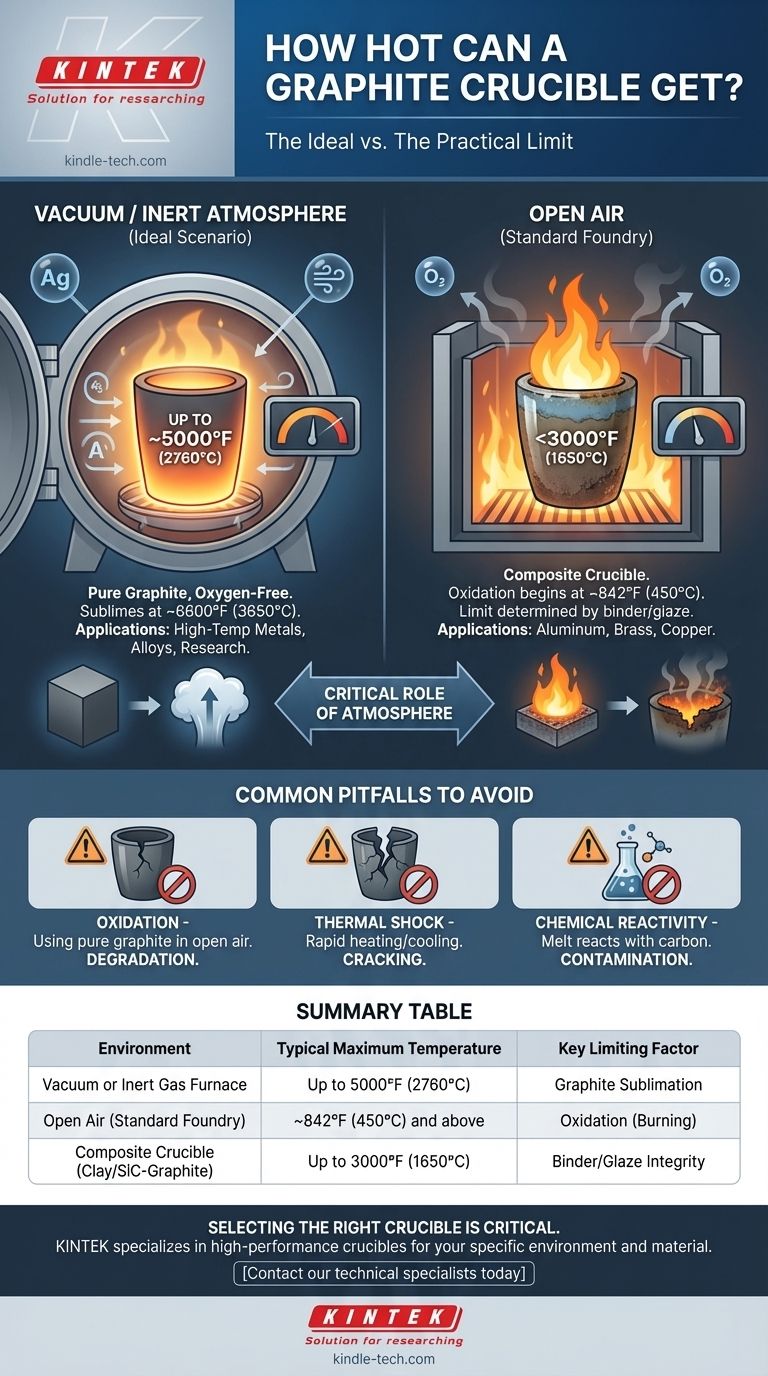
In the right conditions, a pure graphite crucible can withstand temperatures up to approximately 5000°F (about 2760°C). However, this number represents an ideal scenario. The actual, practical temperature limit is dictated almost entirely by the atmosphere in which it is heated.
The theoretical temperature limit of graphite is exceptionally high, but its practical use is a story of two different environments. In open air, oxidation will destroy the crucible at much lower temperatures, while in a vacuum or inert atmosphere, it can approach its true potential.

The Two Factors Defining a Crucible's Limit
The maximum temperature a "graphite crucible" can handle isn't a single number. It depends on the material's intrinsic properties and, more importantly, the environment you place it in.
The Intrinsic Limit of Graphite
Graphite does not melt at atmospheric pressure; instead, it sublimes (turns from a solid directly into a gas) at an extremely high temperature, around 6600°F (3650°C).
This is the absolute theoretical ceiling. The 5000°F (2760°C) figure often cited is a more practical upper working limit for pure graphite components in controlled, non-reactive environments.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere
The most significant constraint for graphite is oxidation.
When heated in the presence of oxygen (like in open air), graphite begins to react and burn away at temperatures as low as 842°F (450°C). This process rapidly accelerates as heat increases, destroying the crucible.
To reach the multi-thousand-degree temperatures graphite is known for, you must use it in an oxygen-free environment, such as a vacuum furnace or a furnace flooded with an inert gas like argon.
Understanding Practical Temperature Ranges
Your application and furnace type will determine the effective temperature range of your crucible.
For High-Temperature Furnaces (Inert/Vacuum)
This is where pure graphite shines. In a controlled, oxygen-free environment, pure graphite crucibles can reliably be used for processes reaching up to 2200°C (3992°F) or higher.
These applications include melting high-temperature metals, producing specialized alloys, and various scientific research processes.
For Standard Foundry Furnaces (Open Air)
For melting common metals like aluminum or copper in a typical foundry, you are likely not using a pure graphite crucible. You are using a composite crucible.
These are typically clay-graphite or silicon carbide-graphite crucibles. They contain graphite for its excellent thermal conductivity but are bound with other materials and covered in a protective glaze to resist oxidation in an open-air furnace.
The limit for these crucibles is determined by the binder and the glaze, not the graphite itself, and is typically well below 3000°F (1650°C).
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Understanding these limitations is key to preventing crucible failure and ensuring safety.
Ignoring Oxidation
The most common mistake is attempting to use a pure graphite crucible in an open-air furnace for high-temperature melts. It will quickly degrade and fail. Always match the crucible type to the furnace atmosphere.
Disregarding Thermal Shock
Graphite and composite crucibles can crack if heated or cooled too quickly. Always follow proper procedures for pre-heating your crucible before introducing a charge and allow for controlled cooling after a pour.
Overlooking Chemical Reactivity
While graphite is relatively inert, some molten materials can react with carbon. This can lead to contamination of your melt or degradation of your crucible over time. Always verify the compatibility of the crucible material with the metal you intend to melt.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct crucible is not about finding the highest temperature rating, but the right tool for your specific environment and material.
- If your primary focus is melting aluminum, brass, or copper in a standard foundry: You need a clay-graphite or silicon carbide-graphite crucible designed for use in an oxidizing atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature metallurgy or research above 1800°C: You need a pure graphite crucible and a vacuum or inert gas furnace to protect it from oxygen.
Ultimately, your operating atmosphere is the most important factor in determining the true temperature limit and lifespan of your crucible.
Summary Table:
| Environment | Typical Maximum Temperature | Key Limiting Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum or Inert Gas Furnace | Up to 5000°F (2760°C) | Graphite Sublimation |
| Open Air (Standard Foundry) | ~842°F (450°C) and above | Oxidation (Burning) |
| Composite Crucible (Clay/SiC-Graphite) | Up to 3000°F (1650°C) | Binder/Glaze Integrity |
Selecting the right crucible is critical for safety and performance. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including a full range of graphite and composite crucibles designed for specific furnace atmospheres and materials. Our experts can help you choose the perfect crucible to maximize temperature capability and lifespan in your unique application.
Contact our technical specialists today to discuss your requirements and ensure optimal results for your melting or research process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Electron Beam Evaporation
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the technical advantages of utilizing corundum-mullite-zirconia crucibles? Ensure Purity for Fe-Cr-Ni Alloys
- What are the technical advantages of using silica glass reaction tubes and crucibles in high-temperature chlorination?
- Why are alumina crucibles used for Al-LLZ sintering? The Secret to Stable Cubic Phase Lithium Garnet
- Which crucible is used for burn sample at high temperature? A Guide to Porcelain, Alumina & More
- Why are high-purity alumina ceramic crucibles used for hot-dip aluminum coatings? Ensure Purity and Thermal Stability
- Why is the design of laboratory-grade ceramic crucibles critical when determining the volatile matter content of flax straw?
- Why are transparent quartz crucibles utilized as containers for MAX phase precursors? Ensuring Visual Control & Purity
- Why are corundum crucibles preferred for magnesium evaporation? Ensure Purity in High-Temperature Reduction



















