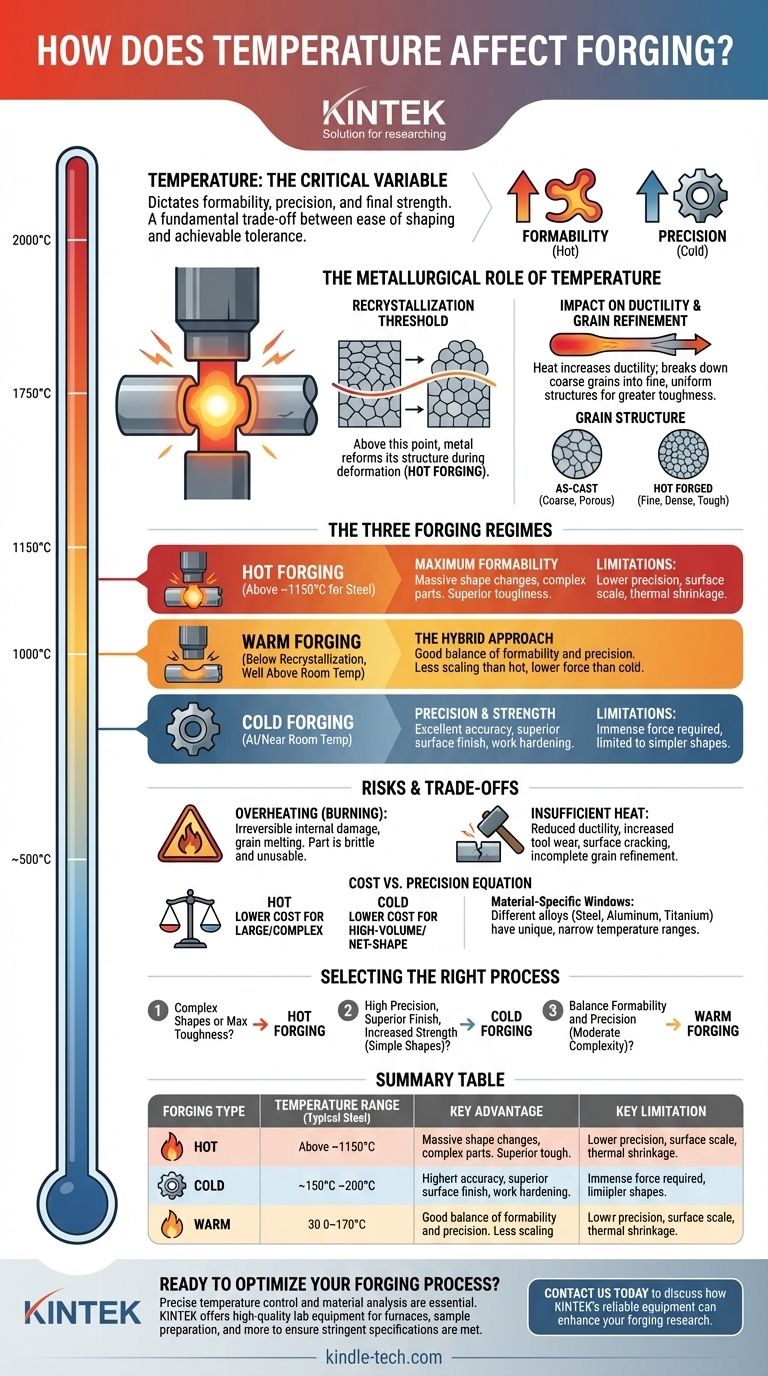
Temperature is the single most critical variable in the forging process. It dictates how a metal behaves under pressure, what shapes are possible, and the final mechanical properties of the finished part. Choosing the correct temperature is not a suggestion but a requirement for success, as it directly controls the metal's internal structure, ductility, and required forming energy.
The core decision in any forging operation revolves around temperature. This choice represents a fundamental trade-off between the ease of shaping a part (formability) and the final precision, surface finish, and strength you can achieve.
The Metallurgical Role of Temperature
To understand forging, you must first understand how heat alters a metal's internal crystal structure. This behavior is the foundation of the entire process.
The Recrystallization Threshold
Every metal has a recrystallization temperature. Above this point, the metal's distorted, stressed grain structure can reform into new, strain-free grains during the deformation process.
This is the key distinction between hot and cold working. Working a metal above this temperature is hot forging; working it below is cold forging.
Impact on Ductility and Malleability
Heating a metal significantly increases its ductility (its ability to be deformed without fracturing) and malleability (its ability to be shaped).
A hot workpiece behaves more like dense clay than a solid, allowing it to be formed into complex geometries with significantly less force than would be required at room temperature.
The Refinement of Grain Structure
When a metal is properly hot forged, the immense pressure breaks down its coarse, as-cast grain structure. The heat then allows new, finer, and more uniform grains to grow.
This grain refinement eliminates internal voids and porosity, resulting in a part that is denser, tougher, and stronger than a cast or machined equivalent.
The Three Forging Temperature Regimes
Forging is not a single process but a category of processes defined by temperature. Each has distinct advantages and applications.
Hot Forging: For Maximum Formability
Hot forging is performed well above the metal's recrystallization temperature. For steel, this is typically around 1150°C (2100°F).
This process allows for massive shape changes and the creation of highly complex parts. The refined grain structure yields superior toughness and ductility. However, it comes at the cost of lower dimensional precision due to thermal shrinkage and the formation of surface scale (oxidation), often requiring secondary machining.
Cold Forging: For Precision and Strength
Cold forging is performed at or near room temperature. It is a process of shaping metal below its recrystallization point.
Because there is no heat involved, parts have excellent dimensional accuracy and a superior surface finish, often requiring no secondary work. The process also induces work hardening, which significantly increases the material's strength and hardness. The primary limitation is that it requires immense forces and is best suited for simpler shapes.
Warm Forging: The Hybrid Approach
Warm forging is a specialized process conducted between the hot and cold forging temperature ranges—below the recrystallization point but well above room temperature.
It offers a strategic compromise. It provides better precision and less scaling than hot forging while improving ductility and reducing the required forming forces compared to cold forging. This makes it a valuable option for parts with moderate complexity that demand good tolerances.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Choosing the wrong temperature or failing to control it precisely can lead to catastrophic failure or a part that does not meet specifications.
The Danger of Overheating
If a metal is heated too close to its melting point, a condition known as burning can occur. The grain boundaries can begin to melt and oxidize, creating irreversible internal damage.
A burned part is extremely brittle and completely unusable, regardless of its appearance. It must be scrapped.
The Problem of Insufficient Heat
For hot forging, insufficient temperature makes the metal less ductile. This means more force is needed to shape it, increasing wear on the dies and machinery.
More critically, it can lead to incomplete forging, surface cracking, and a failure to achieve the desired grain refinement, compromising the part's final mechanical properties.
The Cost vs. Precision Equation
Hot forging is often more cost-effective for large components or complex initial shapes, even with the added cost of finishing.
Cold forging excels in high-volume production of smaller, net-shape parts where the cost of the powerful machinery and robust tooling is offset by the elimination of secondary machining.
Material-Specific Windows
Every alloy has a unique and often narrow forging temperature window. Aluminum alloys are forged at much lower temperatures than steel, and titanium alloys require extremely precise temperature control to avoid detrimental phase changes or contamination. There is no one-size-fits-all temperature.
Selecting the Right Process for Your Application
Your choice must be driven by the end goal for your component. Analyze the trade-offs between formability, precision, and final strength to make an informed decision.
- If your primary focus is creating complex shapes or maximizing toughness: Hot forging is your best choice due to its high ductility and grain refinement benefits.
- If your primary focus is achieving high precision, a superior surface finish, and increased strength for a simpler shape: Cold forging is the ideal process, as it eliminates the need for most secondary machining.
- If your primary focus is balancing formability and precision for a moderately complex part: Warm forging offers a strategic compromise between the extremes of hot and cold processes.
Mastering temperature control is the key to unlocking the full strength, toughness, and reliability potential of the forging process.

Summary Table:
| Forging Type | Temperature Range (Typical Steel) | Key Advantage | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot Forging | Above ~1150°C (2100°F) | Maximum formability, superior toughness | Lower precision, surface scale |
| Cold Forging | At or near room temperature | High precision, superior surface finish, work hardening | High forces required, limited to simpler shapes |
| Warm Forging | Between hot and cold ranges | Good balance of formability and precision | Narrower process window |
Ready to Optimize Your Forging Process?
Choosing the correct forging temperature is critical for achieving the desired mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy in your metal components. The right lab equipment is essential for precise temperature control and material analysis.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of metallurgical laboratories. From furnaces for heat treatment simulations to sample preparation tools, our solutions help you accurately determine and control forging parameters, ensuring your materials meet stringent specifications.
Contact us today via our [#ContactForm] to discuss how KINTEK's reliable equipment can enhance your forging research and development, leading to stronger, more reliable parts.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the importance of muffle furnace? Ensuring Contaminant-Free Heating for Accurate Results
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of a muffle furnace? A Guide to Precision Heating
- What is the temperature verification of muffle furnace? Ensure Accurate Thermal Processing
- Why is it called a muffle furnace? The Key to Contamination-Free High-Temperature Heating
- What is the operation temperature of the muffle furnace? A Guide to Internal and Ambient Ranges



















