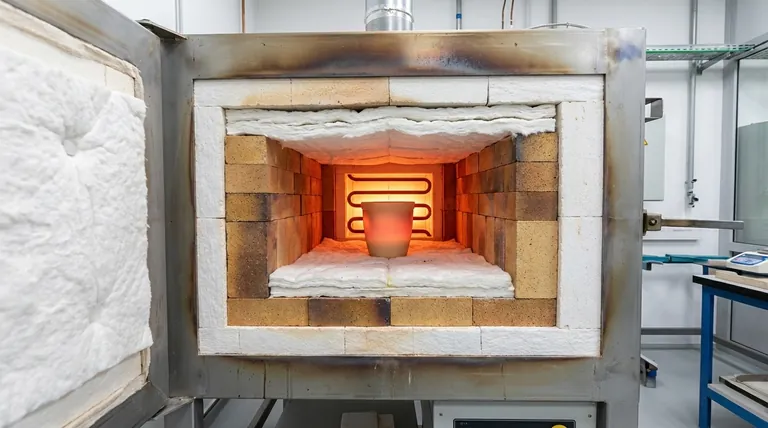
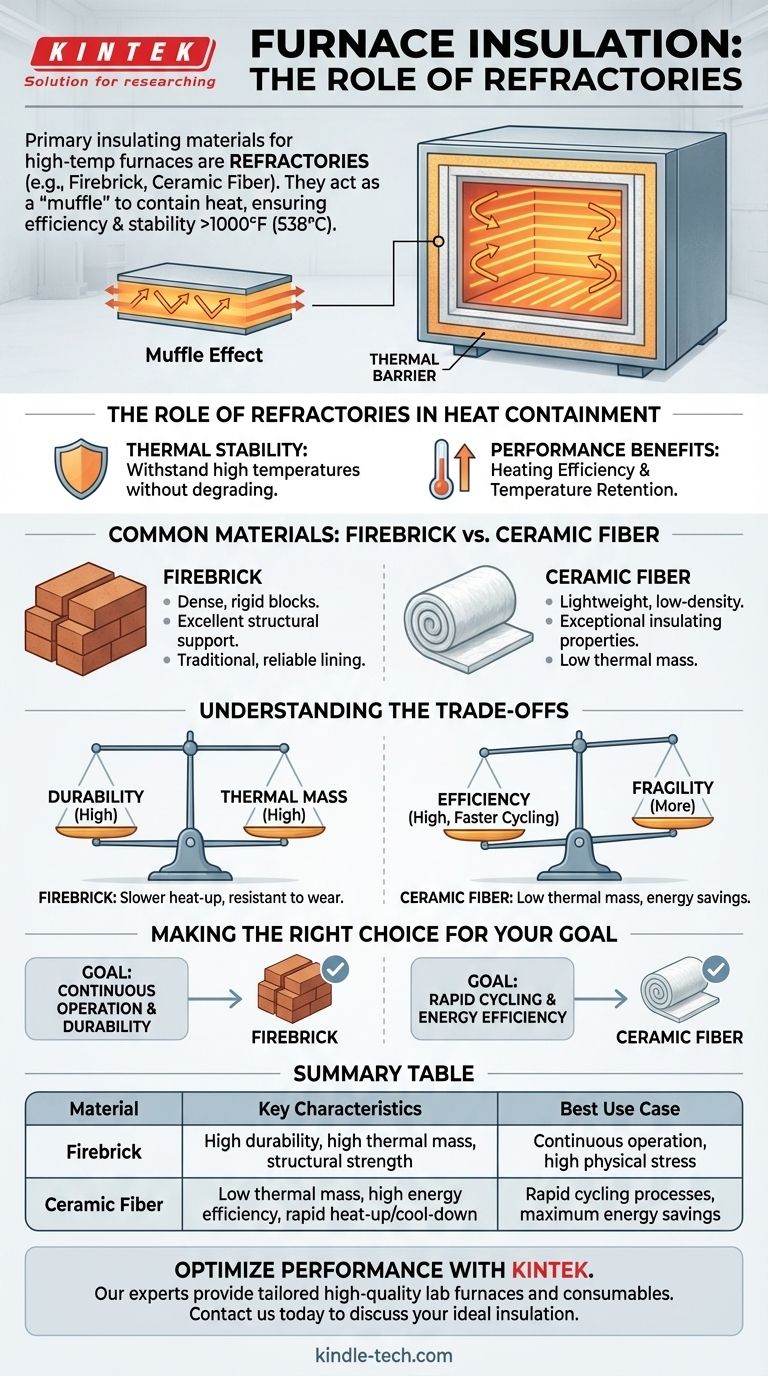
The primary insulating materials used in high-temperature furnaces are a class of non-metallic materials known as refractories. The most common examples you will encounter are firebrick and ceramic fibers. These materials are specifically engineered to retain their structural strength and insulating properties at extreme temperatures, typically above 1000°F (538°C).
The core purpose of furnace insulation is to act as a "muffle," a thermal barrier that prevents heat from escaping. This containment is critical for achieving both energy efficiency and stable, consistent operating temperatures within the furnace chamber.

The Role of Refractories in Heat Containment
To understand why specific materials are used, we must first understand the fundamental job of furnace insulation. It isn't just about keeping the outside cool; it's about controlling the energy inside.
What Defines a Refractory?
A refractory is any material that can withstand high temperatures without degrading. Unlike metals, which conduct heat well, these non-metallic materials are poor conductors.
Their key characteristic is thermal stability, meaning they maintain their physical strength and integrity even when subjected to intense heat over long periods.
The "Muffle" Effect
The insulation in a furnace effectively creates a thermal chamber, or muffle. This barrier is what allows the furnace to reach and maintain its target temperature.
Without it, the heat generated would constantly dissipate into the surrounding environment, making the process incredibly inefficient and unstable.
The Impact on Performance
Proper refractory insulation directly leads to two critical performance benefits.
First is heating efficiency. By preventing heat loss, the furnace requires significantly less energy to maintain its temperature.
Second is temperature retention. A well-insulated chamber holds a stable temperature, which is essential for processes requiring precise thermal control.
Common Refractory Materials Explained
While many types of refractories exist, two dominate the landscape for most high-temperature furnaces and kilns.
Firebrick
Firebrick is a dense, rigid block made from refractory ceramic material. It is a traditional and highly reliable choice for lining furnace interiors.
It provides excellent structural support and insulation, forming the primary thermal barrier in many furnace designs.
Ceramic Fiber
Ceramic fiber is a lightweight, low-density insulating material, often available in the form of flexible blankets, rigid boards, or moldable compounds.
It is prized for its exceptional insulating properties and low thermal mass, meaning it absorbs and stores very little heat itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between firebrick and ceramic fiber is not arbitrary; it involves balancing key performance characteristics.
Durability vs. Thermal Mass
Firebrick is extremely durable and resistant to mechanical wear and abrasion. However, it has a high thermal mass, meaning it takes longer and requires more energy to heat up.
Efficiency vs. Fragility
Ceramic fiber has a very low thermal mass, enabling faster heat-up and cool-down cycles, which improves overall energy efficiency. Its primary trade-off is that it is mechanically more fragile than dense brick.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal insulating material depends entirely on the furnace's intended use and performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is durability and continuous operation: Firebrick is often the superior choice for its ability to withstand constant high heat and physical stress.
- If your primary focus is rapid cycling and energy efficiency: Ceramic fiber is the better option, as its low thermal mass minimizes the energy wasted on heating the insulation itself.
Ultimately, selecting the correct refractory is fundamental to achieving the performance, stability, and economic efficiency your high-temperature process demands.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Characteristics | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Firebrick | High durability, high thermal mass, excellent structural strength | Continuous operation, high physical stress environments |
| Ceramic Fiber | Low thermal mass, high energy efficiency, rapid heat-up/cool-down | Rapid cycling processes, maximum energy savings |
Optimize your furnace's performance and efficiency with the right insulation. The choice between durable firebrick and efficient ceramic fiber is critical for your lab's productivity and energy costs. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and consumables, providing expert solutions tailored to your specific thermal processing needs. Contact our experts today to discuss the ideal insulation for your application and unlock superior temperature control and savings.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Precision Machined Yttria Stabilized Zirconia Ceramic Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Non-Standard Insulator Customization
People Also Ask
- What is the function of alumina setter plates for LATP? Protect Material Purity & Prevent Adhesion
- What functions do high-purity alumina support rods serve in sCO2 experiments? Ensure High-Temp Material Integrity
- What is the maximum temperature for alumina tube? Unlock Its Full Potential with High Purity
- What are the high temperature properties of alumina? Discover Its Stability, Strength, and Limits
- Which of the following is used in furnace to withstand high temperature? Key Materials for Extreme Heat



















