At its core, carburizing is a case-hardening process that infuses carbon into the surface of a low-carbon steel part. This is accomplished by heating the steel in a carbon-rich environment, allowing carbon atoms to diffuse into the surface, and then rapidly cooling (quenching) it. This final quench locks the carbon into the steel's crystalline structure, creating an extremely hard, wear-resistant outer shell while leaving the inner core tough and ductile.
The fundamental goal of carburizing is not just to make steel harder, but to create a composite-like component from a single piece of metal: one with a hard, wear-resistant surface and a tough, fracture-resistant core.
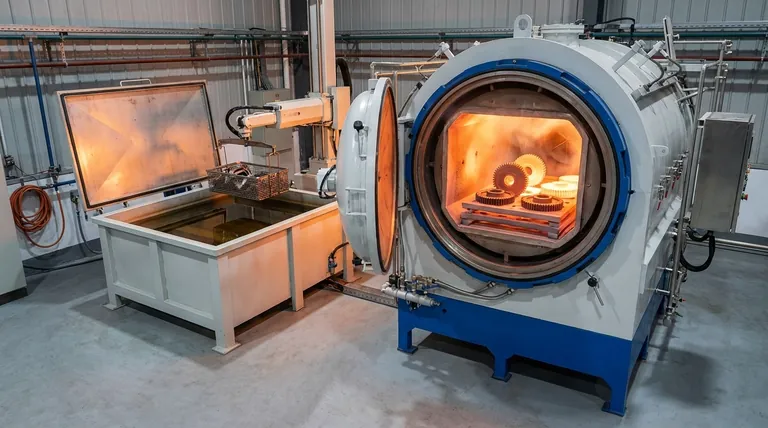

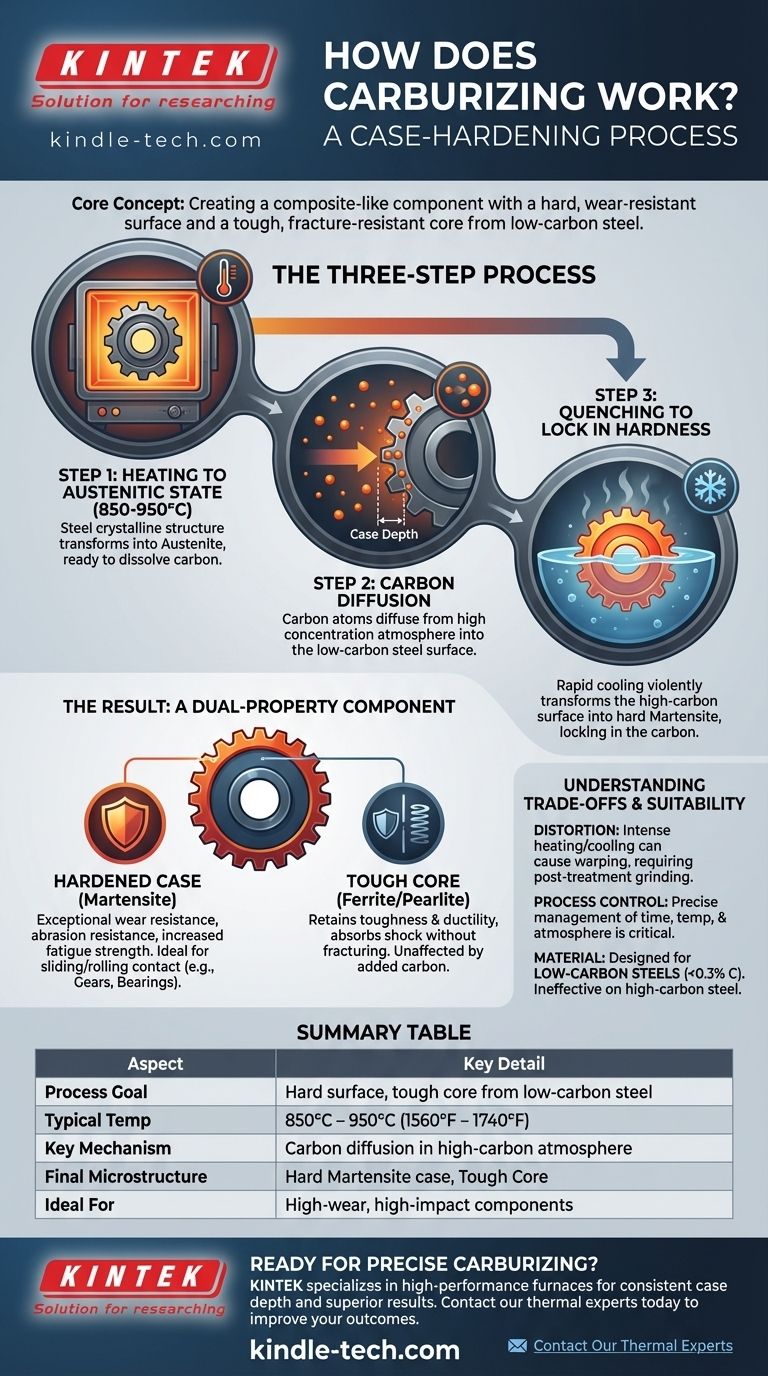
The Science Behind Carburizing: A Three-Step Process
Carburizing is a carefully controlled metallurgical transformation. The entire process hinges on the unique ability of steel to change its atomic structure at high temperatures.
Step 1: Heating to the Austenitic State
First, the low-carbon steel component is placed inside a sealed furnace and heated to a high temperature, typically between 850°C and 950°C (1560°F and 1740°F).
At this temperature, the steel's crystalline structure transforms into a phase called austenite. The key characteristic of austenite is its ability to dissolve a significant amount of carbon—far more than steel can at room temperature.
Step 2: Carbon Diffusion
While the steel is held at this high temperature, a carbon-rich gas, liquid, or solid material is introduced into the furnace. This creates an environment with a very high concentration of carbon atoms surrounding the steel part.
Because of the natural principle of diffusion, atoms move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. The carbon atoms from the atmosphere migrate and diffuse into the surface of the steel, which has a much lower carbon content. The depth of this carbon penetration, known as the case depth, is determined by the time and temperature of the treatment.
Step 3: Quenching to Lock in Hardness
After the desired amount of carbon has penetrated the surface, the part is rapidly cooled, or quenched, typically in oil or water.
This rapid cooling does not give the carbon atoms time to exit the steel's crystal structure. It violently transforms the high-carbon austenite surface into martensite, an extremely hard, brittle, and wear-resistant microstructure. The low-carbon core, which did not absorb extra carbon, transforms into a much softer, tougher structure, preserving its ductility.
The Result: A Dual-Property Component
The final product of carburizing is a component with two distinct and highly desirable zones. This dual nature is what makes the process so valuable in engineering.
The Hardened Case
The high-carbon martensitic surface, or "case," provides exceptional wear resistance, abrasion resistance, and increased fatigue strength. This makes it ideal for components that experience sliding or rolling contact, such as gears and bearings.
The Tough Core
The low-carbon inner "core" remains unaffected by the added carbon. It retains its original properties of toughness and ductility, allowing the component to absorb shock and impact loads without fracturing. A part made entirely of high-carbon steel would be too brittle for such applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, carburizing is not without its challenges. A successful outcome depends on precise control and an understanding of its effects.
Potential for Distortion
The intense heating and rapid cooling involved in quenching can cause the part to warp or change dimensions. This often necessitates post-treatment processes like grinding to bring the component back to its required final tolerances.
Process Control is Critical
The effectiveness of carburizing depends entirely on the precise management of time, temperature, and furnace atmosphere. An incorrect process can result in a case that is too shallow, too deep (leading to brittleness), or inconsistent across the part's surface.
Material Suitability
Carburizing is specifically designed for low-carbon steels (typically with less than 0.3% carbon). These steels have a tough core but need the added surface hardness. Applying this process to a medium or high-carbon steel is ineffective and can result in an extremely brittle part prone to cracking.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
You should consider carburizing when your design requires conflicting properties—surface hardness and core toughness—that cannot be achieved with a single, uniform material.
- If your primary focus is high wear resistance for moving parts: Carburizing is the definitive choice for components like gears, camshafts, and bearings that must endure constant friction.
- If your primary focus is impact strength and durability: Carburizing creates parts that can withstand sudden loads without fracturing while resisting surface damage.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective material selection: The process allows you to use inexpensive, easily machinable low-carbon steel to create a final part with the surface performance of a more expensive and difficult-to-machine high-carbon alloy.
By understanding this process, you can confidently specify components that deliver exceptional surface durability without sacrificing essential core strength.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process Goal | Create a hard surface and tough core from a single piece of low-carbon steel. |
| Typical Temperature | 850°C - 950°C (1560°F - 1740°F) |
| Key Mechanism | Carbon diffusion into the steel surface in a high-carbon atmosphere. |
| Final Microstructure | Hard martensite case, tough ferrite/pearlite core. |
| Ideal For | Gears, bearings, camshafts, and other high-wear, high-impact components. |
Ready to enhance your components with precise carburizing? The effectiveness of this process depends on precise thermal control. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab and industrial furnaces that deliver the accurate, uniform heating required for successful carburizing. Whether you are in R&D or production, our equipment ensures consistent case depth and superior metallurgical results.
Contact our thermal experts today to discuss how our solutions can improve your heat treatment outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of brazing compared to welding? Achieve Clean, Low-Distortion Metal Joining
- Why would you braze instead of weld? Preserve Material Integrity and Join Dissimilar Metals
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- How is the greatest joint strength obtained in brazing? Master the 3 Keys to Superior Metallurgical Bonds
- What is a braze repair process? A Low-Heat Solution for Strong, Seamless Metal Joining



















