In essence, sintering is the critical manufacturing step that transforms a compacted ceramic powder into a dense, solid, and functional component. This process uses heat to bond the individual powder particles together, drastically reducing the empty space (porosity) between them. The primary effects are a significant increase in density, mechanical strength, hardness, and thermal stability, turning a fragile "green" part into a robust ceramic material.
Sintering is not merely heating; it is a controlled process of atomic diffusion that governs the final microstructure of a ceramic. Mastering this transformation is the key to unlocking the specific performance characteristics required for applications ranging from cutting tools to electrical insulators.

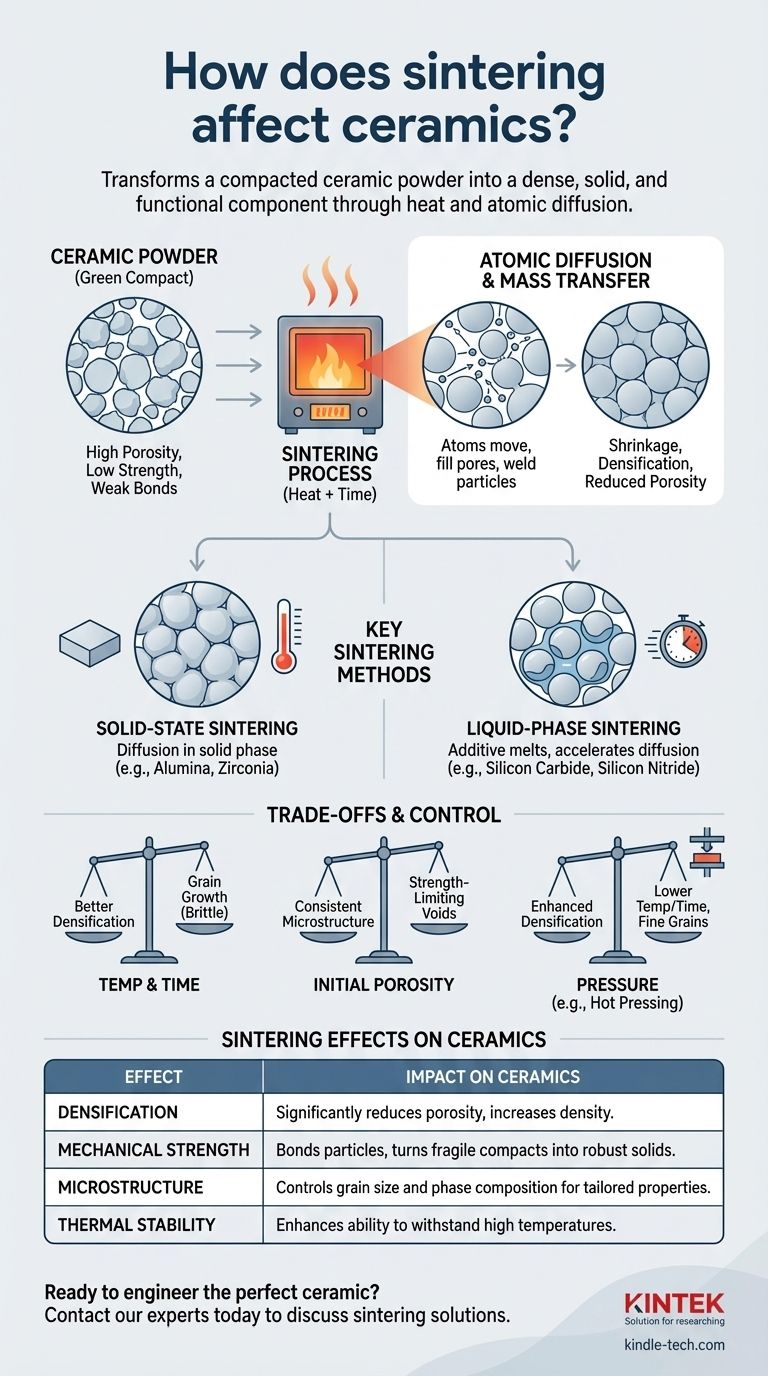
The Fundamental Transformation: From Powder to Solid
Sintering is the bridge between a raw material and a finished ceramic product. The process fundamentally alters the material's internal structure on a microscopic level, leading to dramatic macroscopic changes.
The Starting Point: The "Green" Compact
Before sintering, ceramic powders are pressed or formed into a desired shape. This object, known as a "green" compact, is held together by weak forces and is characterized by high porosity and very low strength.
The Mechanism: Atomic Diffusion and Mass Transfer
When heated to a high temperature (typically below the material's melting point), the atoms at the contact points between powder particles gain enough energy to move. This atomic diffusion causes material to transfer into the empty spaces, or pores, between the particles, effectively welding them together.
The Result: Densification and Reduced Porosity
As material fills the pores, the overall object shrinks and becomes significantly denser. This densification is the primary goal of sintering, as it directly correlates to improved mechanical properties like hardness and strength. A well-sintered ceramic has minimal residual porosity.
Key Sintering Methods and Their Impact
The specific method used depends on the ceramic material and the desired outcome. The two main approaches are solid-state and liquid-phase sintering.
Solid-State Sintering
This is the classic method used for materials like alumina and zirconia. Diffusion occurs entirely in the solid phase, meaning atoms migrate across particle boundaries without any melting. This process often requires very high temperatures and longer durations to achieve full density.
Liquid-Phase Sintering
This method is used for ceramics that are notoriously difficult to densify, such as silicon carbide and silicon nitride. A small amount of an additive is mixed with the ceramic powder. At the sintering temperature, this additive melts and forms a liquid phase that wets the ceramic particles.
This liquid accelerates densification in two ways: it allows particles to rearrange more easily due to capillary forces, and it provides a faster path for atomic diffusion.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Controlling the Outcome
Sintering is a balancing act. The final properties of the ceramic are dictated by precise control over several competing factors.
The Temperature and Time Dilemma
Higher temperatures and longer sintering times promote better densification. However, excessive heat or time can also cause grain growth, where smaller crystal grains merge into larger ones. While density increases, overly large grains can make the ceramic more prone to fracture, reducing its toughness.
The Role of Initial Porosity
The quality of the initial green compact is critical. A part with high or uneven initial porosity will require more aggressive sintering to densify, making it harder to control the final microstructure and increasing the risk of leaving behind strength-limiting voids.
The Influence of Pressure
Applying external pressure during the heating process (e.g., in hot pressing) can significantly enhance densification. Pressure forces the particles into closer contact, accelerating diffusion and allowing for lower sintering temperatures and shorter times. This is a powerful tool for achieving near-full density while minimizing unwanted grain growth.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The optimal sintering strategy depends entirely on the performance requirements of the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and strength (e.g., cutting tools): Use liquid-phase sintering or apply pressure to eliminate nearly all porosity.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production (e.g., ceramic tiles, sanitaryware): Optimize solid-state sintering parameters (time and temperature) to achieve acceptable density without excessive energy consumption.
- If your primary focus is a fine-grained microstructure for exceptional toughness: Use lower temperatures combined with applied pressure to achieve full density while inhibiting grain growth.
By understanding and controlling the sintering process, you can precisely engineer the microstructure of a ceramic to meet its intended purpose.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Effect | Impact on Ceramics |
|---|---|
| Densification | Significantly reduces porosity, increasing density. |
| Mechanical Strength | Bonds particles, turning fragile compacts into robust solids. |
| Microstructure | Controls grain size and phase composition for tailored properties. |
| Thermal Stability | Enhances ability to withstand high temperatures. |
Ready to engineer the perfect ceramic for your application? The sintering process is the key to unlocking the density, strength, and thermal stability your components require. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and expert consumables needed to master this critical transformation. Whether you're developing cutting tools, electrical insulators, or cost-effective ceramic products, our solutions help you achieve precise microstructural control. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's sintering success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs



















