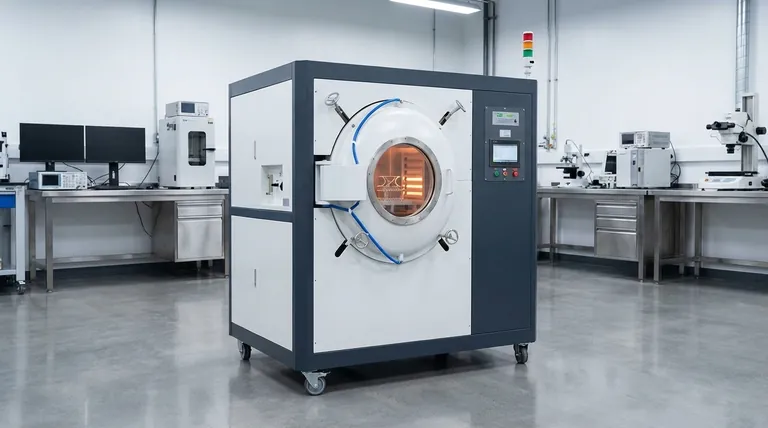
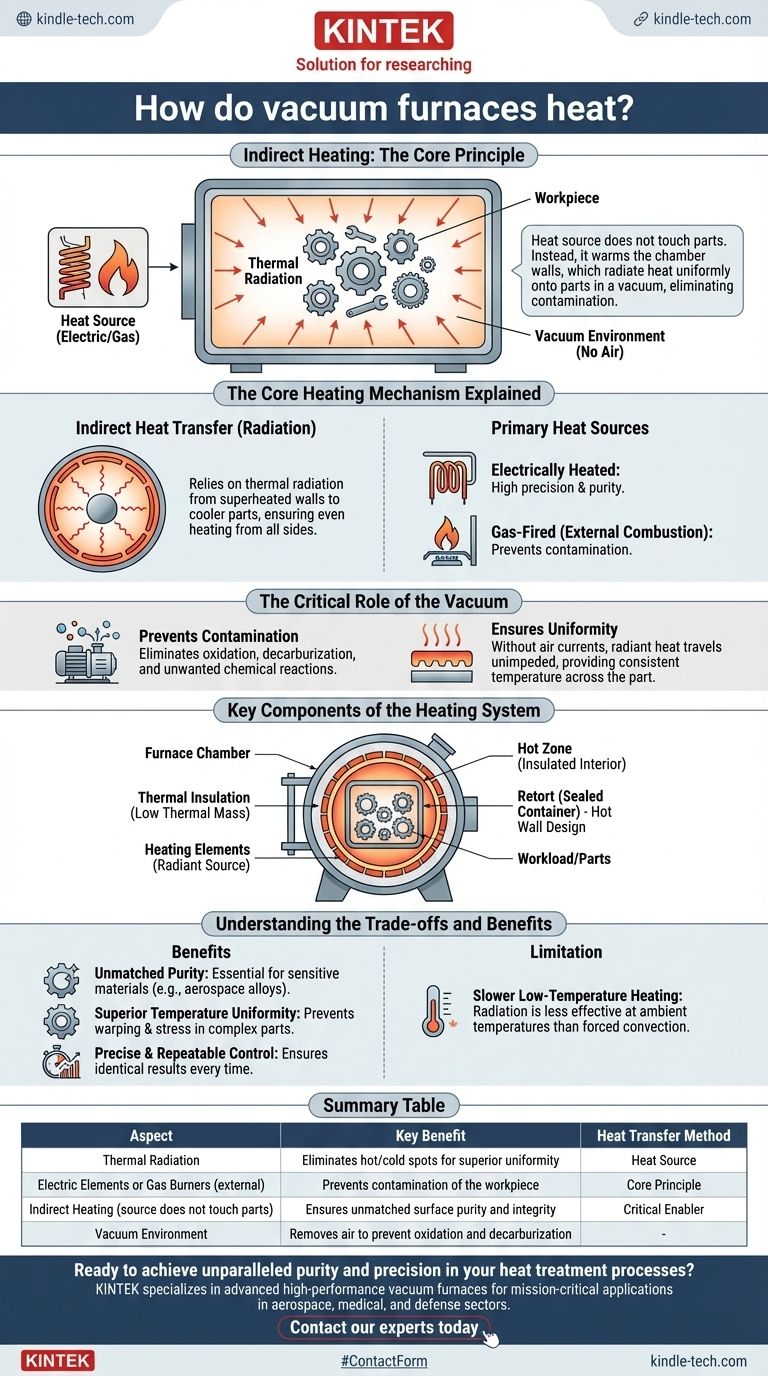
In a vacuum furnace, heating is achieved indirectly. The heat source, typically electric elements or gas burners, does not directly touch the workpiece. Instead, these heaters warm the furnace's internal chamber or a sealed container called a retort, which then radiates heat uniformly onto the parts inside the vacuum.
The core principle is environmental control. By separating the heat source from the parts within a vacuum, the furnace eliminates atmospheric contamination and ensures exceptionally uniform heat transfer, which is critical for high-performance materials.

The Core Heating Mechanism Explained
The unique properties of a vacuum furnace stem directly from how it manages heat transfer in the absence of air. This indirect approach is fundamental to its purpose.
Indirect Heat Transfer
Unlike a conventional oven that uses air (convection) to circulate heat, a vacuum furnace relies primarily on thermal radiation. The heating elements heat the "hot zone" walls, and these superheated surfaces radiate energy to the cooler parts, heating them evenly from all sides.
Primary Heat Sources
While the method of transfer is radiation, the initial energy source can vary. The two most common types are:
- Electrically Heated: These are the most common for high-purity and precision applications, offering extremely accurate temperature control.
- Gas-Fired: These can also be used, with the combustion happening outside the vacuum chamber to prevent any contamination of the workpiece.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
Creating a vacuum is the key that enables the entire process. Removing air and other gases achieves two critical goals:
- It prevents contamination. Oxidation, decarburization, and other unwanted chemical reactions that occur in the presence of air are completely eliminated.
- It ensures uniformity. Without air currents causing hot or cold spots, radiant heat can travel unimpeded, providing consistent temperature across the entire surface of the part.
Key Components of the Heating System
A vacuum furnace is an integrated system where each component is designed to maintain purity and control temperature with high precision.
The Hot Zone
This is the insulated interior of the furnace where the heating takes place. It is engineered to withstand extreme temperatures while also heating and cooling rapidly.
Heating Elements
These are the source of the thermal energy. They are arranged around the hot zone to provide even radiation to the chamber walls or the workload.
Thermal Insulation
To contain the intense heat and allow for rapid temperature changes, vacuum furnaces use advanced insulation, often in the form of rigidized ceramic fiber. This material has low thermal mass, enabling fast heat-up and cool-down cycles.
The Retort (Hot Wall Design)
In a "hot wall" furnace, the parts are placed inside a sealed, vacuum-tight container called a retort. The heaters are located outside this retort, first heating the container's walls, which in turn conduct and radiate that heat to the parts inside.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Benefits
The unique heating method of a vacuum furnace provides distinct advantages, but it's important to understand the context in which it operates best.
Benefit: Unmatched Purity
By removing the atmosphere, you eliminate the source of contamination. This is non-negotiable for sensitive materials like nickel-based superalloys used in aerospace, where surface integrity is paramount.
Benefit: Superior Temperature Uniformity
Radiant heating in a vacuum is exceptionally uniform, preventing the warping or internal stresses that can be caused by uneven heating in conventional furnaces. This is vital for complex geometries and delicate parts.
Benefit: Precise and Repeatable Control
The stable, isolated environment allows for meticulous control over the entire heat treatment cycle. This ensures that processes like annealing, brazing, and hardening are perfectly repeatable, producing identical results every time.
Limitation: Slower Low-Temperature Heating
Because a vacuum furnace relies on radiation, which is most effective at high temperatures, the initial heat-up from ambient temperature can be slower than in a furnace that uses fans for forced convection.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vacuum furnace is driven by the demands of the material and the final application.
- If your primary focus is surface purity and preventing oxidation: A vacuum furnace is the only choice, as its indirect heating in a controlled atmosphere eliminates all sources of contamination.
- If your primary focus is complex and repeatable heat treatments: The unparalleled temperature uniformity and stability of a vacuum furnace ensure consistent, high-quality results for processes like brazing and hardening.
- If your primary focus is processing high-performance alloys: Materials used in aerospace, medical, and defense sectors require the pristine, controlled environment that only a vacuum furnace can provide.
Understanding how a vacuum furnace heats is understanding how it delivers an environment of absolute control for mission-critical components.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Vacuum Furnace Heating | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Transfer Method | Thermal Radiation | Eliminates hot/cold spots for superior uniformity |
| Heat Source | Electric Elements or Gas Burners (external) | Prevents contamination of the workpiece |
| Core Principle | Indirect Heating (source does not touch parts) | Ensures unmatched surface purity and integrity |
| Critical Enabler | Vacuum Environment | Removes air to prevent oxidation and decarburization |
Ready to achieve unparalleled purity and precision in your heat treatment processes?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment, including high-performance vacuum furnaces designed for mission-critical applications. Our solutions are engineered to provide the controlled environment necessary for processing high-performance alloys, complex brazing, and sensitive materials used in aerospace, medical, and defense sectors.
Let us help you enhance your results with superior temperature control and contamination-free processing.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application needs and discover the perfect vacuum furnace solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of a calcination furnace? Precise Control from 800°C to 1300°C
- Why is a high-vacuum high-temperature furnace required for C/C-SiC siliconization? Ensure Perfect Composite Integrity
- What is the process of carburizing? Achieve Superior Surface Hardening with Precision
- What role does a laboratory vacuum drying oven play in processing nanoparticle powder samples? Protect Sample Integrity
- What is the significance of using a high-temperature sintering furnace for PRP? Optimize Preform Structural Engineering
- What properties are affected by heat treatment? A Guide to Hardness, Strength, and Toughness
- Why is a high vacuum environment necessary in sintering equipment for TiAl alloys? Ensure High-Purity Metal Bonding
- What is the role of a laboratory high-temperature resistance furnace in TSR testing? Quantifying Material Durability



















