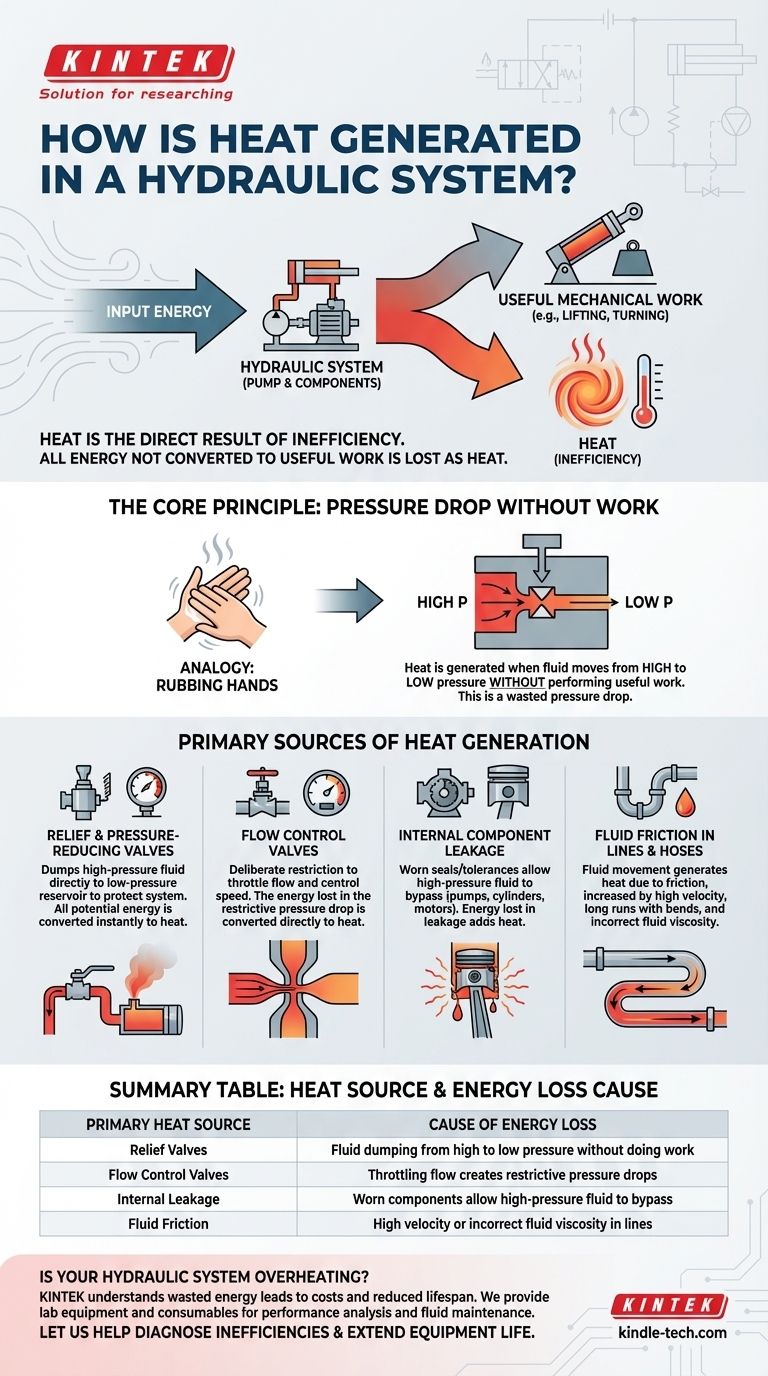
In any hydraulic system, heat is the direct result of inefficiency. All energy that is put into the system but not converted into useful mechanical work (like lifting a load or turning a motor) is lost as thermal energy, or heat. This conversion primarily happens due to pressure drops across system components and friction within the fluid and mechanics.
The core principle to understand is that heat is generated whenever hydraulic fluid moves from a high-pressure zone to a low-pressure zone without performing useful work. Managing system heat is fundamentally about managing these energy-wasting pressure drops.
The Core Principle: Pressure Drops Without Work
Every hydraulic system operates by putting fluid under pressure. This pressure represents stored potential energy. When that potential energy is released without moving an actuator, it dissipates directly into the fluid as heat.
The Physics of Heat Generation
The amount of power lost to heat is a direct function of the pressure drop and the flow rate across that drop. A small flow over a large pressure drop or a large flow over a small pressure drop can both generate significant heat. This lost energy must go somewhere, and it heats the fluid, components, and reservoir.
An Intuitive Analogy
Think of rubbing your hands together to create warmth. The pressure you apply and the speed of the motion dictate how quickly they warm up. In hydraulics, fluid friction and restrictions act similarly, converting the energy from the pump into thermal energy instead of productive work.
Primary Sources of Heat Generation
While every component contributes some inefficiency, a few key areas are responsible for the vast majority of heat generation in a typical system.
Relief and Pressure-Reducing Valves
These are often the single largest source of heat. A pressure relief valve dumps high-pressure fluid directly to the low-pressure reservoir to protect the system from over-pressurization. When fluid flows across it, all the potential energy is converted instantly to heat. A system where the pump constantly flows over the relief valve is essentially a very expensive heater.
Flow Control Valves
Any valve that throttles flow, such as a needle valve or a non-compensated flow control, creates a deliberate restriction. This restriction causes a pressure drop to control the speed of an actuator. The energy lost in this pressure drop is converted directly to heat.
Internal Component Leakage
As components wear, their internal tolerances loosen. This allows high-pressure fluid to leak past seals and internal clearances back to a low-pressure area.
- Pumps: Internal leakage (or "slippage") reduces pump efficiency, with the lost energy adding heat to the fluid.
- Cylinders and Motors: Fluid leaking past piston seals or motor gears means the pump must work harder to maintain pressure and flow, with the leaked energy becoming heat.
Fluid Friction in Lines and Hoses
The fluid itself generates heat as it moves. This friction is increased by:
- High velocity from undersized lines.
- Long plumbing runs with many sharp bends or fittings.
- Using a fluid with a viscosity that is too high for the operating temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs
It is impossible to create a hydraulic system that generates zero heat. Efficiency comes with costs and design compromises that must be balanced.
Inefficiency by Design
Some heat-generating components are essential for function and safety. A pressure relief valve is a non-negotiable safety device. A flow control valve may be necessary for precise operational control. The goal is not to eliminate them, but to design a circuit where they are used only when necessary, not continuously.
Open-Center vs. Closed-Center Systems
An open-center system is simple and inexpensive but generates significant heat because the full pump flow is constantly circulating, even at idle, creating pressure drops across the valves. A closed-center, pressure-compensated system is more efficient and generates less heat, as the pump only produces the required flow and pressure on demand, but it is more complex and costly.
The Cost of Efficiency
Using larger diameter hoses to reduce fluid velocity, choosing high-efficiency piston pumps over gear pumps, and implementing load-sensing systems all reduce heat generation. However, these choices increase the initial cost and complexity of the system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Based on these principles, you can approach heat issues methodically by identifying the source of the wasted energy.
- If your primary focus is designing a new, efficient system: Prioritize right-sizing your pump and lines, and consider using a load-sensing or pressure-compensated design to minimize wasted flow.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting an overheating system: Use an infrared thermometer to find the hottest component. This is often a relief valve that is set too low or a valve causing a constant pressure drop.
- If your primary focus is maintenance and longevity: Ensure you are using the correct fluid viscosity for your climate, keep your heat exchangers clean, and listen for the tell-tale signs of aeration or cavitation.
Ultimately, understanding heat generation is understanding the energy efficiency of your entire hydraulic circuit.
Summary Table:
| Primary Heat Source | Cause of Energy Loss |
|---|---|
| Relief Valves | Fluid dumping from high to low pressure without doing work |
| Flow Control Valves | Throttling flow creates restrictive pressure drops |
| Internal Leakage | Worn components allow high-pressure fluid to bypass |
| Fluid Friction | High velocity or incorrect fluid viscosity in lines |
Is your hydraulic system running inefficiently or overheating? The experts at KINTEK understand that wasted energy as heat leads to increased operating costs and reduced equipment lifespan. We specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables necessary for analyzing system performance and maintaining optimal fluid conditions. Let our team help you diagnose inefficiencies and extend the life of your critical systems. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation tailored to your laboratory's hydraulic needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 100L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Circulator for Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath Water Bath Cooling
- 100L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 80L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Circulator for Water Bath Cooling and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- 20L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 10L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
People Also Ask
- Why is it necessary to equip corn cob hydrolysis systems with rapid cooling? Maximize Glucose and Xylose Yield
- What is the importance of a Recirculating Cooling Water System? Protect Your Lab and Master Reaction Control
- Why is a cooling circulation system necessary during the plasma-assisted synthesis of silver nanoparticles?
- What is the purpose of using a cooling water system after wheat straw pretreatment? Optimize Sugar Yield and Safety
- Why is a high-performance cooling circulator necessary in silica membrane desalination? Boost Your Permeate Mass Transfer



















