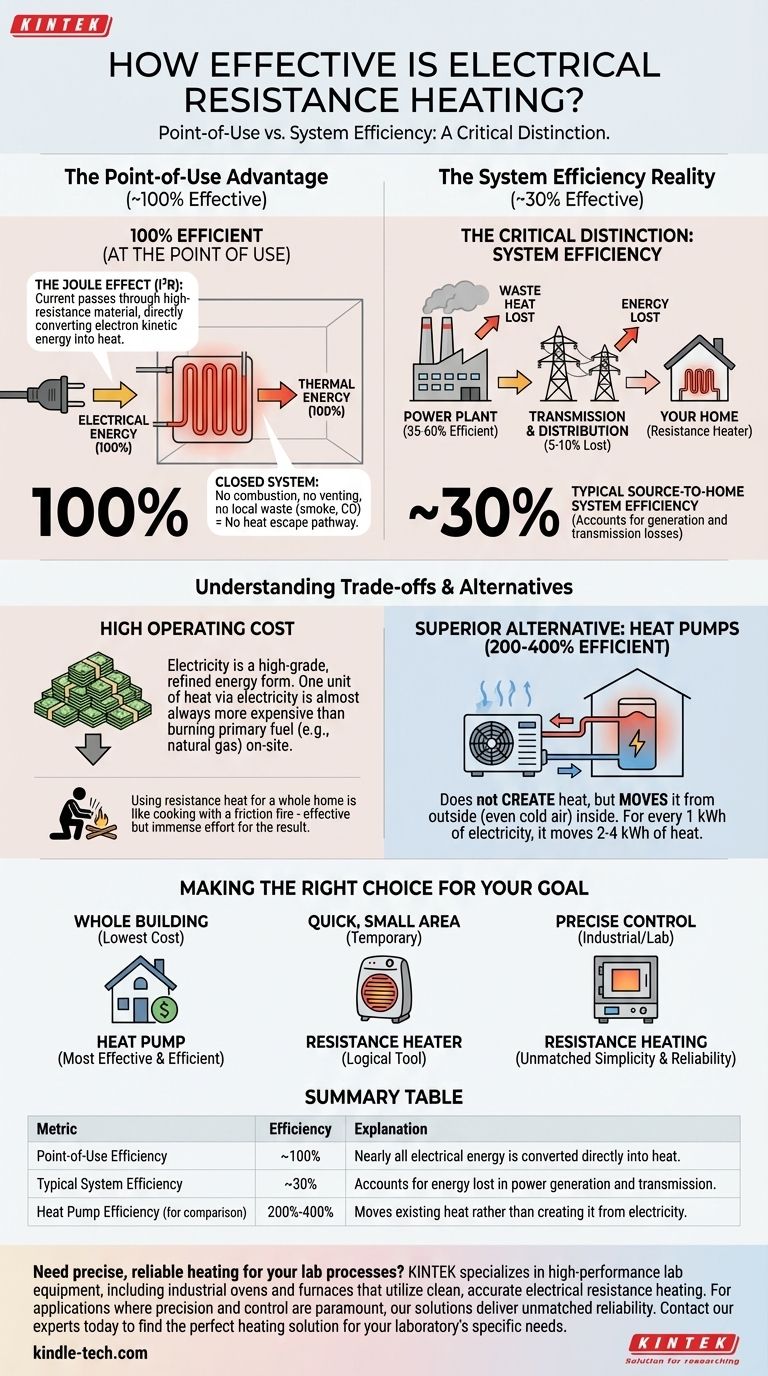
At the point of use, electrical resistance heating is nearly 100% effective. It excels at converting electrical energy directly into thermal energy with virtually no waste. Every watt of electricity drawn by the heater is transformed into a watt of heat delivered to the surrounding space.
While resistance heating is perfectly efficient in its immediate energy conversion, this number can be misleading. True effectiveness must also account for the cost and efficiency of generating and transmitting that electricity in the first place, making it one of the most expensive and least system-efficient ways to heat a building.
How Resistance Heating Achieves 100% Efficiency
The perfect conversion rate of electrical resistance heating is a direct result of its simple physical principle. It is a closed system with no need for combustion or venting.
The Joule Effect (I²R)
This process is based on a principle known as the Joule effect. When an electric current passes through a material with high electrical resistance, such as a nichrome wire, the flow of electrons is impeded.
These electrons collide with the atoms of the resistive material. Each collision transfers kinetic energy, which manifests as heat. Because this happens in a closed circuit, nearly all the electrical energy is converted directly into thermal energy.
No Byproducts, No Local Waste
Unlike a furnace that burns fuel, a resistance heater has no byproducts like smoke or carbon monoxide. It doesn't require a flue or chimney to vent exhaust gases.
Because there is no exhaust, there is no pathway for heat to escape, as there is with a traditional furnace chimney. All the energy consumed is released as heat directly into the target area.
The Critical Distinction: Device vs. System Efficiency
The "100% effective" figure only describes the final step of the energy journey. To understand its true cost and environmental impact, you must look at the entire system from the power plant to your room.
Point-of-Use Efficiency
This is the number most often cited. It measures how effectively the device in your room—the space heater or electric baseboard—converts the electricity it receives into heat. For resistance heating, this is ~100%.
Source Energy Efficiency
This is the crucial, often-overlooked metric. It accounts for the energy lost when generating and delivering electricity to your building.
A power plant burning natural gas or coal to generate electricity is typically only 35% to 60% efficient. A significant amount of the fuel's energy is lost as waste heat at the plant.
Furthermore, another 5% to 10% of the generated electricity is lost during transmission and distribution over power lines.
When you combine these factors, the total "source-to-home" system efficiency of electric resistance heating can be as low as 30%.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The perfect device efficiency of resistance heating makes it seem ideal, but its low system efficiency makes it a poor choice for many common applications, especially for heating an entire building.
The High Cost of Electricity
Electricity is a high-grade, refined form of energy. As a result, one unit of heat energy (measured in kWh or BTUs) delivered via electricity is almost always more expensive than the same unit delivered by burning a primary fuel like natural gas on-site.
Using resistance heat for a whole home is like cooking every meal over a fire you started by rubbing two sticks together—it works, but you used an immense amount of effort for a simple result.
The Superior Alternative: Heat Pumps
A modern heat pump is also electrically powered, but it doesn't create heat—it moves it. Using a refrigeration cycle, it extracts existing heat from the outside air (even when it's cold) and transfers it inside.
This process allows a heat pump to achieve an efficiency of 200% to 400%. For every 1 kWh of electricity it consumes, it can move 2 to 4 kWh of heat into your home. This makes it vastly more cost-effective and system-efficient than resistance heating.
Where Resistance Heating Excels
Despite its high operating cost, resistance heat is the perfect solution for specific, targeted applications. Its low installation cost, simplicity, and ability to provide instant, precise heat make it ideal for small space heaters, radiant floor warming, or industrial processes requiring clean, exact temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right technology, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is heating a whole building at the lowest operating cost: An electric heat pump is the most effective and efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is quick, temporary, or supplemental heat in a small area: A simple and inexpensive resistance heater is a perfectly logical tool.
- If your primary focus is clean, precise temperature control for an industrial or specific process: Resistance heating provides unmatched simplicity and reliability where its higher energy cost is justified.
Ultimately, understanding the difference between device efficiency and overall system efficiency is the key to making an informed and truly effective heating decision.
Summary Table:
| Metric | Efficiency | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Point-of-Use Efficiency | ~100% | Nearly all electrical energy is converted directly into heat. |
| Typical System Efficiency | ~30% | Accounts for energy lost in power generation and transmission. |
| Heat Pump Efficiency (for comparison) | 200%-400% | Moves existing heat rather than creating it from electricity. |
Need precise, reliable heating for your lab processes? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including industrial ovens and furnaces that utilize clean, accurate electrical resistance heating. For applications where precision and control are paramount, our solutions deliver unmatched reliability. Contact our experts today to find the perfect heating solution for your laboratory's specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What are the specific functions of graphite molds in the vacuum hot-press sintering process? Expert Insights for Ceramics
- What is the role of graphite molds during the hot pressing of LSLBO ceramics? Essential for High-Density Electrolytes
- What role do high-temperature pressure molds play in SiCp/Al fabrication? Enhancing Densification and Thermal Uniformity
- What role does a high-purity graphite mold play during hot pressing? Optimize Boron Carbide Sintering at 1850°C
- Why is precise temperature and pressure control necessary for combustible cartridge cases? Ensure Structural Integrity



















