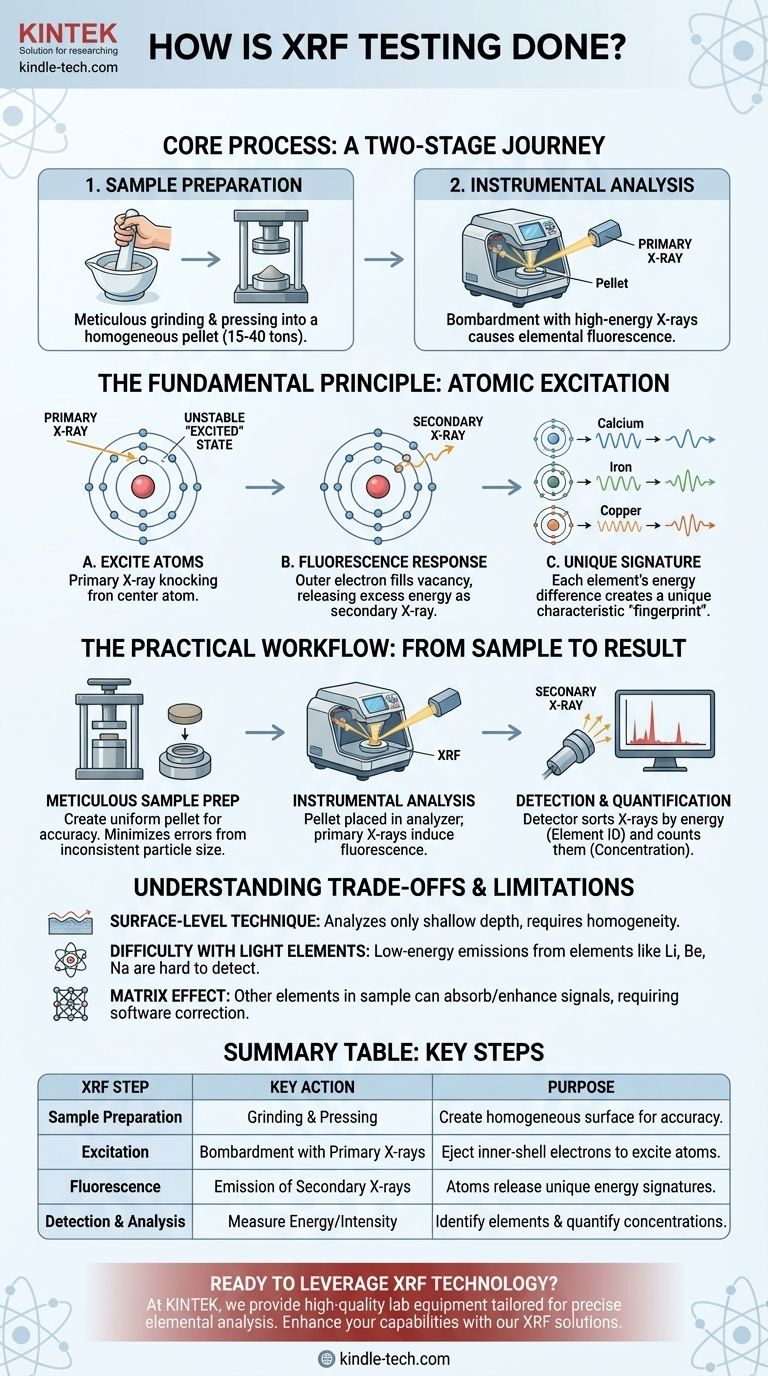
At its core, X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) testing is a two-stage process. First, a material sample is carefully prepared—often by grinding it into a fine powder and pressing it into a solid pellet. Second, an analyzer bombards this sample with high-energy X-rays, causing the elements within to "fluoresce" and emit their own unique, secondary X-rays that are then detected and measured to determine the material's elemental composition.
The fundamental principle of XRF is that every element emits a characteristic X-ray signature when excited. By precisely measuring these unique energy "fingerprints," an analyzer can rapidly identify which elements are present in a sample and in what concentrations.
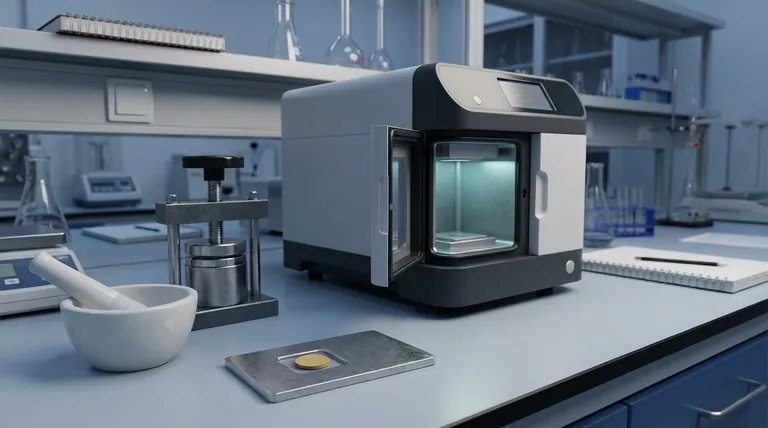

The Fundamental Principle: Atomic Excitation
XRF is a non-destructive analytical technique that leverages the physics of atoms. The process does not rely on chemical reactions but on energy transfers within the atomic structure of each element.
How Primary X-rays Excite Atoms
An XRF analyzer generates a beam of high-energy X-rays, often called primary X-rays. This beam is directed at the surface of the prepared sample.
When a primary X-ray strikes an atom in the sample with sufficient force, it can knock an electron out of one of its inner orbital shells (e.g., the K or L shell). This event leaves the atom in an unstable, "excited" state.
The "Fluorescence" Response
An atom cannot remain in this unstable state. To regain stability, an electron from a higher-energy outer shell immediately drops down to fill the vacancy left by the ejected electron.
As this electron moves to a lower energy level, it must release the excess energy. It does so by emitting a secondary X-ray, a process known as fluorescence.
Why Each Element Has a Unique Signature
The energy of this emitted secondary X-ray is the critical piece of the puzzle. The energy difference between the inner and outer electron shells is unique and precisely defined for every single element.
This means a calcium atom will always emit secondary X-rays with a different, specific energy than an iron or copper atom. This unique energy is the element's signature, allowing the analyzer to identify it with certainty.
The Practical Workflow: From Sample to Result
While the underlying physics is complex, the operational workflow is a systematic process designed to ensure accuracy and repeatability.
Step 1: Meticulous Sample Preparation
For many lab-based XRF analyses, the goal is to create a perfectly homogeneous sample with a flat, uniform surface. This minimizes analytical errors caused by inconsistent particle size or density.
The sample is often milled into a fine powder, mixed with a binding agent, and placed into a pellet die. A press then applies immense pressure—anywhere from 15 to 40 tons—to create a dense, solid pellet ready for analysis.
Step 2: Instrumental Analysis
The prepared pellet is placed inside the XRF spectrometer. The instrument bombards the sample with its primary X-ray beam.
The atoms in the sample fluoresce, emitting their characteristic secondary X-rays back toward the instrument's detector.
Step 3: Detection and Quantification
An X-ray detector inside the analyzer captures these incoming secondary X-rays. It sorts them by their specific energy levels and counts the number of X-rays detected at each level.
The analyzer's software then correlates the energy level to a specific element and the intensity (the number of X-rays counted) to that element's concentration. The final output is typically a report listing the elements and their relative amounts.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Like any analytical technique, XRF has specific characteristics that make it ideal for some applications and less suitable for others.
It's a Surface-Level Technique
The primary X-rays only penetrate a very shallow depth into the sample. Therefore, the results reflect the composition of the surface, not necessarily the bulk material. This is why proper sample preparation to ensure homogeneity is so critical for accurate bulk analysis.
Difficulty with Light Elements
XRF struggles to reliably detect very light elements (e.g., lithium, beryllium, sodium). The secondary X-rays emitted by these elements are very low-energy and are often absorbed by the air or the detector window before they can be measured.
The "Matrix Effect"
The X-rays emitted by one element can be absorbed or enhanced by other elements present in the sample matrix. This "matrix effect" can skew concentration results and requires sophisticated mathematical corrections within the analyzer's software to ensure accuracy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding how XRF works is key to deciding if it's the correct tool for your analytical needs.
- If your primary focus is rapid quality control or alloy identification: XRF is an exceptional choice due to its high speed and non-destructive nature.
- If your primary focus is precise compositional analysis of minerals, cements, or metals: The rigorous sample preparation of lab-based XRF provides highly accurate and repeatable results.
- If your primary focus is detecting trace elements or very light elements: You may need to consider alternative techniques like Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) spectroscopy.
By understanding the journey from raw sample to final result, you can effectively leverage the power of XRF for elemental analysis.
Summary Table:
| XRF Testing Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Preparation | Grinding & Pressing into a Pellet | Create a homogeneous, flat surface for accurate analysis |
| Excitation | Bombardment with Primary X-rays | Eject inner-shell electrons to create excited atoms |
| Fluorescence | Emission of Secondary X-rays | Atoms release unique energy signatures as they stabilize |
| Detection & Analysis | Measure Energy/Intensity of X-rays | Identify elements and quantify their concentrations |
Ready to leverage XRF technology for your laboratory?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored for precise elemental analysis. Whether you're conducting quality control, alloy identification, or compositional analysis, our XRF solutions offer the accuracy and reliability you need.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our expertise can enhance your analytical capabilities. Get in touch via our contact form to speak with one of our specialists!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable XRD Sample Holders for Diverse Research Applications
- XRF Boric Acid Lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for Laboratory Use
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- How can corrosion of the sample holder be prevented when using corrosive chemicals? Protect Your Lab's Integrity
- What is the minimum sample required for XRD analysis? Optimize Your Material Analysis
- How should a sample holder be handled to ensure its longevity? Protect Your Lab Investment and Data Integrity
- What are the factors that affect melting and boiling point? Unlock the Science of Phase Transitions
- Does higher heat capacity mean higher melting point? Unraveling the Critical Difference













