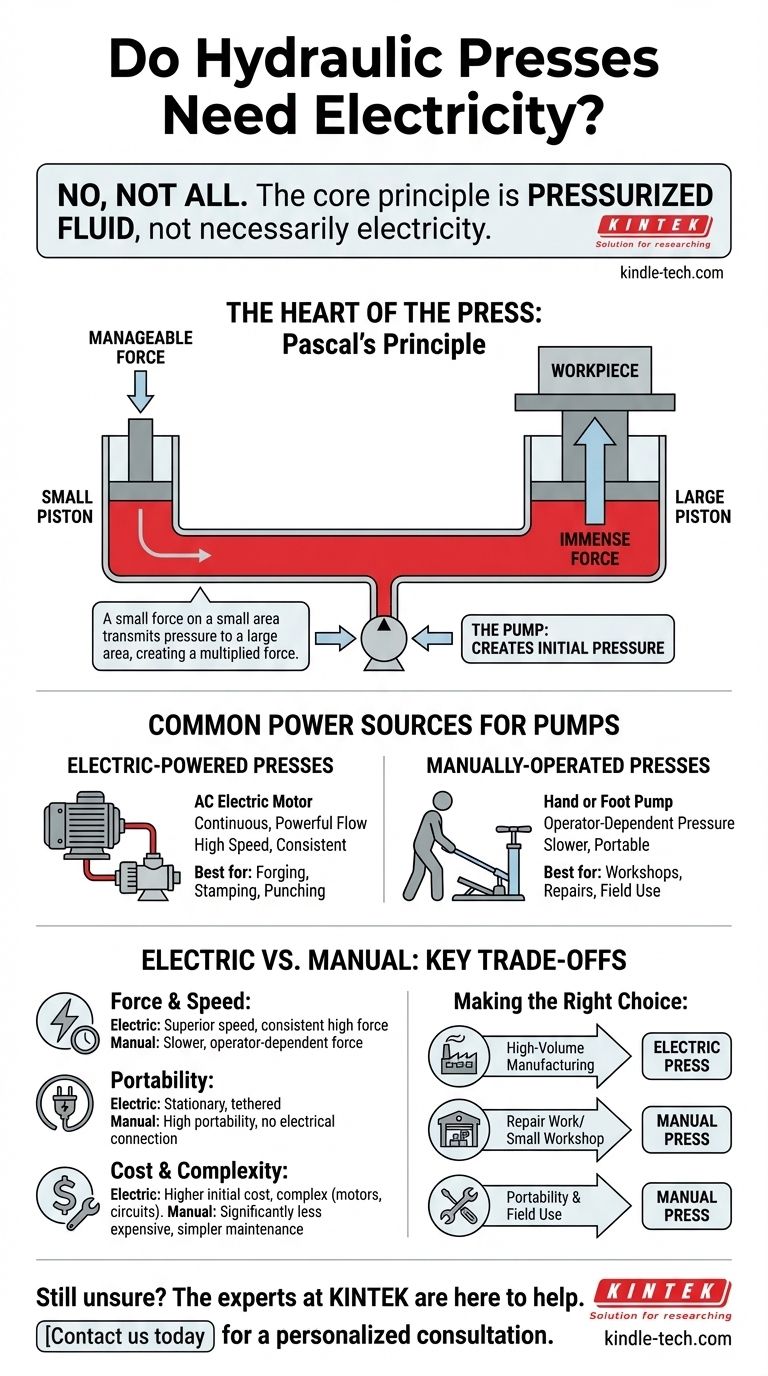
In short, no, not all hydraulic presses need electricity. While most industrial-scale presses rely on electric motors to power their hydraulic pumps, many smaller or specialized presses are operated entirely by manual force, such as a hand or foot pump. The true power source is hydraulic fluid under pressure; how that pressure is generated is what varies.
The core principle to understand is that a hydraulic press requires pressurized fluid, not necessarily electricity. The choice between an electric motor or a manual pump to create that pressure depends entirely on the required force, speed, and application of the press.

The Heart of the Press: The Hydraulic Pump
A hydraulic press operates on a simple but powerful concept known as Pascal's Principle. This principle states that pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted undiminished throughout the fluid.
How Hydraulic Force Works
Think of a small piston pushing fluid through a tube into a much larger cylinder with a larger piston. The force you apply to the small piston is massively multiplied when it acts on the surface area of the large piston.
This is the genius of hydraulics: it allows a small, manageable force to be converted into an immense, powerful force capable of shaping metal.
The Pump's Role: Creating Pressure
The system cannot create energy on its own. A pump is required to generate the initial flow and pressure in the hydraulic fluid. This pump is the component that requires an external power source.
Common Power Sources for Hydraulic Pumps
The method used to drive the pump is what determines whether a hydraulic press needs electricity. The two primary categories are electric and manual.
Electric-Powered Presses
In most industrial settings, the hydraulic pump is driven by an AC electric motor. This provides a continuous and powerful flow of hydraulic fluid.
These systems are ideal for high-speed, repetitive tasks like forging, stamping, and punching because the motor can build and maintain pressure quickly and consistently without human effort.
Manually-Operated Presses
For smaller workshops, repair jobs, or applications where portability is key, manual pumps are common. These are often called H-frame or shop presses.
The operator uses a long lever handle or a foot pedal to manually pump hydraulic fluid into the cylinder. Each stroke of the pump builds more pressure, slowly extending the main piston to perform the work.
Electric vs. Manual: Key Trade-offs
Choosing between an electric and a manual press involves balancing power, portability, and cost. Neither is universally better; they are simply suited for different tasks.
Force and Speed
An electric press offers superior speed and can deliver consistent force for long production runs with no operator fatigue.
A manual press is much slower and its force application depends on the effort of the operator. It is best suited for jobs where precision and feel are more important than speed, such as pressing bearings or performing custom fabrication.
Portability and Location
Manual presses have a clear advantage in portability. Since they require no electrical connection, they can be used anywhere, from a garage with limited wiring to a mobile field service vehicle.
Electric presses are typically larger, heavier, and tethered to a high-voltage power source, making them stationary installations.
Cost and Complexity
Manual presses are mechanically simpler, which makes them significantly less expensive to purchase and easier to maintain. Repairs often involve simple seal replacements.
Electric presses are more complex systems with motors, switches, and control circuits. This increases their initial cost and the complexity of maintenance and troubleshooting.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine the right type of press, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing: You need the speed and consistency of an electric-powered hydraulic press.
- If your primary focus is repair work or a small workshop: A manual shop press offers more than enough force for most tasks at a fraction of the cost and complexity.
- If your primary focus is portability and field use: A manual press is your only practical option, as it is completely self-contained.
Understanding the role of the pump demystifies the power source and empowers you to select the right tool for the job.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Electric Press | Manual Press |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | AC Electric Motor | Hand or Foot Pump |
| Typical Force | High | Low to Medium |
| Speed | Fast, Continuous | Slow, Operator-Dependent |
| Portability | Low (Stationary) | High (Self-Contained) |
| Best For | High-volume manufacturing, forging | Workshops, repairs, field use |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Still unsure which hydraulic press is right for your application? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in lab equipment and consumables, serving diverse laboratory needs. Whether you require a high-force electric press for industrial production or a portable manual press for precise workshop tasks, we can guide you to the perfect solution. Contact us today for a personalized consultation and discover how the right hydraulic press can enhance your efficiency and results.
Visual Guide
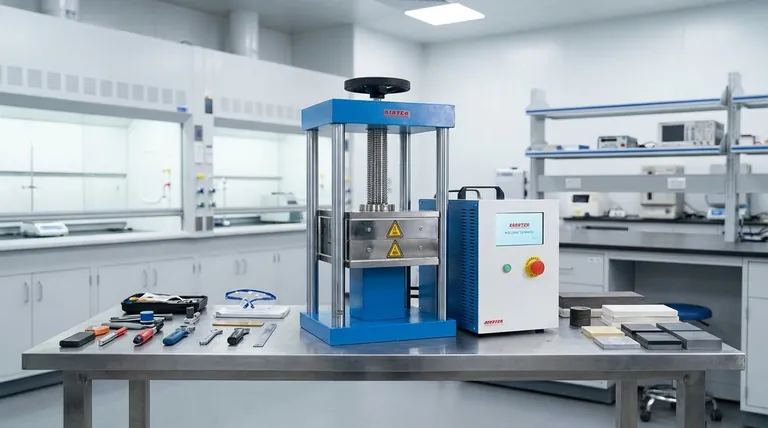
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Manual Lab Heat Press
People Also Ask
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy
- What is the advantage of KBr? Unmatched IR Transparency for Precise Spectroscopy



















