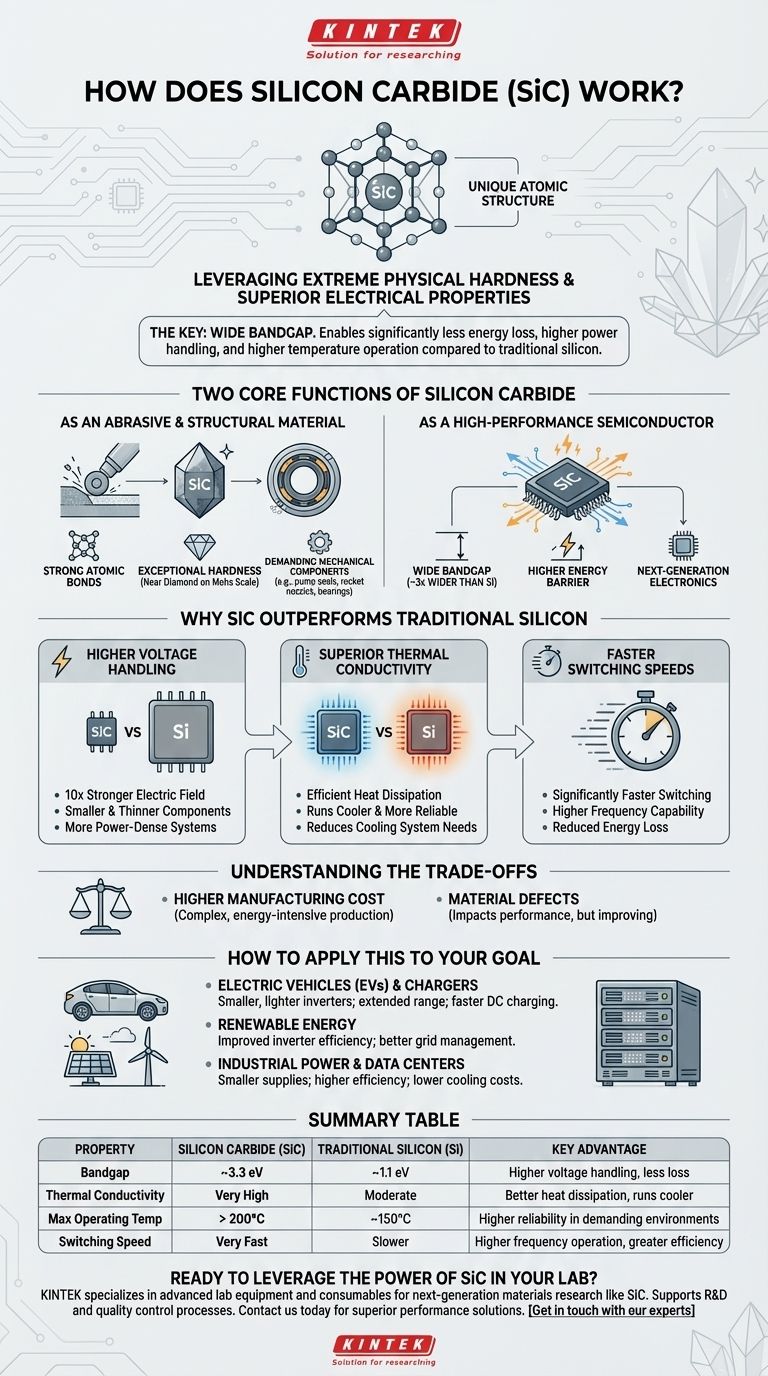
At its core, silicon carbide (SiC) works by leveraging its unique atomic structure, which gives it a combination of extreme physical hardness and superior electrical properties. Unlike traditional silicon, SiC can withstand much higher voltages, temperatures, and switching frequencies. This allows it to function as both a highly durable structural material and a next-generation semiconductor for high-power electronics.
The essential reason silicon carbide is revolutionary is its wide bandgap. This fundamental electrical property allows SiC devices to operate with significantly less energy loss, handle much more power, and run at higher temperatures than their silicon counterparts, enabling a new class of smaller, faster, and more efficient technology.

The Two Core Functions of Silicon Carbide
Silicon carbide's utility stems from two distinct sets of properties: its physical resilience and its electrical characteristics. Understanding both is key to grasping its importance.
As an Abrasive and Structural Material
The bond between silicon and carbon atoms in a SiC crystal is incredibly strong and stable.
This atomic structure results in a material with exceptional hardness, ranking just below diamond on the Mohs scale. This is why SiC has a long history of use in abrasive and cutting applications like sandpaper and grinding wheels.
This same durability and resistance to high temperatures make it ideal for demanding mechanical components in environments where other materials would fail, such as in high-performance pump seals, bearings, and even rocket engine nozzles.
As a High-Performance Semiconductor
The most significant modern application of SiC is in electronics, where it functions as a semiconductor, but one with critical advantages over pure silicon (Si).
The key is the material's bandgap, which is the amount of energy required for an electron to break free and conduct electricity. SiC has a bandgap roughly three times wider than that of silicon.
This wide bandgap is the source of all its electronic advantages. It acts as a higher energy barrier, allowing the material to handle conditions that would destroy a standard silicon chip.
Why SiC Outperforms Traditional Silicon
The practical benefits of SiC's wide bandgap are transformative for power electronics, enabling performance benchmarks that are simply not possible with silicon.
Higher Voltage Handling
SiC can withstand an electric field nearly ten times stronger than silicon before it breaks down.
This allows engineers to design components that are significantly smaller and thinner for the same voltage rating, leading to more compact and power-dense systems.
Superior Thermal Conductivity
SiC is extremely efficient at dissipating heat. It conducts thermal energy far better than silicon.
This means SiC components run cooler and are more reliable under heavy loads. It also reduces the need for large, heavy, and expensive cooling systems, further shrinking the size of the final product.
Faster Switching Speeds
In power electronics, components must switch on and off rapidly to control energy flow. SiC devices can switch significantly faster than silicon devices.
This higher frequency capability reduces energy loss during the switching process, which is a major source of inefficiency in power converters.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its clear advantages, SiC is not a universal replacement for silicon. Its adoption involves specific challenges that must be considered.
Higher Manufacturing Cost
Producing a high-purity, single-crystal SiC wafer is a complex and energy-intensive process.
As noted in its production for heating elements, the material must be sintered at extremely high temperatures (over 2000°C). This complexity makes SiC components more expensive to manufacture than their silicon equivalents.
Material Defects
The crystal growth process for silicon carbide is more difficult to control than for silicon.
This can result in a higher density of crystalline defects, which can impact device performance and manufacturing yield. However, fabrication technology is rapidly improving to mitigate this issue.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The choice to use or invest in SiC technology depends entirely on the performance demands of the application.
- If your primary focus is electric vehicles and chargers: SiC enables smaller, lighter, and more efficient inverters, extending vehicle range and enabling much faster DC charging stations.
- If your primary focus is renewable energy: SiC dramatically improves the efficiency of solar inverters and power grid management systems, converting more generated power into usable electricity.
- If your primary focus is industrial power or data centers: SiC-based power supplies are smaller, more efficient, and produce less waste heat, lowering operational and cooling costs.
Silicon carbide is a foundational material for building the next generation of high-power, high-efficiency electronic systems.
Summary Table:
| Property | Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Traditional Silicon (Si) | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bandgap | ~3.3 eV | ~1.1 eV | Higher voltage handling, less energy loss |
| Thermal Conductivity | Very High | Moderate | Better heat dissipation, runs cooler |
| Max Operating Temperature | > 200°C | ~150°C | Higher reliability in demanding environments |
| Switching Speed | Very Fast | Slower | Higher frequency operation, greater efficiency |
Ready to leverage the power of silicon carbide in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed to work with and test next-generation materials like SiC. Whether you are developing more efficient power electronics, renewable energy systems, or high-temperature components, our solutions support your R&D and quality control processes.
Contact us today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior performance and efficiency with the right tools for the job.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Sheets Zinc Sulfide ZnS Window
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Thermocouple Protection Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the application of RRDE? Unlock Quantitative Catalyst and Reaction Insights
- How should a platinum wire/rod electrode be cleaned before use? A Guide to Reliable Electrochemical Data
- What is the common role of a platinum disk electrode? A Guide to Its Primary Use as a Working Electrode
- What are the performance characteristics of platinum wire/rod electrodes? Unmatched Stability for Your Lab
- What is a common application for the platinum wire/rod electrode? The Essential Guide to Counter Electrodes