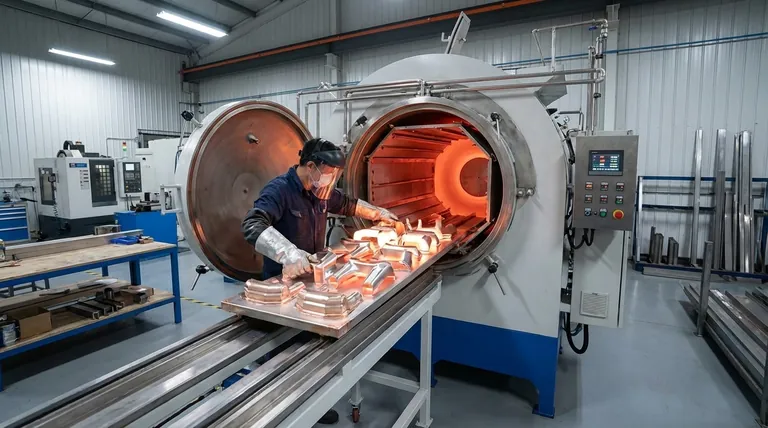
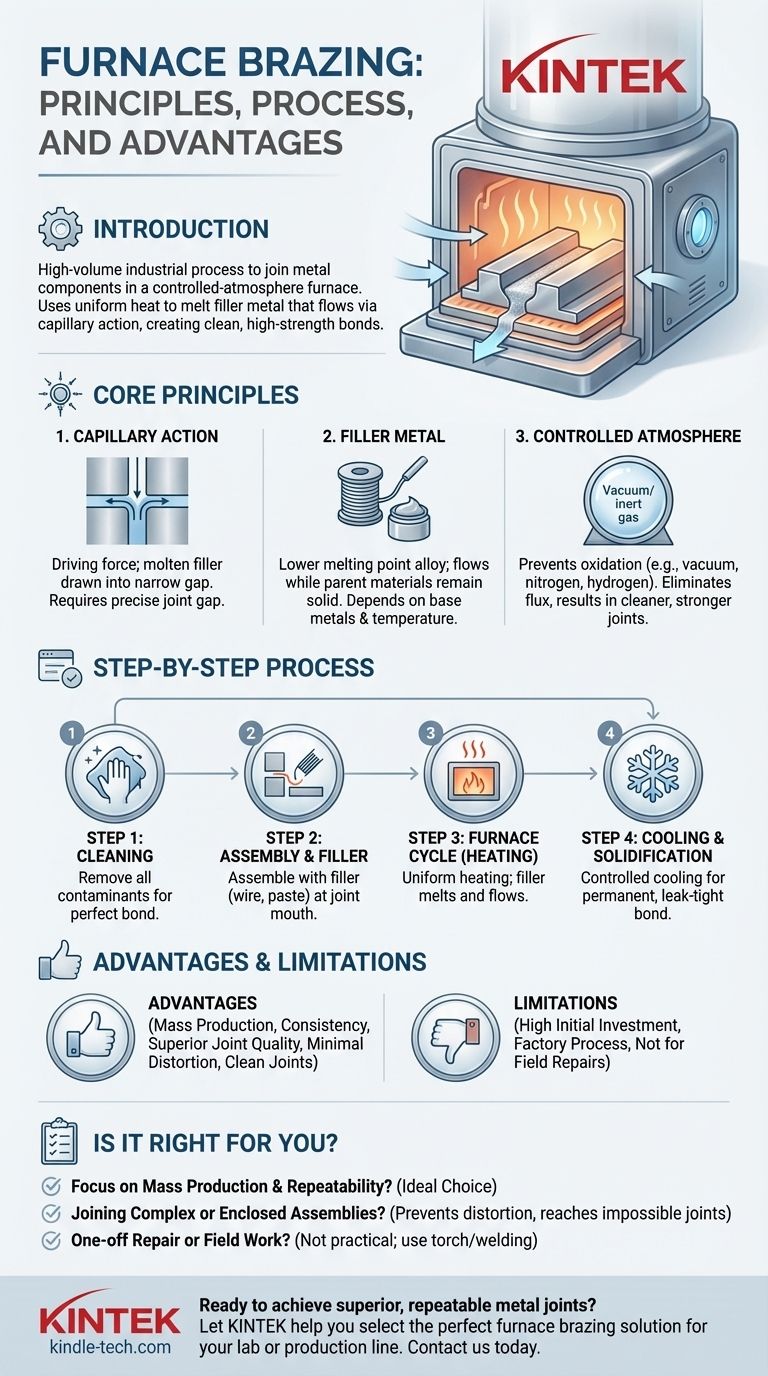
Furnace brazing is a high-volume industrial process used to join metal components together within a controlled-atmosphere furnace. Unlike handheld torch brazing, the entire assembly is heated uniformly, causing a pre-placed filler metal to melt and flow into the joint through capillary action. The process is defined by its precision, repeatability, and ability to create clean, high-strength bonds without melting the parent materials.
The core principle of furnace brazing is not about repairing a furnace, but rather using a furnace as a tool. It leverages uniform, controlled heat to melt a filler alloy, which is drawn into a tight-fitting joint to form a powerful metallurgical bond across the entire assembly.

The Fundamental Principles of Furnace Brazing
To understand the furnace brazing process, you must first grasp the core principles that make it a reliable and effective joining method. It's a precise science, not just a heating-and-cooling cycle.
Capillary Action: The Driving Force
The success of any brazing operation hinges on capillary action. This is the physical force that draws the molten filler metal into the narrow gap between the two base components.
For this to work, the parts must be designed with a specific, consistent gap. Too wide, and capillary action fails; too tight, and the filler cannot flow.
The Role of the Filler Metal
The filler metal is the lynchpin of the process. It is an alloy designed with a melting point that is lower than the base materials being joined.
This allows the filler to become liquid and flow into the joint while the parent components remain solid and dimensionally stable. The choice of filler depends on the base metals, service temperature, and strength requirements.
The Importance of a Controlled Atmosphere
Furnace brazing typically takes place in a controlled atmosphere, such as a vacuum or an environment filled with inert gas like nitrogen or hydrogen.
This atmosphere prevents the formation of oxides on the metal surfaces as they heat up. By preventing oxidation, the furnace eliminates the need for aggressive chemical fluxes, resulting in cleaner, stronger joints and reducing post-braze cleaning operations.
The Step-by-Step Furnace Brazing Process
Furnace brazing is a systematic process where preparation and control are paramount. Each step is critical to achieving a successful outcome.
Step 1: Meticulous Cleaning
All contaminants—such as oils, grease, dirt, and oxides—must be removed from the surfaces to be joined. A perfectly clean surface is essential for the filler metal to "wet" the base metals and form a strong bond.
Step 2: Precise Assembly and Filler Placement
The clean components are assembled into their final configuration, often held in place with specialized fixtures. The filler metal, in the form of a wire, paste, or pre-formed shim, is placed at the mouth of the joint before the assembly enters the furnace.
Step 3: The Furnace Cycle (Heating)
The entire assembly is loaded into the furnace. The furnace then executes a pre-programmed heating cycle, raising the temperature of the components uniformly to the specified brazing temperature. This is the point at which the filler metal melts and flows into the joint.
Step 4: Cooling and Solidification
After a designated time at temperature, the assembly is cooled in a controlled manner. As it cools, the filler metal solidifies, creating a permanent, leak-tight, and strong metallurgical bond between the components.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Advantages
While powerful, furnace brazing is not a universal solution. Understanding its specific strengths and limitations is key to using it effectively.
Advantage: High-Volume and Consistency
The primary advantage of furnace brazing is its suitability for mass production. A furnace can process dozens or even hundreds of assemblies in a single batch, ensuring high consistency from part to part.
Advantage: Superior Joint Quality
The controlled atmosphere minimizes oxidation, and the uniform heating prevents thermal distortion that can occur with localized heating from a torch. This results in extremely clean, strong, and aesthetically pleasing joints.
Limitation: High Initial Investment
Brazing furnaces, particularly vacuum or controlled-atmosphere models, represent a significant capital investment. This makes the process best suited for production environments rather than small shops or one-off projects.
Limitation: Not Suited for On-Site Repairs
Furnace brazing is fundamentally a factory process. It is entirely impractical for field repairs or joining large structures that cannot be placed inside a furnace. For those applications, methods like torch brazing or welding are necessary.
Is Furnace Brazing Right for Your Application?
Choosing the right joining method depends entirely on your project's goals, scale, and logistical constraints.
- If your primary focus is mass production and repeatability: Furnace brazing is the ideal choice for its ability to produce consistent, high-quality joints in large batches.
- If your primary focus is joining complex or enclosed assemblies: The uniform heating of a furnace prevents distortion and can create bonds in joints that are impossible to reach with a torch.
- If your primary focus is a one-off repair or field work: Furnace brazing is not a practical option; you must use a portable method like torch brazing or welding.
Ultimately, selecting the right manufacturing process is the first step toward sound engineering and a successful final product.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation | Meticulous Cleaning & Assembly | Remove contaminants; place filler metal for proper flow. |
| Heating | Uniform Heating in Controlled Atmosphere | Melt filler metal via capillary action without oxidizing parts. |
| Cooling | Controlled Solidification | Create a permanent, leak-tight, high-strength metallurgical bond. |
| Outcome | High-Volume Production | Achieve consistent, clean, and distortion-free joints efficiently. |
Ready to achieve superior, repeatable metal joints in your lab or production line?
Furnace brazing is a precise, high-volume process ideal for creating clean, strong bonds without distortion. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables you need to implement this technology effectively.
Let our experts help you select the perfect furnace brazing solution for your specific materials and production goals.
Contact us today to discuss how our specialized equipment can enhance your manufacturing process and deliver consistent, high-quality results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- Which element made stainless steel difficult to brazed? It's Chromium's Oxide Layer
- What is the most important factor influencing the strength of the brazed joint? Master Joint Clearance for Maximum Strength
- What is oxidation in brazing? How to prevent it for strong, durable joints
- Why would you braze instead of solder? For Superior Joint Strength and High-Temperature Performance
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing



















