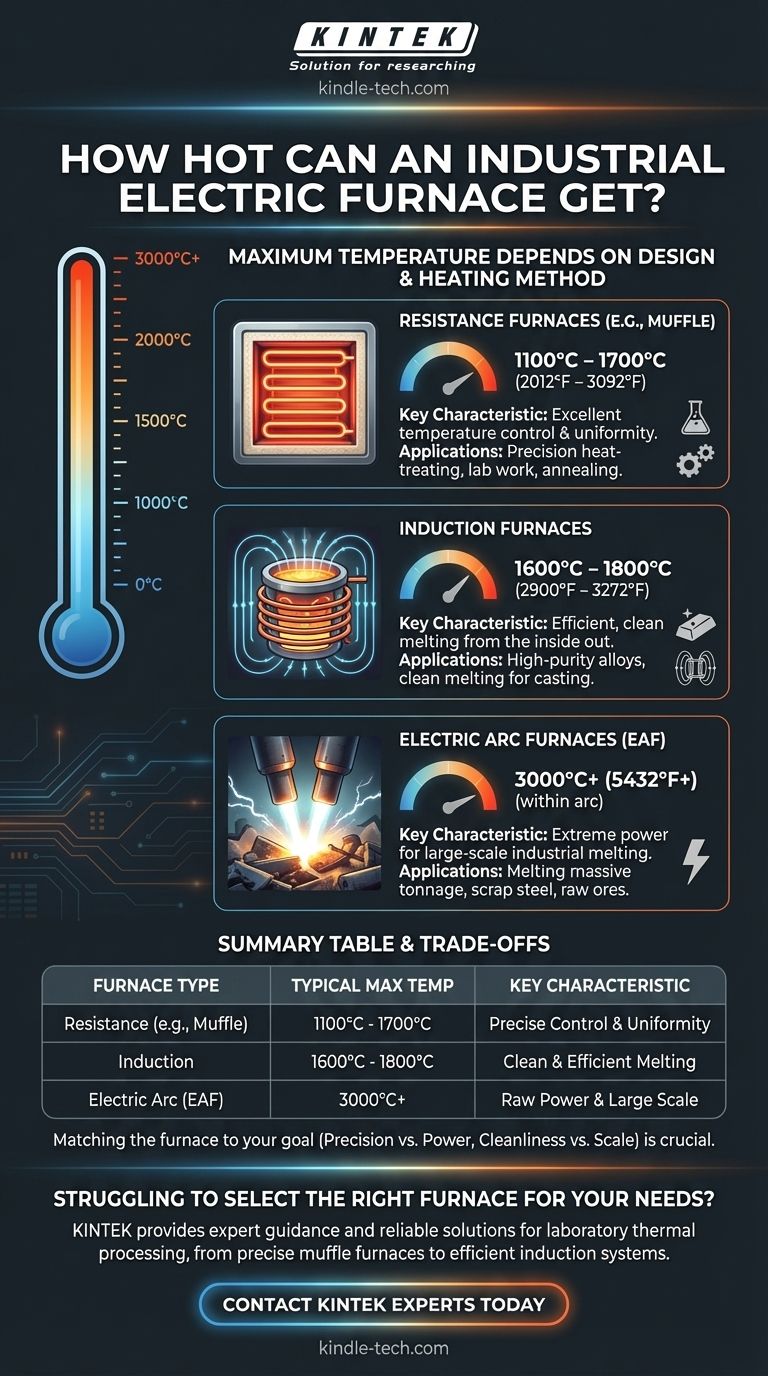
The maximum temperature of an industrial electric furnace depends entirely on its design and heating method. While common models operate between 1100°C and 1800°C, a specialized electric arc furnace can generate temperatures in excess of 3000°C (5432°F) within the arc itself, making it one of the hottest pieces of industrial equipment.
The term "electric furnace" is not a monolith. The technology used—be it resistance, induction, or electric arc—is the primary factor that dictates its maximum temperature, with each type being engineered for vastly different industrial applications.

Why Furnace Type Dictates Temperature
The method used to generate heat is the fundamental difference between electric furnace technologies. This distinction is critical because it determines not only the peak temperature but also the furnace's efficiency, precision, and suitability for a given task.
Resistance Furnaces (e.g., Muffle Furnace)
A resistance furnace works much like a common toaster, passing electricity through high-resistance heating elements. These elements glow hot and radiate heat into an insulated chamber.
This design offers excellent temperature uniformity and control.
Based on their construction and heating elements, muffle furnaces and other resistance types typically reach maximum temperatures between 1100°C and 1700°C (2012°F to 3092°F).
Induction Furnaces
Induction furnaces use powerful, alternating magnetic fields to induce an electric current directly within the metallic material (the "charge") to be heated.
This process is incredibly efficient as the material heats itself from the inside out, minimizing heat loss.
Depending on the power and design, induction furnaces can reliably achieve temperatures of 1600°C to 1800°C (2900°F to 3272°F), and sometimes more.
Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF)
The electric arc furnace represents the pinnacle of raw heating power. It uses massive graphite electrodes to pass an enormous current through the material, creating a sustained electric arc.
This arc is a plasma discharge with immense energy density.
The temperature within the arc itself can exceed 3000°C (5432°F), allowing it to melt massive quantities of scrap steel and other raw materials in a relatively short time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace is not simply about finding the highest temperature. Each technology comes with a distinct set of operational advantages and disadvantages that make it suitable for specific purposes.
Precision vs. Raw Power
Resistance furnaces, like the muffle furnace, offer the most precise temperature control and uniformity. This makes them ideal for sensitive applications like laboratory analysis, annealing, and intricate heat-treating.
Electric arc furnaces, in contrast, are instruments of brute force. Their primary goal is melting massive tonnage, where raw power is far more important than pinpoint thermal accuracy.
Application and Material Purity
Induction furnaces are prized for their clean melting process. Since the heat is generated within the metal itself without any external flame or arc, contamination is minimized, making them perfect for producing high-purity alloys.
Muffle furnaces can also provide a highly controlled atmosphere, protecting the material inside from oxidation. The EAF process is inherently less "clean" and is designed for refining raw materials, not producing delicate alloys.
Scale and Cost
Electric arc furnaces are massive, capital-intensive installations used in steel mills and foundries. Their operational scale is enormous.
Induction and resistance furnaces are available in a much wider range of sizes, from small tabletop lab units to large industrial systems, making them far more accessible for a variety of manufacturing and research needs.
Matching the Furnace to Your Goal
To select the right technology, you must first define your primary objective. The process dictates the tool.
- If your primary focus is precision heat-treating, lab work, or drying: A resistance muffle furnace provides the temperature stability and control you require.
- If your primary focus is clean and efficient melting of metals for casting or alloy production: An induction furnace offers the best combination of speed, efficiency, and purity.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial melting of scrap steel or other raw ores: The unparalleled power of an electric arc furnace is the correct solution.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental heating mechanism is the key to selecting the furnace that will best serve your specific thermal processing needs.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical Max Temperature | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance (e.g., Muffle) | 1100°C - 1700°C | Excellent temperature control & uniformity |
| Induction | 1600°C - 1800°C | Efficient, clean melting from the inside out |
| Electric Arc (EAF) | 3000°C+ | Extreme power for large-scale industrial melting |
Struggling to select the right furnace for your application's temperature and precision needs? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert guidance and reliable solutions for all your laboratory thermal processing challenges. Whether you need the precise control of a muffle furnace or the efficiency of an induction system, we can help you achieve optimal results. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis



















