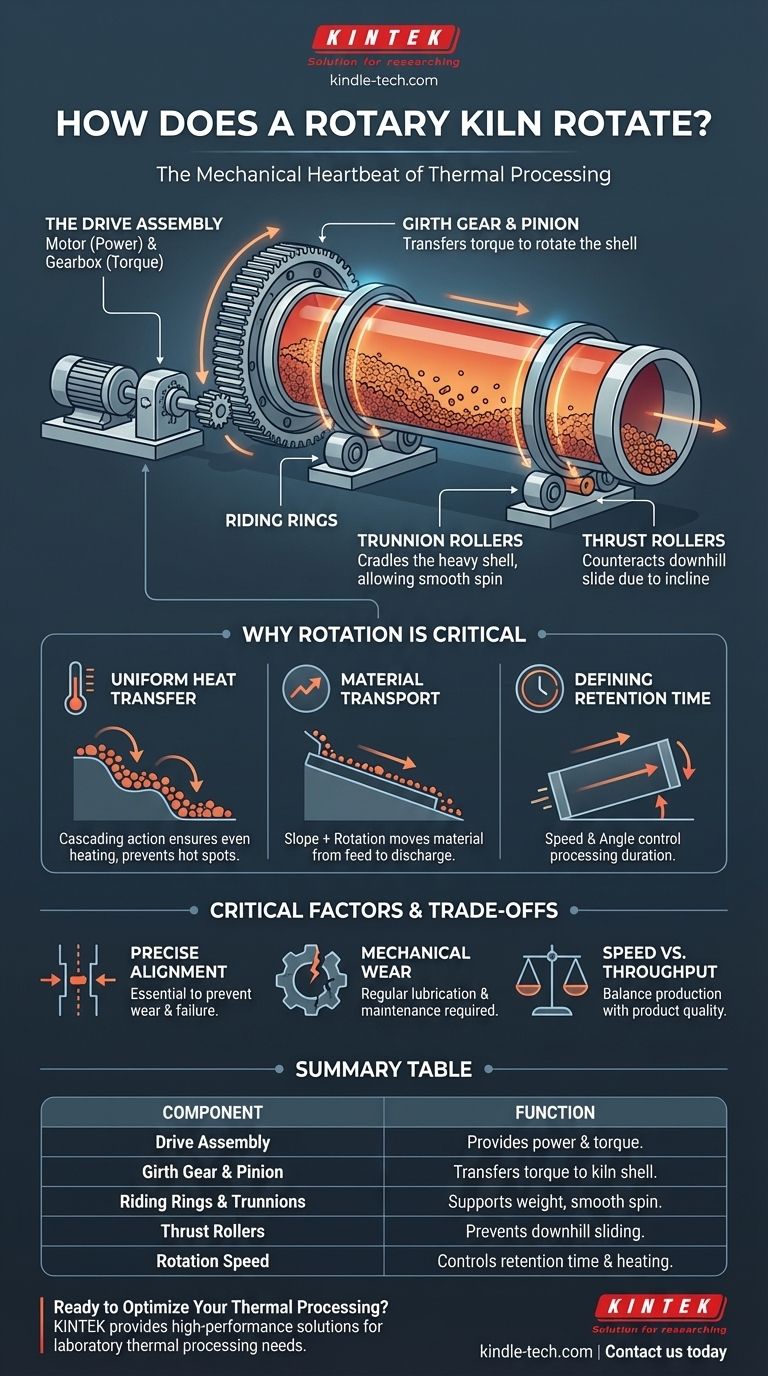
At its core, a rotary kiln rotates using a powerful motor and a massive gear system. The kiln itself is a large, heavy cylinder, which is turned by a large ring gear (called a girth gear) fixed around its circumference. This entire assembly is supported by sets of rollers, allowing the massive structure to spin smoothly on its axis.
The rotation of a kiln is not merely for mixing. It is a precisely engineered system where a motor-driven gear turns the cylindrical shell, while support rollers bear the load. This motion, combined with a slight downward slope, is the fundamental mechanism for both uniformly heating and slowly transporting material through the furnace.

The Core Mechanics of Rotation
To understand how a rotary kiln rotates, it's best to break down the system into its primary mechanical components. Each part has a distinct and critical function.
The Drive Assembly: The Source of Power
The entire process begins with the drive assembly. This typically consists of a high-torque electric motor connected to a gearbox.
The motor provides the raw power, and the gearbox reduces the speed while increasing the torque significantly. This is necessary to overcome the immense inertia and weight of the kiln shell and the material inside it.
The Girth Gear: Translating Power to Motion
The torque from the gearbox is transferred to a small gear called a pinion. This pinion engages with a massive ring gear, known as the girth gear, that is bolted directly onto the kiln's cylindrical shell.
As the pinion turns, it forces the much larger girth gear to rotate, which in turn rotates the entire kiln assembly. This gear arrangement provides the final mechanical advantage needed to turn the heavy structure at a slow, controlled speed.
Support System: Riding Rings and Trunnion Rollers
A rotary kiln is incredibly heavy, especially when filled with material and lined with refractory brick. It cannot support its own weight.
Instead, the kiln shell is supported by two or more massive steel bands known as riding rings or support tyres. These rings rest on sets of heavy-duty rollers called trunnion rollers. This system acts like a cradle, bearing the full radial load of the kiln and allowing it to spin with minimal friction.
Thrust Rollers: Managing Axial Position
Because the kiln is set at a slight incline (or slope), gravity constantly tries to pull it downhill.
To counteract this axial force and keep the kiln from sliding off its trunnion rollers, one or more thrust rollers are positioned to push against the side of a riding ring. These rollers keep the entire assembly perfectly positioned along its longitudinal axis.
Why Rotation is a Critical Process Variable
The rotation of the kiln is not just a background function; it is a primary tool for process control. The speed and nature of the rotation directly influence the final product.
Ensuring Uniform Heat Transfer
As the kiln rotates, the material inside is gently tumbled. This action, known as "cascading," constantly exposes new surfaces to the hot gas and the heated refractory wall.
This constant mixing is essential for achieving uniform heating and preventing hot spots or under-processed sections within the material bed.
Controlling Material Transport
The kiln is always installed at a slight downward angle, typically between 1 and 4 degrees.
The combination of this slope and the rotation is what causes the material to move slowly from the feed end to the discharge end. Without rotation, the material would simply sit in place.
Defining Retention Time
The retention time—the duration the material spends inside the kiln—is a critical parameter for ensuring a complete chemical reaction or physical change.
This time is directly controlled by adjusting the kiln's rotational speed and its angle of inclination. A slower rotation or a shallower slope increases retention time, while a faster rotation or a steeper slope decreases it.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Factors
Operating a rotary kiln involves balancing performance with mechanical reality. The forces involved are immense, and small issues can lead to major problems.
The Importance of Precise Alignment
The alignment of the trunnion rollers and the overall straightness of the kiln shell are absolutely essential for smooth operation.
Misalignment concentrates the massive weight of the kiln onto small areas of the rollers and riding rings. This leads to excessive and uneven wear, vibrations, and increased power consumption, ultimately risking catastrophic failure of the support components.
Mechanical Stress and Wear
The drive gear, riding rings, and rollers are under constant mechanical stress. They are all considered wear parts that require regular inspection and maintenance.
Lubrication of the gear mesh and the support roller bearings is critical to minimize friction and extend the life of these expensive components.
Speed vs. Throughput
There is a direct trade-off between the speed of production (throughput) and the quality of the process.
Increasing the rotational speed moves material through the kiln faster, increasing output. However, this reduces retention time, which may result in an incomplete reaction and a lower-quality product. Finding the optimal balance is key to efficient operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The operational focus for a rotary kiln depends entirely on your primary objective, whether it's production volume, equipment longevity, or product quality.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Control is paramount; optimize the rotational speed and kiln slope to achieve the target retention time and uniform heat transfer.
- If your primary focus is maintenance and longevity: Prioritize regular inspection and lubrication of the drive gear, pinion, riding rings, and all support rollers to prevent premature wear.
- If your primary focus is product quality: You must achieve the perfect balance between the temperature profile and the rotational speed to ensure the material is processed uniformly for the exact required duration.
Ultimately, the rotation of a kiln is the mechanical heartbeat that drives the entire thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Drive Assembly (Motor & Gearbox) | Provides power and torque to rotate the kiln. |
| Girth Gear & Pinion | Transfers torque from the drive to rotate the kiln shell. |
| Riding Rings & Trunnion Rollers | Supports the kiln's weight and allows it to spin smoothly. |
| Thrust Rollers | Prevents the inclined kiln from sliding downhill. |
| Rotation Speed | Controls material retention time and heating uniformity. |
Ready to Optimize Your Thermal Processing?
Understanding the precise mechanics of a rotary kiln is the first step toward maximizing your process efficiency, product quality, and equipment longevity. The right design and maintenance are critical for success.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable solutions for laboratory thermal processing needs. Whether you are scaling up a process or require consistent, high-quality results, our expertise can help you achieve your goals.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and drive your projects forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the parts of a carbon regeneration kiln? A Guide to Its Core Components and Function
- What biomass is used to make biochar? The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Feedstock
- How does a rotary kiln operate? Master Continuous High-Temperature Processing
- What are the two components of material movement inside a rotating cylinder? Optimize Your Kiln & Dryer Performance
- What are the industrial applications of fluidization? Unlock Efficient Heat & Mass Transfer for Your Process
- What is the thermal regeneration of activated carbon? Restore Performance & Cut Costs
- What is sintering process in steel industry? The Essential Bridge to Efficient Ironmaking



















