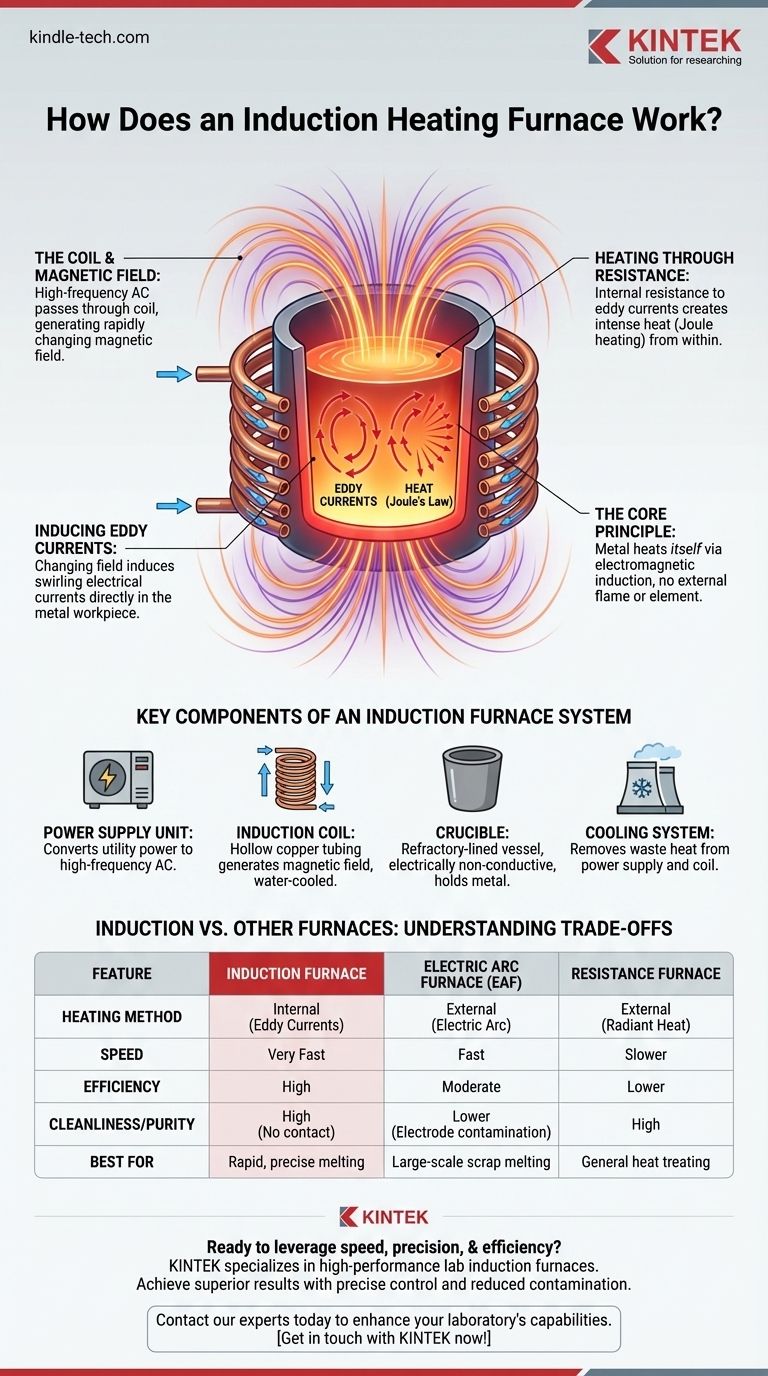
At its core, an induction heating furnace works by using a powerful, changing magnetic field to make a piece of metal heat itself from the inside out. Unlike a conventional oven that heats from the outside, an induction furnace uses no direct flame or external heating element. Instead, a high-frequency alternating current is passed through a copper coil, creating an electromagnetic field that induces electrical currents directly within the metal, causing it to heat up rapidly due to its own internal resistance.
An induction furnace is fundamentally different from other electric furnaces. Instead of using external heat sources like arcs or glowing elements, it transforms the metal workpiece itself into the source of heat through the principle of electromagnetic induction.

The Core Principle: Electromagnetic Induction
The process is a direct application of two fundamental physics principles: Faraday's Law of Induction and Joule's Law.
The Coil and the Magnetic Field
The system begins with a coil, typically made of highly conductive copper tubing. A precisely controlled, high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed through this coil.
According to electromagnetic theory, any electric current generates a magnetic field. Because the current is alternating, it produces a magnetic field that rapidly changes its polarity and intensity.
Inducing Eddy Currents
When a conductive material, like steel or aluminum, is placed inside this alternating magnetic field, the field penetrates the metal.
This changing magnetic field induces its own electrical currents that swirl within the metal. These are known as eddy currents. The metal workpiece essentially becomes the secondary winding of a transformer, with the furnace coil being the primary.
Heating Through Resistance (Joule's Law)
All metals have some amount of electrical resistance. As the powerful eddy currents flow through the metal, they encounter this resistance and lose energy.
This lost energy is converted directly into heat. This phenomenon is called Joule heating. Because the eddy currents are generated inside the material, the heat is also generated internally, leading to extremely fast and efficient heating.
Key Components of an Induction Furnace System
An induction furnace is more than just a coil; it is a precisely engineered system where each component plays a critical role.
The Power Supply Unit
This is the brain and muscle of the furnace. It takes standard utility power and converts it into the high-frequency AC needed for induction. It typically consists of a transformer, an inverter to generate the high frequency, and a capacitor bank to optimize the circuit's efficiency.
The Induction Coil
This is the component that creates the magnetic field. It is almost always made from hollow copper tubing so that cooling water can be passed through it. Without constant cooling, the high current flowing through the coil would cause it to quickly melt.
The Crucible
The crucible is the refractory-lined vessel that holds the metal charge. It must be made from a material that is both temperature-resistant and electrically non-conductive. This ensures that only the metal charge heats up, not the container holding it.
The Cooling System
A robust cooling system, usually a closed-loop water circuit, is essential. It removes the immense waste heat generated by the power supply and the induction coil, preventing catastrophic failure of the equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Induction vs. Other Furnaces
To truly appreciate induction heating, it is helpful to contrast it with other common electric furnace technologies.
Induction vs. Electric Arc Furnaces
An Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) melts metal using an extremely high-voltage electric arc that jumps from graphite electrodes to the metal charge. This is a violent, intensely hot external process.
Induction furnaces, by contrast, have no electrodes and no arc. The heating is internal, non-contact, and far more controlled, resulting in a cleaner melt with fewer impurities.
Induction vs. Resistance Furnaces
A Resistance Furnace operates like a kitchen oven or toaster. It uses heating elements made of metal or ceramic that glow hot when electricity passes through them. This heat then radiates onto the workpiece.
This is an indirect heating method that is slower and often less energy-efficient than induction, where the heat is generated exactly where it is needed—inside the part itself.
The Advantages of Induction
The direct, internal heating method gives induction furnaces several key advantages:
- Speed: Heating is exceptionally rapid.
- Efficiency: More energy goes into heating the metal and less is wasted heating the furnace chamber.
- Control: The power can be adjusted instantly, allowing for very precise temperature control.
- Cleanliness: There are no combustion byproducts or electrode materials to contaminate the metal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace technology depends entirely on your process requirements for speed, purity, and scale.
- If your primary focus is rapid, clean, and precise melting of metals: An induction furnace is the superior choice due to its direct internal heating method.
- If your primary focus is melting massive volumes of raw scrap steel: An electric arc furnace is often the more dominant and economical technology at that scale.
- If your primary focus is general heat treating or annealing at controlled temperatures: A conventional resistance furnace can be a simpler and less expensive option.
Understanding the core principle of internal heating is the key to leveraging the unique speed, efficiency, and control that induction technology offers.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Induction Furnace | Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) | Resistance Furnace |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Internal (Eddy Currents) | External (Electric Arc) | External (Radiant Heat) |
| Speed | Very Fast | Fast | Slower |
| Efficiency | High | Moderate | Lower |
| Cleanliness/Purity | High (No contact) | Lower (Electrode contamination) | High |
| Best For | Rapid, precise melting | Large-scale scrap melting | General heat treating |
Ready to leverage the speed, precision, and efficiency of induction heating in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including induction furnaces designed for rapid, clean melting and heat treatment processes. Our solutions help you achieve superior results with precise temperature control and reduced contamination.
Contact our experts today to discuss how an induction furnace can enhance your laboratory's capabilities. Let us help you find the perfect solution for your specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis



















