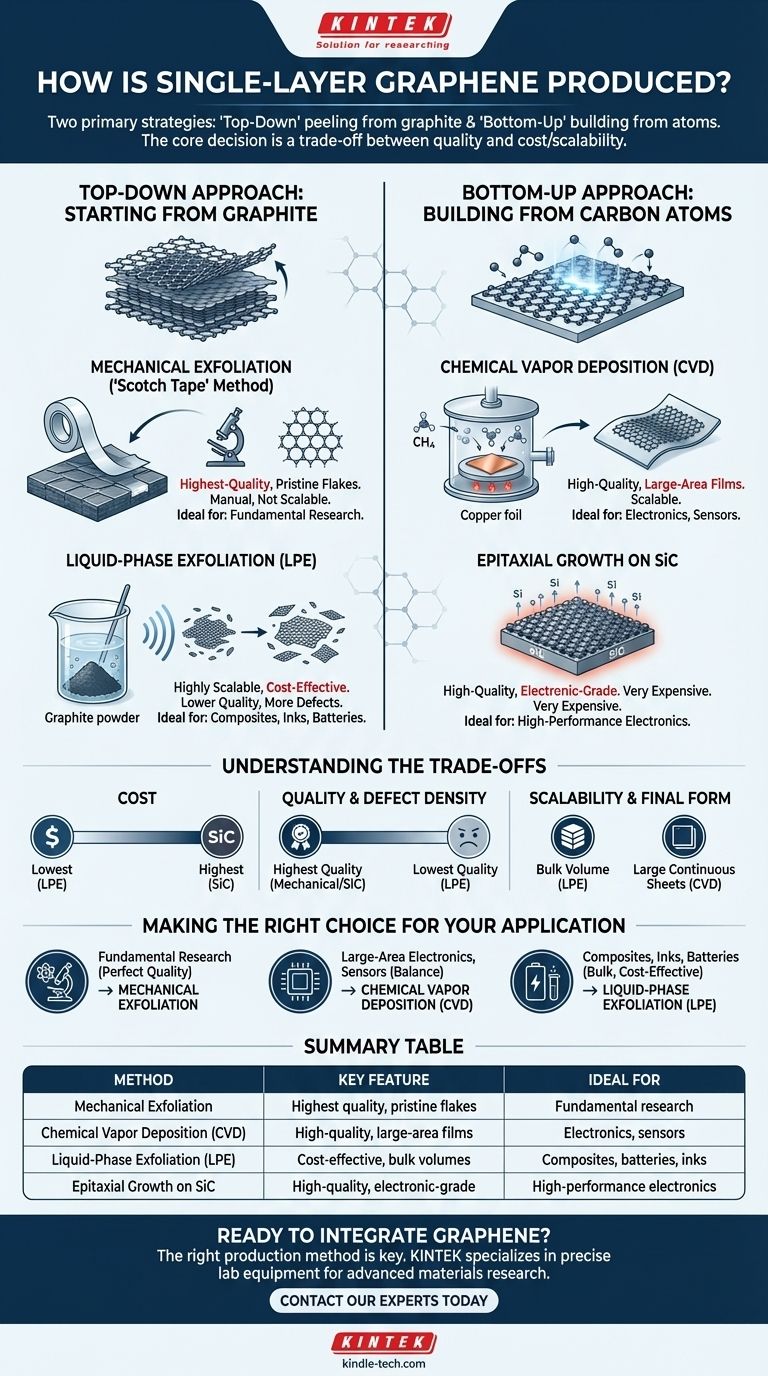
To produce single-layer graphene, manufacturers use two primary strategies: a "top-down" approach that peels layers from graphite, and a "bottom-up" approach that builds the atomic layer from carbon-containing gases. The most prominent methods are mechanical exfoliation for research, liquid-phase exfoliation for bulk composites, and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) for large-area electronics, which is considered the most promising technique for industrial scale.
The method used to produce graphene is not a question of "best" but one of "best for a purpose." The core decision is a trade-off between the final product's quality and crystal perfection versus the cost and scalability of the manufacturing process.

The "Top-Down" Approach: Starting from Graphite
This strategy involves separating the individual layers of graphene from a larger piece of graphite, much like peeling away the pages of a book. It is mechanically intensive but conceptually straightforward.
Mechanical Exfoliation (The "Scotch Tape" Method)
This is the original, Nobel Prize-winning method. It involves using adhesive tape to peel progressively thinner flakes from a piece of highly-ordered graphite until a single atomic layer is isolated.
This technique yields the highest-quality, most pristine graphene flakes known. However, the process is manual, produces extremely small flakes (micrometers in size), and is not scalable for any form of mass production. It remains the gold standard for fundamental scientific research.
Liquid-Phase Exfoliation (LPE)
In LPE, bulk graphite powder is mixed into a liquid solvent and subjected to high-energy processes, like sonication, which use sound waves to break the graphite apart into flakes.
This method is highly scalable and cost-effective for producing large volumes of graphene "ink" or dispersions. The resulting material is ideal for use in composites, conductive coatings, and batteries, but the individual flakes are small and have more defects, resulting in lower electrical performance compared to other methods.
The "Bottom-Up" Approach: Building from Carbon Atoms
This strategy constructs the graphene sheet atom by atom on a substrate surface. It offers greater control over the final product's area and is the focus of commercialization for electronics.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is the leading method for producing high-quality, large-area graphene films. The process involves heating a metal catalyst, typically a copper (Cu) foil, to high temperatures (around 1000°C) inside a vacuum chamber.
A carbon-containing gas, such as methane (CH4), is then introduced. The high heat causes the gas molecules to decompose, and the carbon atoms deposit onto the surface of the copper foil, self-assembling into a continuous, single layer of graphene. The graphene can then be transferred to a target substrate like silicon or flexible plastic.
Epitaxial Growth on Silicon Carbide (SiC)
This method involves heating a wafer of silicon carbide to very high temperatures (over 1300°C) in a vacuum. The heat causes the silicon atoms on the surface to sublimate (turn directly into a gas), leaving behind the carbon atoms.
These remaining carbon atoms then rearrange themselves to form a high-quality graphene layer directly on the SiC wafer. While this produces exceptionally high-quality electronic-grade graphene, the high cost and temperature requirements of the SiC wafers make it a very expensive process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a production method requires a clear understanding of the compromises between cost, quality, and scale.
Cost
Liquid-Phase Exfoliation is by far the cheapest method for bulk production. CVD has moderate equipment costs but can be scaled effectively. Epitaxial growth on SiC is the most expensive due to the cost of the substrate wafers.
Quality and Defect Density
Mechanical exfoliation and SiC growth produce the highest-quality graphene with the fewest atomic defects, making them ideal for high-performance electronics and research. CVD graphene is also high-quality but is typically polycrystalline (made of many smaller crystal domains stitched together), which can slightly limit its ultimate electronic performance. LPE produces the lowest-quality flakes with the most defects.
Scalability and Final Form
CVD is the champion of scalability for large, continuous sheets, with roll-to-roll production of meter-scale films demonstrated. LPE is the champion of scalability for bulk volume, producing kilograms of graphene dispersion. Mechanical exfoliation is fundamentally unscalable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your goal dictates the correct production method.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research requiring perfect crystal quality: Mechanical exfoliation is the undisputed standard for creating individual, pristine test devices.
- If your primary focus is large-area electronics, sensors, or transparent conductors: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) offers the best balance of high quality and industrial scalability.
- If your primary focus is creating composites, conductive inks, or battery additives: Liquid-Phase Exfoliation (LPE) provides the most cost-effective path to producing large quantities of graphene material in bulk.
Ultimately, the production of graphene is a solved problem; the challenge now lies in matching the right type of graphene to the right application.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Feature | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Exfoliation | Highest quality, pristine flakes | Fundamental research |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | High-quality, large-area films | Electronics, sensors |
| Liquid-Phase Exfoliation (LPE) | Cost-effective, bulk volumes | Composites, batteries, inks |
| Epitaxial Growth on SiC | High-quality, electronic-grade | High-performance electronics |
Ready to integrate graphene into your laboratory workflow? The right production method is key to your success. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for advanced materials research and development. Whether you are exploring fundamental properties or scaling up for industrial applications, our expertise can help you achieve your goals. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty



















