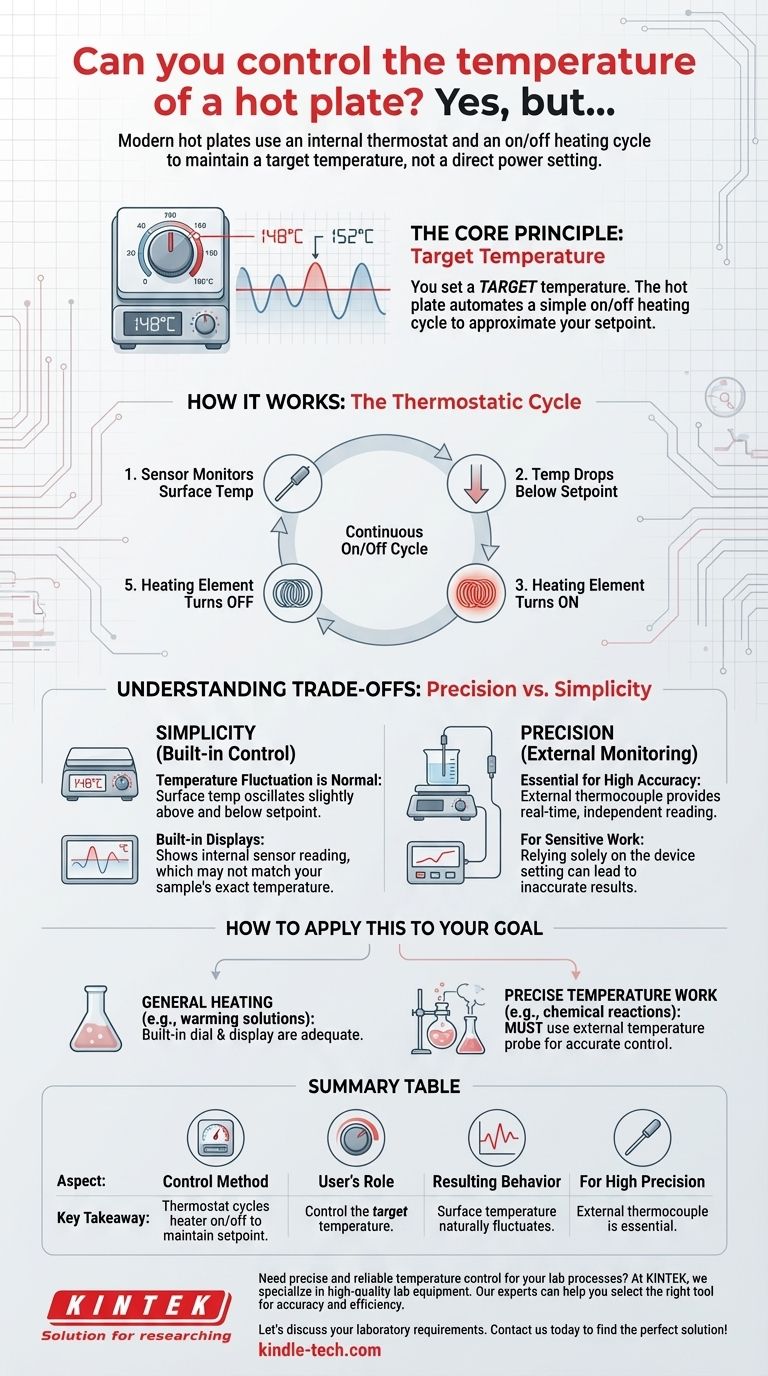
Yes, you can control the temperature of a modern hot plate. You set a target temperature using a control dial or digital input. The device then uses an internal thermostat to automatically turn the heating element on and off, working to maintain the temperature around that preset value.
The core principle is that you control the target temperature, not the heating power directly. The hot plate automates a simple on/off heating cycle to approximate your setpoint, which means the actual surface temperature will naturally fluctuate around that value.

How Hot Plate Temperature Control Works
Understanding the mechanism behind your hot plate's temperature control is key to using it effectively, whether for simple warming or for more precise applications.
The Thermostatic Cycle
A hot plate operates much like the thermostat in your home. When you set a desired temperature, an internal sensor monitors the plate's surface.
If the temperature drops below your setpoint, the heating element turns on. Once the sensor detects that the temperature has reached the preset value, the heating element turns off. This on-and-off cycle repeats continuously to maintain the average temperature.
Setting the Target Temperature
The user's primary control is the dial or digital interface, often labeled with temperature degrees. This input doesn't adjust the power of the heater; it only changes the temperature target that the internal thermostat aims to achieve.
The Role of the Internal Sensor
The accuracy of the entire system depends on this internal sensor. It provides the feedback that triggers the heating element. The placement and sensitivity of this sensor determine how closely the plate's temperature matches the display.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Precision vs. Simplicity
While this automated system is simple and effective for many tasks, it comes with inherent limitations that are critical to understand for sensitive work.
Temperature Fluctuation is Normal
Because the heater is either fully on or fully off, the actual surface temperature does not hold perfectly steady. It will always oscillate slightly above and below your setpoint as the heating element cycles on and off.
The Limitation of Built-in Displays
The digital display on the control panel shows the reading from its internal sensor. However, this may not be the exact temperature of your sample or the precise spot on the surface you are using. For general heating, this is fine, but it is a potential source of error in scientific experiments.
Why Precise Control Requires External Monitoring
For applications demanding high accuracy, the built-in control system is often insufficient. Relying solely on the device's setting can lead to inaccurate results. This is why external monitoring is the standard for precise laboratory work.
An external thermocouple placed directly in your sample or on the working surface provides a true, real-time temperature reading, independent of the hot plate's internal system.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your approach should depend entirely on the level of precision your task requires.
- If your primary focus is general heating (e.g., warming a solution): The hot plate's built-in dial and display are perfectly adequate for the job.
- If your primary focus is precise temperature-sensitive work (e.g., a chemical reaction): You must use an external temperature probe, like a thermocouple, to get an accurate reading and manually adjust the hot plate's setting to achieve your true target temperature.
By understanding that a hot plate manages an average temperature rather than a constant one, you can control your process with confidence.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Control Method | Set a target temperature; the hot plate's thermostat cycles the heating element on/off to maintain it. |
| User's Role | You control the target temperature, not the direct heating power. |
| Resulting Behavior | The actual surface temperature naturally fluctuates around the setpoint. |
| For High Precision | An external thermocouple is essential for accurate, real-time sample temperature reading. |
Need precise and reliable temperature control for your lab processes?
Understanding your equipment is the first step to achieving consistent results. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including hot plates designed for both general heating and demanding applications. Our experts can help you select the right tool for your specific needs, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in your work.
Let's discuss your laboratory requirements. Contact us today to find the perfect solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Small Constant Temperature Heated Magnetic Stirrer Heater and Stirrer
- High Performance Laboratory Stirrers for Diverse Applications
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Magnetic Stirring Bar
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-precision hot plate play in N-CXG synthesis? Achieve Perfect Precursor Homogenization
- What is the function of a magnetic stirring hot plate in zirconia-alumina synthesis? Master Solution Combustion Prep
- What is the purpose of continuous magnetic stirrer operation in photocatalytic Cr(VI) reduction? Optimize Efficiency
- What roles do a magnetic stirrer and nitrogen protection play in Fe3O4 synthesis? Master Purity and Particle Size
- What role does a constant temperature heating magnetic stirrer play in MFC-HAp synthesis? Achieve Material Homogeneity



















