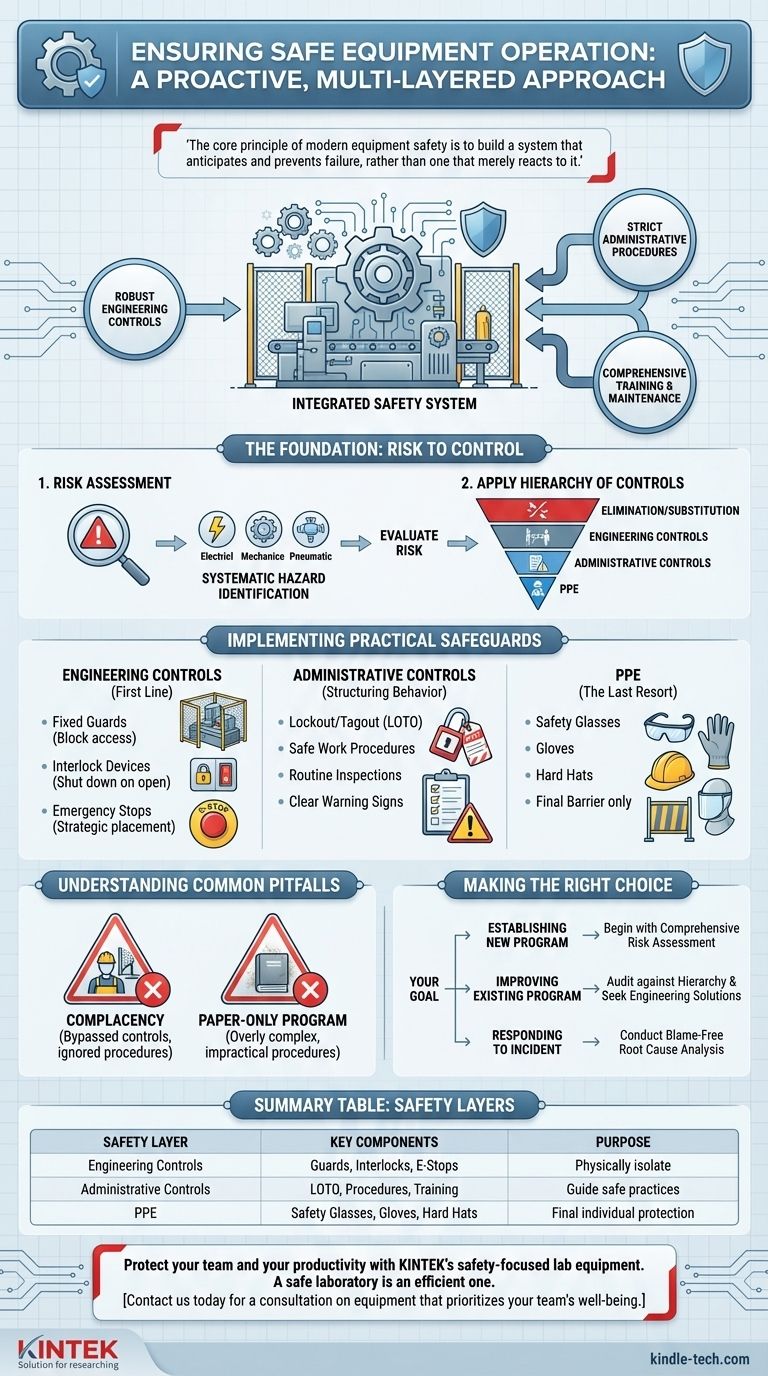
Ensuring the safe operation of equipment is not achieved through a single action, but through an integrated, multi-layered system. This system combines robust engineering controls like physical guards and interlocks, strict administrative procedures such as Lockout/Tagout (LOTO), comprehensive operator training, and a consistent preventive maintenance schedule.
The core principle of modern equipment safety is to build a system that anticipates and prevents failure, rather than one that merely reacts to it. True safety is achieved by prioritizing the elimination or engineering-out of hazards, fundamentally recognizing that relying solely on human behavior is an unreliable and insufficient strategy.

The Foundation: From Risk Assessment to Control
To build a truly safe environment, you must first understand the specific dangers you face. A structured approach ensures no hazard is overlooked and that your efforts are directed at the most significant risks.
Start with a Thorough Risk Assessment
Before any control can be implemented, you must conduct a risk assessment. This is a systematic process of identifying all potential hazards associated with a piece of equipment and evaluating the risk of harm they pose.
This involves asking critical questions: What are the energy sources (electrical, mechanical, pneumatic)? Where are the pinch points? What could go wrong during normal operation, maintenance, or a malfunction?
Apply the Hierarchy of Controls
The Hierarchy of Controls is the fundamental framework for implementing safety measures. It prioritizes methods in order of effectiveness, moving from most to least reliable.
- Elimination/Substitution: The most effective step is to remove the hazard entirely or replace it with a less hazardous alternative.
- Engineering Controls: If elimination isn't possible, physically isolate people from the hazard. This is the most critical layer for machinery.
- Administrative Controls: Change the way people work through procedures, training, and signage.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Equip the worker with protection. This is the last line of defense, as it does not remove the hazard itself.
Implementing Practical Safeguards
With a clear understanding of the risks, you can implement specific, layered controls. The goal is to make the safe way of operating the easiest and most obvious way.
Engineering Controls: Your First Line of Defense
These are physical modifications to the equipment designed to prevent contact with hazards. They are the most reliable because they function independently of human behavior.
Key examples include fixed guards that block access to moving parts, interlock devices that shut down the machine if a guard is opened, and strategically placed emergency stop buttons.
Administrative Controls: Structuring Safe Behavior
These are the procedures and rules you put in place to guide safe work practices. They are essential but less reliable than engineering controls because they depend on human compliance.
The most critical administrative control is Lockout/Tagout (LOTO), a formal procedure for de-energizing machinery during service or maintenance to prevent unexpected startup. Other examples include safe work procedures, routine inspections, and clear warning signs.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): The Last Resort
PPE, such as safety glasses, gloves, or hard hats, is crucial but should never be the primary method of protection. It only protects the individual wearer and does nothing to mitigate the underlying hazard.
Always consider PPE the final barrier after all other controls in the hierarchy have been implemented.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
A safety program is not a one-time project; it is a continuous process that requires vigilance. Understanding its failure points is as important as understanding its components.
The Pitfall of Complacency
The most common point of failure is complacency. Controls are forgotten, procedures are bypassed for convenience, and guards are removed for a "quick" adjustment.
This is why regular audits, refresher training, and visible leadership commitment are non-negotiable. Safety must be treated as an operational value, not a bureaucratic hurdle.
The Danger of a "Paper-Only" Program
A safety manual that sits on a shelf is useless. Procedures must be practical, understood by everyone who uses them, and consistently enforced.
If a written procedure is overly complex or doesn't match the reality of the work, it will be ignored. Procedures must be living documents, reviewed and updated regularly with input from the operators who use them daily.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your immediate actions should be guided by the current state of your safety program.
- If your primary focus is establishing a new safety program: Begin with a comprehensive risk assessment for every piece of machinery to build a strong, risk-based foundation.
- If your primary focus is improving an existing program: Audit your current measures against the Hierarchy of Controls and actively seek opportunities to replace administrative rules or PPE reliance with more robust engineering solutions.
- If your primary focus is responding to a near-miss or incident: Conduct a blame-free root cause analysis to understand the systemic failures—not just the human error—that allowed the event to occur, and use those lessons to strengthen every layer of your safety system.
Ultimately, a safe operation is the product of a deliberate and unwavering commitment to proactive risk management.
Summary Table:
| Safety Layer | Key Components | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Engineering Controls | Fixed guards, interlocks, emergency stops | Physically isolate people from hazards |
| Administrative Controls | LOTO procedures, training, inspections | Guide safe work practices and compliance |
| PPE | Safety glasses, gloves, hard hats | Final barrier for individual protection |
Protect your team and your productivity with KINTEK's safety-focused lab equipment.
A safe laboratory is an efficient one. KINTEK specializes in providing robust, reliable equipment designed with integrated safety features—from intuitive interlocks to fail-safe mechanisms. We serve laboratories by ensuring our products not only meet but exceed safety standards, reducing risk and enhancing operational continuity.
Let our experts help you build a proactive safety culture. Contact us today for a consultation on equipment that prioritizes your team's well-being.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of hot pressing for PEO electrolytes? Achieve superior density and solvent-free performance.
- What are the advantages of using a hot press for Li7P2S8I0.5Cl0.5? Boost Conductivity with Precision Densification
- What role does a laboratory plate hot press play in the vulcanization and molding of fluorosilicone rubber (F-LSR)?
- Why is a laboratory hot press required for Oxygen Depolarized Cathodes? Ensure Precision Molding and Conductivity.
- What role does a hot press play in treating the CAL-GPE interface? Optimize Performance for Flexible Lithium Batteries



















