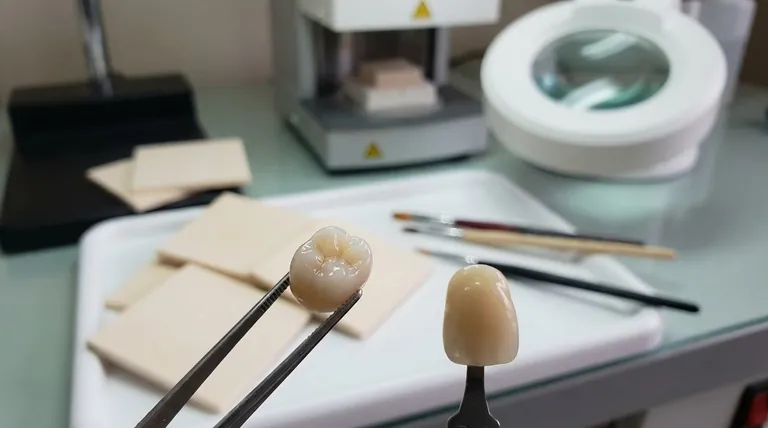
Yes, modern ceramic crowns are renowned for their ability to look remarkably natural. They are specifically engineered from materials that mimic the light-handling properties of natural tooth enamel. This allows them to blend seamlessly with surrounding teeth in a way that older metal-based crowns simply cannot.
The natural appearance of a ceramic crown is not automatic. It is the result of choosing the right type of ceramic for the right tooth and pairing it with the skill of an experienced dentist and dental laboratory.
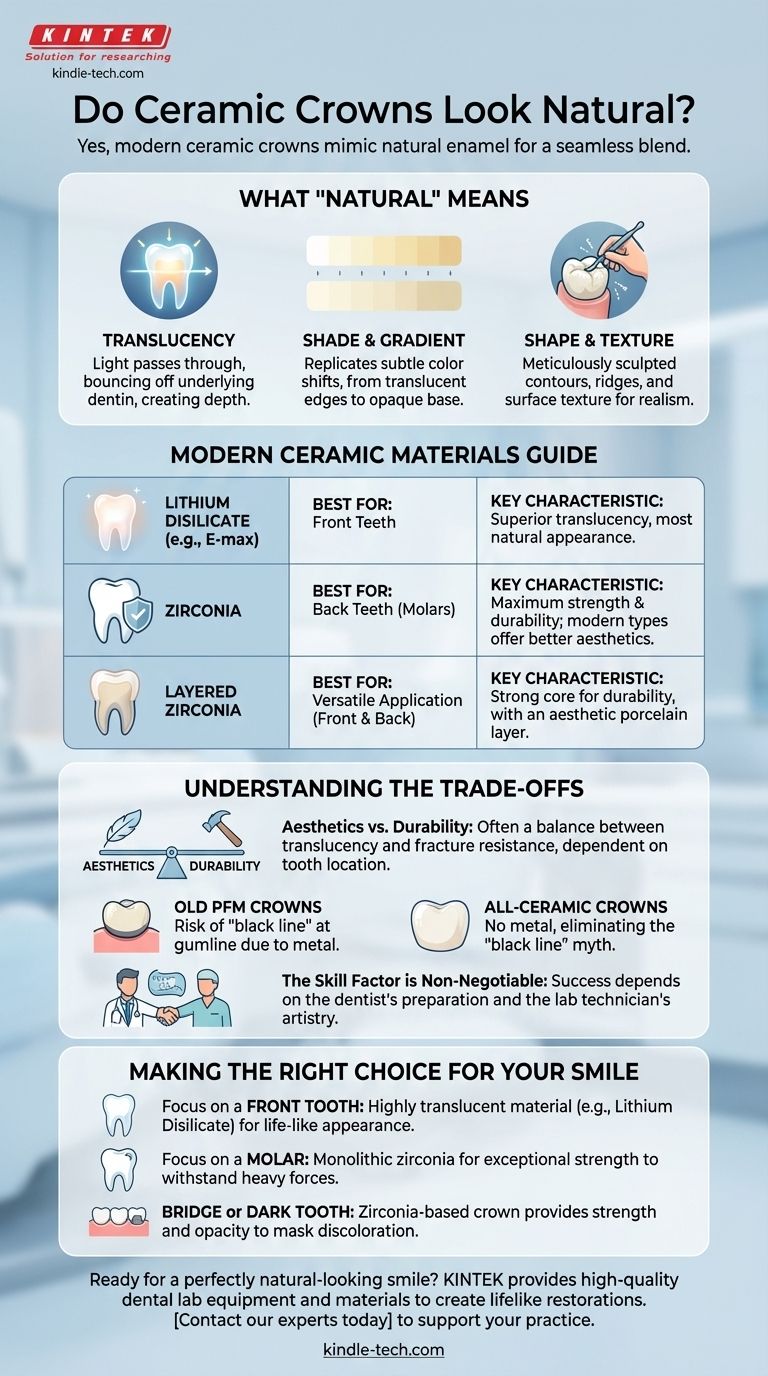
What "Natural" Means for a Dental Crown
Achieving a natural look goes beyond just matching the color. It involves replicating the complex optical and physical properties of a real tooth.
The Importance of Translucency
Natural tooth enamel isn't fully opaque; it has a degree of translucency. This means light passes partially through it, bounces off the underlying dentin, and reflects back out, creating depth and vitality.
The best ceramic materials are chosen for their ability to replicate this exact effect, preventing the crown from looking flat or artificial.
Perfecting the Shade and Gradient
A tooth is not one solid color. It typically has a subtle color gradient, being slightly more translucent near the biting edge and more opaque and yellowed near the gumline.
Skilled lab technicians use multiple shades of ceramic and apply external stains to recreate this gradient, ensuring the crown is indistinguishable from its neighbors.
Replicating Shape and Surface Texture
A natural tooth has unique contours, ridges, and a specific surface texture that reflects light in a certain way. A master technician will meticulously sculpt the crown to match the anatomy of the tooth it is replacing and mirror the characteristics of the adjacent teeth.
A Guide to Modern Ceramic Materials
Different types of all-ceramic crowns offer different balances of strength and aesthetics. The location of the tooth is the primary factor in material selection.
Lithium Disilicate (e.g., E-max)
This is often considered the gold standard for highly visible front teeth. Its exceptional translucency allows it to interact with light almost identically to natural enamel.
While strong enough for most applications, its primary advantage is its superior cosmetic appearance.
Zirconia
Zirconia is the strongest ceramic material available, making it the ideal choice for molars and other back teeth that endure immense chewing forces.
Traditionally, zirconia was more opaque, but modern "translucent zirconia" has significantly improved aesthetics, making it a more versatile option than ever before.
Layered Zirconia
This option offers a "best of both worlds" approach. It uses a strong, opaque zirconia core for durability, which is then covered with a more aesthetic, layered porcelain.
This combination provides the strength needed for a back tooth while achieving the beautiful, life-like appearance required for a front tooth.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While modern ceramics are excellent, it's crucial to understand their limitations and the factors that influence the final result.
Aesthetics vs. Durability
The core trade-off is often between translucency and strength. The most beautiful materials, like lithium disilicate, are not as fracture-resistant as the strongest materials, like zirconia. This is why material choice is so dependent on the tooth's location and function.
The "Black Line" Myth
You may have heard of crowns creating a dark line at the gumline. This is characteristic of older Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM) crowns, where the underlying metal coping can become visible if the gums recede.
All-ceramic crowns contain no metal, completely eliminating the risk of this unsightly "black line" effect.
The Skill Factor is Non-Negotiable
An advanced ceramic material is only a tool. The final aesthetic success is critically dependent on the skill of your dentist in preparing the tooth and the artistry of the dental lab technician who fabricates the crown. A perfect material can still look poor in the wrong hands.
Making the Right Choice for Your Smile
Your final decision should be a collaborative one with your dental professional, based on your specific clinical needs and aesthetic goals.
- If your primary focus is a front tooth: A highly translucent material like lithium disilicate is often the most life-like and aesthetically superior choice.
- If your primary focus is a molar: The exceptional strength of a monolithic zirconia crown is necessary to withstand heavy biting forces.
- If you need a bridge or have a dark underlying tooth: A zirconia-based crown provides the strength and opacity required to mask discoloration and support a multi-tooth structure.
Choosing the right material in partnership with your dentist ensures your new crown will be a seamless and confident part of your smile.
Summary Table:
| Material | Best For | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium Disilicate (E-max) | Front Teeth | Superior translucency, most natural appearance |
| Zirconia | Back Teeth (Molars) | Maximum strength and durability |
| Layered Zirconia | Versatile Application | Strong core with aesthetic porcelain layer |
Ready to achieve a perfectly natural-looking smile with a ceramic crown?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality dental lab equipment and materials that empower technicians to create lifelike restorations. Whether you are a dental lab focused on precision or a clinic dedicated to aesthetic excellence, our products support the creation of beautiful, durable ceramic crowns.
Let's discuss how we can support your practice. Contact our experts today to find the right solutions for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Precision Machined Yttria Stabilized Zirconia Ceramic Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Ceramic Ring
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- Are ceramic implants more expensive than titanium? Unpacking the Cost-Benefit Analysis
- What is sintering dental materials? The Key to Durable, High-Strength Dental Restorations
- If a dental laboratory's ceramic restorations lack ideal aesthetics, what is the first step? Calibrate Your Furnace.
- What is the disadvantage of ceramic for implant? Understanding the Risk of Fracture and Long-Term Durability
- What is a dental furnace? The Essential Tool for High-Quality Dental Restorations
- What is the firing temperature for dental ceramics? Mastering the Critical Cycle for Strong, Aesthetic Restorations
- What properties of dental zirconia parts are affected by the sintering temperature? Master Thermal Precision
- What is the main disadvantage of zirconia? Balancing Strength, Aesthetics, and Tooth Wear













