane torch is often sufficient for soldering and some low-temperature brazing on small copper pipes, offering maximum convenience.
Ultimately, selecting the right fuel is about matching the thermal energy you can produce to the thermal demands of your specific project.
Summary Table:
| Fuel Type | Flame Temperature (with Oxygen) | Key Advantage | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxy-Natural Gas | ~5,000°F (2,770°C) | Low cost, piped utility supply | Fixed workshops, cost-effective copper/steel brazing |
| Oxy-Acetylene | ~5,600°F (3,100°C) | Highest temperature, fast heating | Thick materials, large assemblies, high-speed work |
| Air-Propane | ~3,500°F (1,950°C) | Portability, convenience | Small repairs, low-temperature brazing |
Ready to Optimize Your Brazing Process?
Choosing the right fuel and equipment is critical for achieving strong, clean brazed joints. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab and workshop equipment, including brazing torches and gas systems tailored to your specific needs. Whether you're working in a fixed workshop or require portable solutions, our expertise ensures you get the thermal performance and efficiency your projects demand.
Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how we can support your brazing applications with reliable equipment and expert guidance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of autoclaving in hospitals? Achieve Unmatched Sterilization for Patient Safety
- What is a lab autoclave? Your Guide to Sterilization with Pressurized Steam
- Do you need to autoclave glassware? A Guide to Sterilization vs. Cleaning
- Why is it important to autoclave the prepared reagents before using? Ensure Sterility and Reliable Results
- What are the sizes of autoclaves? A Guide to Choosing the Right Capacity for Your Lab



















