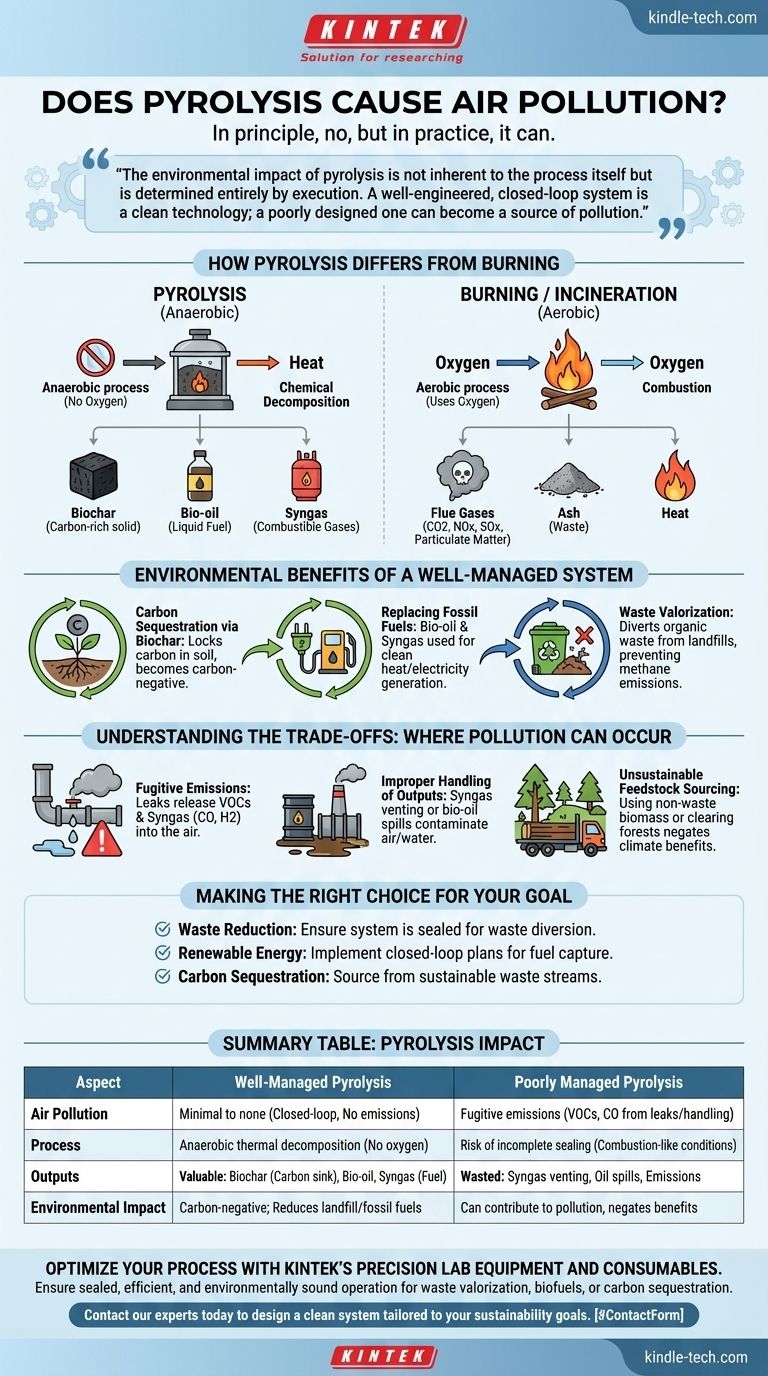
In principle, no, but in practice, it can. Unlike burning, which is direct combustion with oxygen, pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of material in a near-total absence of oxygen. This fundamental difference means a properly controlled pyrolysis system does not produce the common air pollutants associated with incineration, like nitrogen oxides (NOx) and sulfur oxides (SOx). However, air pollution becomes a significant risk if the process is poorly managed, the equipment leaks, or the resulting products are handled improperly.
The environmental impact of pyrolysis is not inherent to the process itself but is determined entirely by execution. A well-engineered, closed-loop system is a clean technology for waste valorization and energy production; a poorly designed or operated one can become a source of pollution.

How Pyrolysis Differs from Burning
To understand the pollution risk, it is crucial to distinguish pyrolysis from simple incineration or burning. They are fundamentally different chemical processes.
The Critical Role of Oxygen
Pyrolysis is an anaerobic (or near-anaerobic) process. Material is heated in a sealed container, causing it to break down chemically without combusting.
Burning, or incineration, is an aerobic process. It uses oxygen to combust material, releasing energy as heat and light, and creating flue gases that are released directly into the atmosphere.
Products vs. Pollutants
The output of pyrolysis is a set of valuable, contained products: biochar (a solid carbon-rich material), bio-oil (a liquid fuel), and syngas (a mixture of combustible gases).
The primary outputs of burning are heat, ash, and a mixture of flue gases that include significant air pollutants like carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter.
The Environmental Benefits of a Well-Managed System
When executed correctly, pyrolysis offers significant environmental advantages by converting waste streams into valuable assets.
Carbon Sequestration via Biochar
Biochar is a highly stable form of carbon. When added to soil, it effectively locks that carbon away for hundreds or even thousands of years, making it a carbon-negative technology. This process removes carbon dioxide from the atmospheric cycle.
Replacing Fossil Fuels
The bio-oil and syngas produced during pyrolysis can be used as fuels for generating heat or electricity. Using these biofuels reduces the demand for fossil fuels, thereby cutting the greenhouse gas emissions associated with their extraction and combustion.
Waste Valorization
Pyrolysis provides a powerful solution for managing organic waste, including agricultural residues, wood waste, and even certain plastics and municipal solid waste. It diverts this material from landfills, where it would otherwise decompose and release methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Where Pollution Can Occur
Despite its potential, pyrolysis is not without risks. The potential for air pollution arises not from the core process, but from its imperfect implementation.
Fugitive Emissions from Leaky Systems
If the pyrolysis reactor is not perfectly sealed, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and syngas (which contains carbon monoxide and hydrogen) can escape into the atmosphere. These fugitive emissions are a direct source of air pollution and also represent a loss of valuable product.
Improper Handling of Outputs
The syngas and bio-oil must be captured and managed. If syngas is simply vented into the atmosphere instead of being used as fuel, it becomes a pollutant. Likewise, spills or incomplete combustion of bio-oil can contaminate air and water.
Unsustainable Feedstock Sourcing
The overall environmental benefit depends heavily on the source of the biomass. If purpose-grown crops are used inefficiently or if healthy forests are cleared to supply a pyrolysis plant, the resulting deforestation and habitat loss can negate any climate benefits. The most sustainable approach uses waste materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use pyrolysis technology must be based on a clear understanding of its operational demands.
- If your primary focus is waste reduction: Pyrolysis is an excellent method for diverting organic waste from landfills, but you must ensure the system is properly sealed and can handle your specific waste stream.
- If your primary focus is renewable energy: This technology effectively creates biofuels, but you must have a closed-loop plan to safely capture and utilize the syngas and bio-oil produced.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration: Producing biochar is a proven carbon-negative strategy, but its climate benefit is only realized when the biomass feedstock is sourced from sustainable waste streams.
Ultimately, a well-engineered and responsibly managed pyrolysis system is a powerful tool for sustainability, not a source of pollution.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Well-Managed Pyrolysis | Poorly Managed Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Air Pollution | Minimal to none; closed-loop system prevents emissions | Fugitive emissions (VOCs, CO) from leaks or improper handling |
| Process | Anaerobic thermal decomposition without oxygen | Risk of incomplete sealing or combustion-like conditions |
| Outputs | Valuable products: biochar (carbon sequestration), bio-oil, syngas (fuel) | Wasted products; syngas venting, oil spills, or emissions |
| Environmental Impact | Carbon-negative; reduces landfill waste and fossil fuel use | Can contribute to air/water pollution and negate climate benefits |
Optimize your pyrolysis process with KINTEK’s precision lab equipment and consumables. Whether you're researching waste valorization, biofuel production, or carbon sequestration, our reactors, gas handling systems, and analytical tools ensure a sealed, efficient, and environmentally sound operation. Contact our experts today to design a clean, high-yield pyrolysis system tailored to your sustainability goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy



















