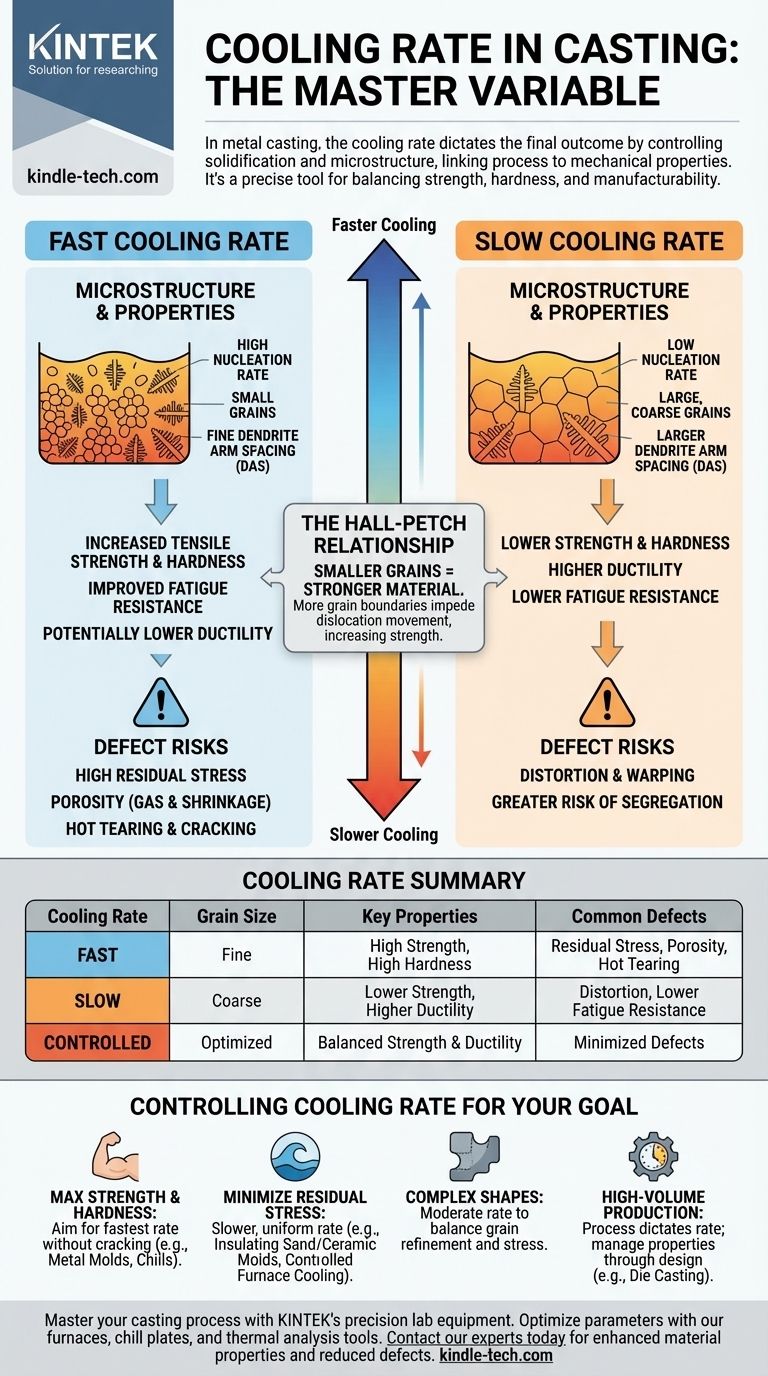
In metal casting, the cooling rate is the master variable that dictates the final outcome of the part. It directly controls the solidification process at a microscopic level, which in turn determines the resulting grain structure of the metal. This microstructure is the fundamental link between the casting process and the final mechanical properties of the component, such as its strength, hardness, and ductility.
The cooling rate is not simply "fast" or "slow," but a precise tool for process control. While faster cooling generally yields a stronger, finer-grained casting, it also increases the risk of defects like thermal shock and porosity. The goal is to find the optimal rate that balances desired properties with manufacturability.

The Fundamental Link: Cooling Rate and Microstructure
To understand the effects of cooling rate, you must first understand how metal solidifies. The final properties of a cast part are born in the moments it transitions from a liquid to a solid.
Solidification and Grain Formation
When molten metal cools, solidification begins at many points simultaneously, a process called nucleation. From these points, crystals called grains begin to grow.
A fast cooling rate promotes a high rate of nucleation, creating many small grains before any have a chance to grow large. A slow cooling rate results in fewer nucleation sites, giving each grain more time to grow, leading to a large, coarse-grained structure.
The Hall-Petch Relationship
This principle is central to metallurgy: smaller grains result in a stronger material. The boundaries between grains act as barriers that impede the internal slipping (dislocation movement) that occurs when a metal deforms.
More grains mean more grain boundaries, creating more obstacles and thus increasing the material's strength and hardness. This is why a rapidly cooled, fine-grained casting is almost always stronger than a slowly cooled, coarse-grained one of the same alloy.
Dendrite Arm Spacing (DAS)
During solidification, crystals often grow in a tree-like pattern called dendrites. The distance between the "arms" of these dendrites is the Dendrite Arm Spacing (DAS).
Faster cooling leads to a much finer DAS. A fine dendritic structure is highly desirable as it improves mechanical properties and reduces the likelihood of microporosity being trapped between the arms.
How Cooling Rate Dictates Mechanical Properties
The microscopic changes in grain size and structure directly translate into the macroscopic engineering properties we rely on.
Strength and Hardness
As explained by the Hall-Petch relationship, a faster cooling rate produces smaller grains, which directly increases tensile strength and hardness.
This is one of the most significant and predictable effects of accelerating the cooling process.
Ductility and Toughness
Ductility, the ability to deform without fracturing, often has an inverse relationship with strength. Therefore, a very strong, rapidly cooled casting may be more brittle.
However, the fine-grained structure from faster cooling can sometimes improve fracture toughness, as the many grain boundaries can help arrest the propagation of a crack. The outcome depends heavily on the specific alloy.
Fatigue Resistance
Fatigue failure is often initiated by microscopic defects. A faster, well-controlled cooling rate can lead to a finer microstructure and reduce the size of pores or inclusions.
This cleaner, finer structure significantly improves the material's resistance to fatigue, making it last longer under cyclic loading.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Defects
Pushing for the fastest possible cooling rate is not a universal solution. It introduces significant risks that must be managed to produce a successful casting.
The Risk of High Residual Stress
When a casting cools, it contracts. If the cooling is non-uniform—with the outside solidifying and shrinking much faster than the molten interior—immense internal stresses can build up.
These residual stresses can cause the part to warp after machining or, in severe cases, to crack spontaneously days or weeks after casting.
Porosity and Gas Entrapment
Molten metal can hold more dissolved gas than solid metal. If the solidification front moves too quickly, dissolved gases have no time to escape and become trapped, forming gas porosity.
Similarly, rapid cooling can isolate pockets of liquid metal, preventing them from being fed by risers as they shrink. This creates voids known as shrinkage porosity.
Hot Tearing and Cracking
During the final stages of solidification, the casting is a mushy, semi-solid structure with very low strength. If thermal stresses from rapid cooling are too high during this vulnerable phase, the casting can literally be torn apart. This defect is known as hot tearing.
How to Control Cooling Rate for Your Goal
Controlling the cooling rate is an active process that involves manipulating the mold, the casting design, and post-casting treatments. The ideal rate is always a function of your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and hardness: Aim for the fastest cooling rate your alloy and geometry can tolerate without cracking, often using metal molds (die casting) or strategically placed copper "chills."
- If your primary focus is minimizing residual stress and distortion: A slower, more uniform cooling rate is necessary, typically achieved with insulating sand molds, ceramic molds, or controlled furnace cooling cycles.
- If your primary focus is producing complex shapes prone to hot tearing: A moderate cooling rate is optimal to balance grain refinement with stress reduction, carefully managing section thicknesses and mold design.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production: The choice is often dictated by the process (e.g., die casting is inherently fast), and the goal is to design the part and process to manage the resulting properties and stresses.
Ultimately, mastering the cooling rate transforms casting from a simple forming process into a precise act of material engineering.
Summary Table:
| Cooling Rate | Grain Size | Key Properties | Common Defects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fast | Fine | High Strength, High Hardness | Residual Stress, Porosity, Hot Tearing |
| Slow | Coarse | Lower Strength, Higher Ductility | Distortion, Lower Fatigue Resistance |
| Controlled | Optimized | Balanced Strength & Ductility | Minimized Defects |
Master your casting process with KINTEK's precision lab equipment. Whether you're developing new alloys or optimizing production parameters, our furnaces, chill plates, and thermal analysis tools provide the exact control you need to achieve the perfect cooling rate for your application. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you enhance material properties and reduce defects in your castings.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 100L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Circulator for Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath Water Bath Cooling
- 80L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Circulator for Water Bath Cooling and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- 100L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 5L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 50L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-precision chiller core in natural gas hydrate synthesis? Master Thermal Stability for Lab Success
- Why is it necessary to equip corn cob hydrolysis systems with rapid cooling? Maximize Glucose and Xylose Yield
- Why is a high-performance cooling circulator necessary in silica membrane desalination? Boost Your Permeate Mass Transfer
- Why is a cooling circulation system or chiller necessary for SFE? Prevent Gas Locking and Ensure High-Pressure Flow
- What is the importance of a Recirculating Cooling Water System? Protect Your Lab and Master Reaction Control



















