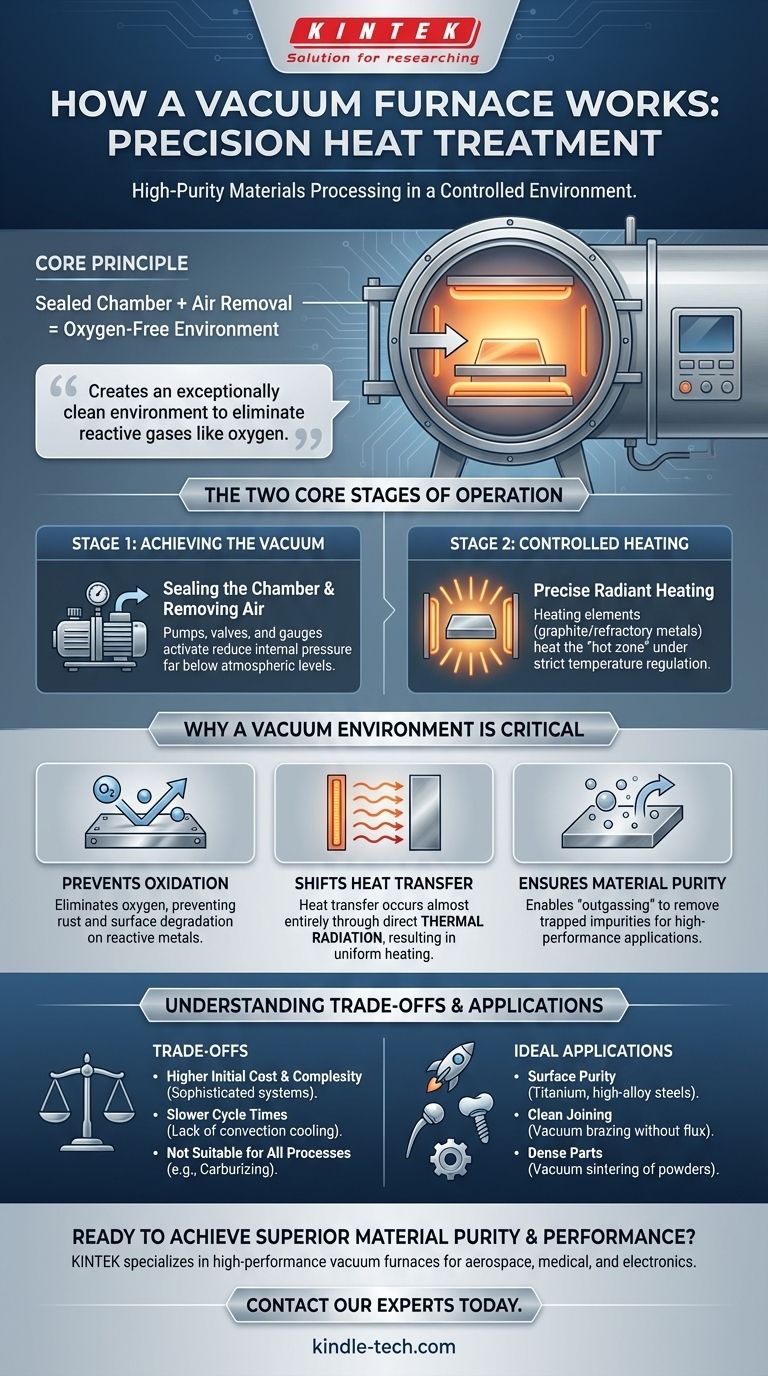
At its core, a vacuum furnace works by heating materials inside a sealed chamber from which nearly all the air has been removed. This simple-sounding process is critical because it eliminates the reactive gases, primarily oxygen, that would otherwise contaminate or damage materials at high temperatures. The result is an exceptionally clean and controlled environment for precision heat treatment.
The fundamental purpose of a vacuum furnace is not just to heat materials, but to fundamentally control their environment. By creating a vacuum, it prevents unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation, allowing for high-purity processing that is impossible in a standard atmosphere.
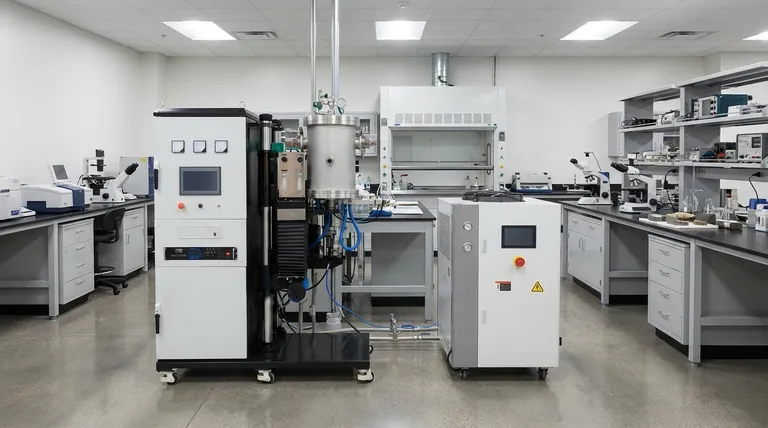

The Two Core Stages of Operation
Every vacuum furnace cycle, regardless of its specific application, follows two fundamental stages. These stages are managed by a sophisticated control system to ensure precision and repeatability.
Stage 1: Achieving the Vacuum
The process begins by sealing the material inside the furnace chamber.
A powerful vacuum system, consisting of pumps, valves, and gauges, then activates to remove the air and other gases from the chamber.
This reduces the internal pressure far below standard atmospheric pressure, creating the vacuum environment necessary for clean processing.
Stage 2: Controlled Heating
Once the desired vacuum level is reached, the heating system is engaged.
Heating elements, often made of graphite or refractory metals, heat the chamber's interior, known as the "hot zone."
The temperature is precisely regulated—controlling the heating rate, holding time at a specific temperature, and cooling rate—to achieve the desired changes in the material's properties.
Why a Vacuum Environment Is Critical
Removing the atmosphere fundamentally changes the physics of the heating process and unlocks unique material processing capabilities.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
This is the primary benefit. At high temperatures, most metals will rapidly react with oxygen in the air, forming oxides (like rust).
A vacuum eliminates this oxygen, allowing metals like titanium, stainless steel, and superalloys to be heated without compromising their surface integrity or chemical composition.
Shifting How Heat Moves
In a normal furnace, heat is transferred significantly through convection, as hot air circulates.
In a vacuum, there is virtually no air to circulate. Heat transfer occurs almost entirely through thermal radiation—direct energy transfer from the hot elements to the material.
This results in highly uniform, predictable, and clean heating, as the material isn't in contact with combusted gases or a circulating atmosphere.
Ensuring Material Purity
The vacuum can also pull trapped gases from within the material itself, a process known as outgassing.
This further purifies the material, which is essential for applications in the aerospace, medical, and electronics industries where material purity is paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to using them effectively.
Higher Initial Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are complex machines involving sealed chambers, high-performance pumps, and sophisticated control systems.
This makes them significantly more expensive to purchase and maintain than conventional atmospheric furnaces.
Slower Cycle Times
Creating a vacuum and later cooling the material within that vacuum can be a slow process compared to atmospheric methods.
Because there is no air to help transfer heat, cooling cycles often rely on backfilling the chamber with an inert gas like argon or nitrogen to speed up the process.
Not Suitable for All Processes
Some heat treatment processes, like carburizing, specifically require a reactive atmosphere to introduce elements into the material's surface.
These processes are by definition incompatible with a vacuum environment and must be done in specialized atmospheric furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heating technology depends entirely on the material you are processing and the properties you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is surface purity and preventing oxidation: A vacuum furnace is essential for heat-treating reactive metals like titanium or high-alloy steels.
- If your primary focus is joining complex parts with exceptional cleanliness: Vacuum brazing provides strong, clean joints without the need for corrosive flux chemicals.
- If your primary focus is creating dense, solid parts from powders: Vacuum sintering or a vacuum hot press is the required technology to achieve high density and superior material properties.
Ultimately, a vacuum furnace provides unparalleled control over the heating environment, enabling the creation of materials with superior purity, strength, and performance.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Achieving Vacuum | Air is removed from the sealed chamber by a vacuum pump system. | Creates an oxygen-free environment to prevent contamination. |
| 2. Controlled Heating | Heating elements radiate heat to the material under precise temperature control. | Achieves desired material properties like strength and purity without oxidation. |
Ready to achieve superior material purity and performance in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance vacuum furnaces and lab equipment, designed to meet the stringent demands of industries like aerospace, medical, and electronics. Our solutions provide the clean, controlled environment necessary for precision heat treatment, brazing, and sintering.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK vacuum furnace can enhance your research, improve product quality, and drive innovation in your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the critical temperature of heat treatment? Unlock the Key to Steel's Hardness and Performance
- What are the advantages of brazing over braze welding? Achieve Stronger, Cleaner, and Repeatable Joints
- Which type of furnace is used for heat treatment? Match Your Process to the Perfect Heat Treating Solution
- What is the function of calciner? Unlock Material Transformation for Your Industry
- What is the application of quenching effect? Achieve Superior Hardness and Strength in Materials
- How much will a new furnace cost? Get the Full Price Breakdown for Your Home
- What is the role of a high-temperature industrial furnace in 11% Cr steel treatment? Ensuring Structural Uniformity
- What is the atmosphere of a brazing furnace? Control Gases for Perfect Metal Joining



















