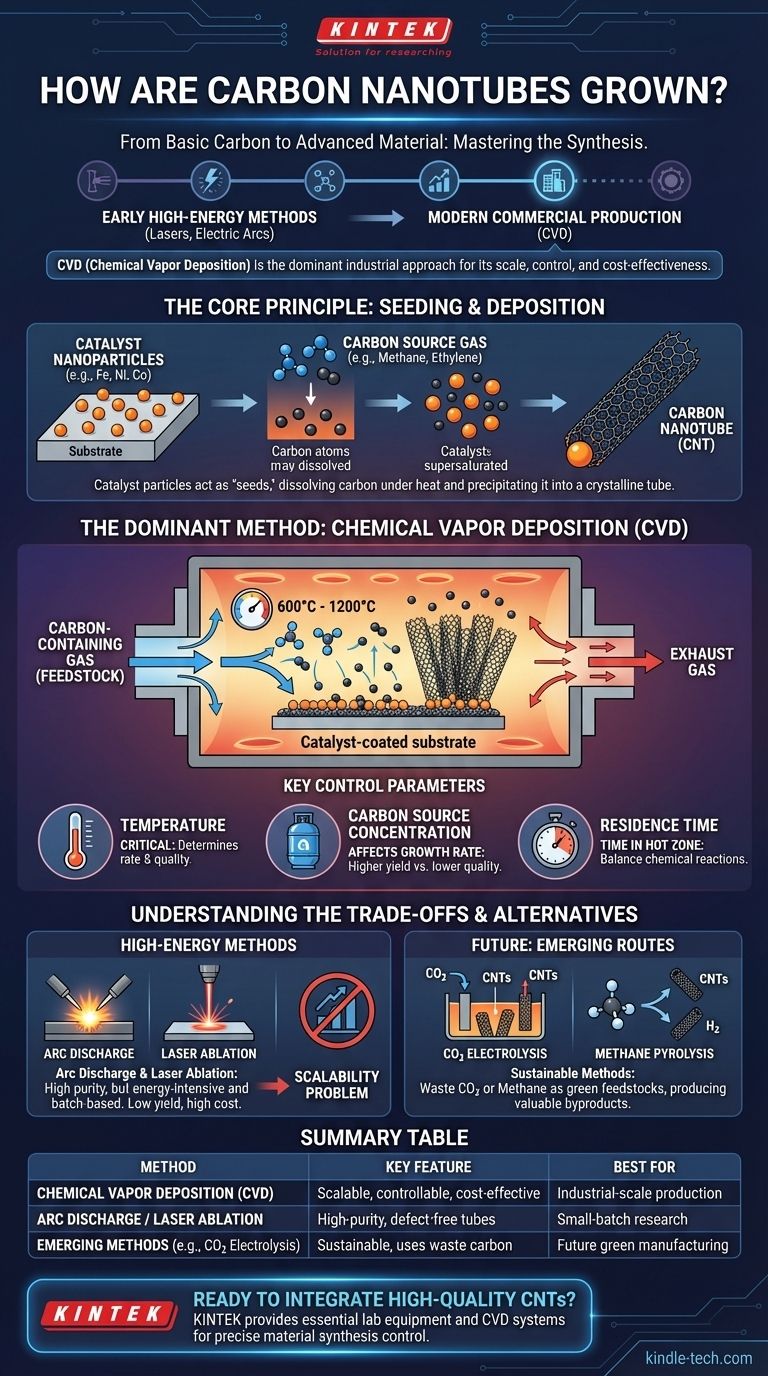
At its core, growing a carbon nanotube involves providing a carbon source and the right energy conditions to assemble carbon atoms into a cylindrical, tube-like structure. While early methods used high-energy techniques like lasers or electric arcs, the vast majority of modern, commercial-scale production relies on a more controllable process called Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
The key to understanding carbon nanotube synthesis is recognizing that it is not just one method, but a family of processes. The choice of method is a trade-off between scale, cost, and the final quality of the nanotubes produced, with CVD representing the most balanced and dominant approach for industrial applications.

The Core Principle: Seeding and Deposition
Before examining specific methods, it's crucial to understand the fundamental mechanism. Nearly all CNT growth relies on a catalyst.
The Role of the Catalyst Particle
A substrate is prepared with a thin layer of metallic catalyst nanoparticles, typically iron, nickel, or cobalt.
These nanoparticles act as "seeds." Under high heat, carbon-containing gas molecules break down, and the carbon atoms dissolve into or onto the catalyst particle.
When the catalyst becomes supersaturated with carbon, the carbon atoms precipitate out in a crystalline, tubular structure, forming the nanotube. The diameter of the catalyst particle often dictates the diameter of the resulting nanotube.
The Dominant Method: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is the workhorse of the carbon nanotube industry because it is highly scalable and offers excellent control over the final product.
How CVD Works
The process involves placing the catalyst-coated substrate into a furnace. The furnace is heated to a specific temperature, typically between 600°C and 1200°C.
A carbon-containing gas (the feedstock or carbon source), such as methane, ethylene, or acetylene, is then flowed through the chamber.
The high heat causes the gas to decompose, depositing carbon atoms onto the catalyst particles, where they self-assemble into nanotubes.
Key Control Parameters
The success of CVD synthesis hinges on precise control over several operating parameters.
- Temperature: This is one of the most critical factors. It determines the rate of gas decomposition and the quality of the resulting nanotubes. Too low, and growth is inefficient; too high, and amorphous carbon or other unwanted structures may form.
- Carbon Source Concentration: The amount of carbon feedstock gas introduced affects the growth rate. A higher concentration can increase yield but also risks creating lower-quality, multi-walled, or defective tubes.
- Residence Time: This is the length of time the carbon gas spends in the hot zone of the reactor. It must be long enough for the chemical reactions to occur but short enough to prevent undesirable side reactions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While CVD is dominant, older methods still exist and highlight the engineering compromises involved in CNT production.
High-Energy Methods: Arc Discharge and Laser Ablation
Arc discharge involves striking a high-current electric arc between two carbon electrodes in an inert gas atmosphere. The intense heat vaporizes the carbon, which then condenses to form nanotubes.
Laser ablation uses a high-power laser to vaporize a carbon target. An inert gas sweeps the vaporized carbon from the hot zone to a cooler surface, where it condenses into nanotubes.
The Scalability Problem
Both arc discharge and laser ablation are energy-intensive and operate in batches, making them difficult and expensive to scale for industrial production. While they can produce very high-quality nanotubes, their low yield and high cost have relegated them to niche research applications.
In contrast, CVD operates at lower temperatures and pressures and can be configured for continuous production, making it far more economically viable for the tons of material required by industry.
The Future: Emerging Synthesis Routes
Research is actively exploring more sustainable and cost-effective ways to produce CNTs.
From Waste CO2 to Nanotubes
One promising method involves capturing carbon dioxide (CO2) and using electrolysis in molten salts. An electric current breaks down the CO2, releasing oxygen and providing the carbon atoms needed to grow nanotubes on a cathode.
Methane Pyrolysis
Another green approach is the pyrolysis (thermal decomposition without oxygen) of methane. This process splits methane into solid carbon—in the form of carbon nanotubes—and valuable, clean-burning hydrogen gas (H2), creating two valuable products from a single feedstock.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal synthesis method is defined by the intended application of the carbon nanotubes.
- If your primary focus is industrial-scale production: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the only practical choice due to its scalability, control, and superior cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is high-purity, defect-free samples for fundamental research: Arc discharge or laser ablation may be considered for small batches, though advanced CVD techniques are also highly capable.
- If your primary focus is environmental sustainability and future processes: Emerging methods like CO2 electrolysis or methane pyrolysis represent the next generation of CNT manufacturing.
Ultimately, mastering the growth of carbon nanotubes is about precisely controlling the transformation of simple carbon sources into advanced, high-performance materials.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Scalable, controllable, cost-effective | Industrial-scale production |
| Arc Discharge / Laser Ablation | High-purity, defect-free tubes | Small-batch research |
| Emerging Methods (e.g., CO2 Electrolysis) | Sustainable, uses waste carbon | Future green manufacturing |
Ready to integrate high-quality carbon nanotubes into your research or production line? KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables essential for advanced material synthesis, including CVD systems. Our expertise ensures you have the reliable tools needed to achieve precise control over your CNT growth process. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs and accelerate your material science innovations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods



















