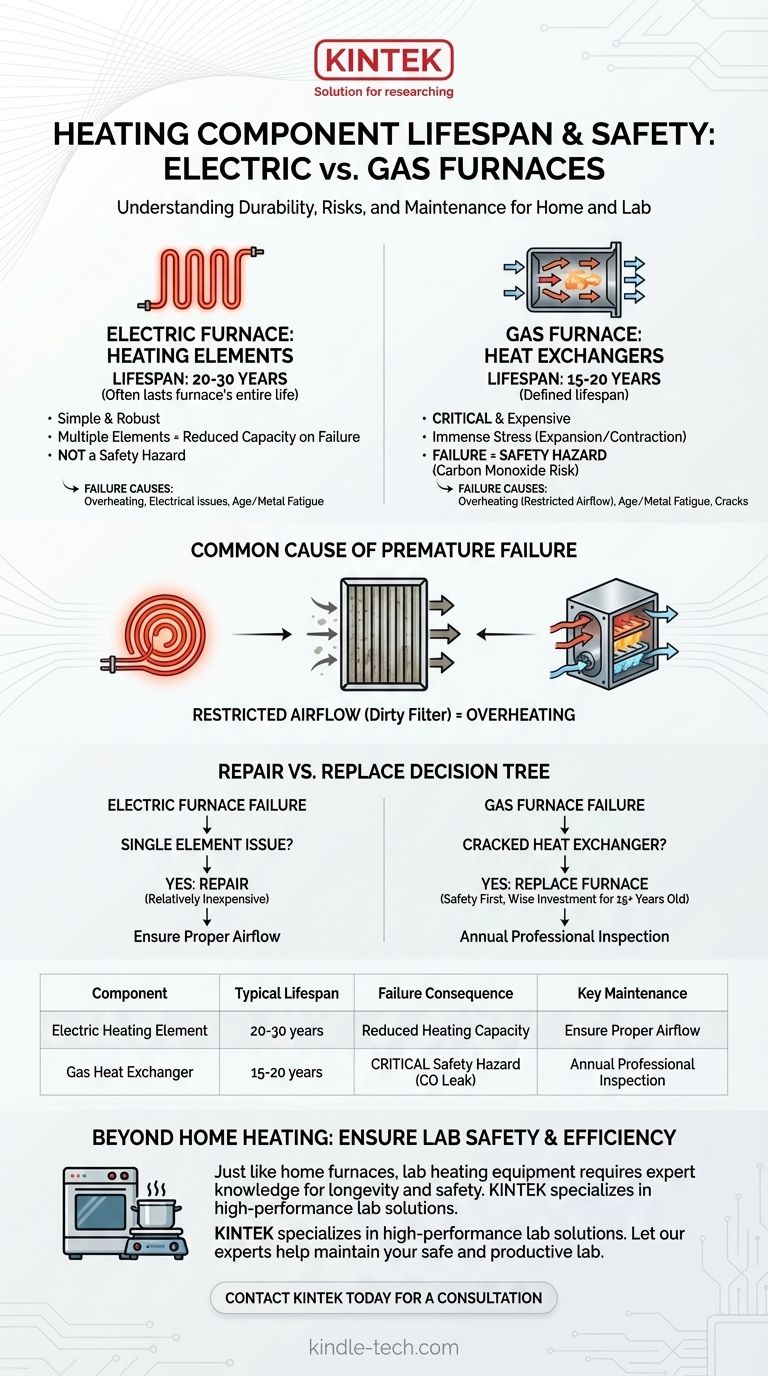
In an electric furnace, a heating element, also known as a heating coil, can often last for the entire 20 to 30-year lifespan of the unit itself. However, it's crucial to understand that this component is fundamentally different from the core heating part of a gas furnace—the heat exchanger—which has a more defined lifespan of 15 to 20 years and carries significant safety implications if it fails.
The question of how long a heating component lasts is less about a fixed number of years and more about the type of furnace you own. For electric furnaces, failure is a maintenance issue; for gas furnaces, failure of the heat exchanger is a critical safety and replacement event.
The Critical Distinction: Electric Elements vs. Gas Heat Exchangers
Your question touches on a common point of confusion. The term "heating element" almost always refers to the component in an electric furnace, while a gas furnace uses a completely different technology to generate heat.
Electric Furnace Heating Elements
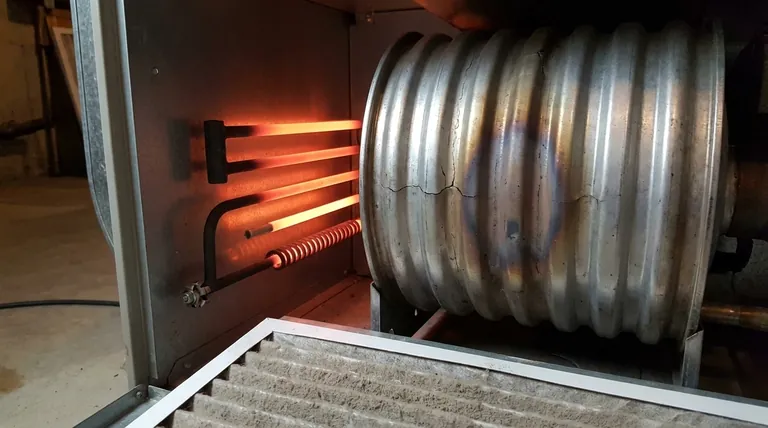
An electric furnace works much like a giant toaster. It uses multiple heating elements—coils made of a resistant metal alloy like nichrome—that glow red hot when electricity passes through them. A blower motor then pushes air over these red-hot coils to heat your home.
These elements are relatively simple, robust, and designed for longevity. Because there are several of them in a single furnace, the failure of one element often results in reduced heating capacity, not a total shutdown.
Gas Furnace Heat Exchangers
A gas furnace generates heat through combustion inside a sealed metal chamber called a heat exchanger. As the gas burns, the hot exhaust gases pass through the inside of this chamber, heating its metal walls. Your home's air is then blown across the outside of the chamber, absorbing the heat without ever touching the toxic combustion fumes.
The heat exchanger is the single most critical and expensive component in a gas furnace. Its lifespan of 15-20 years is dictated by the immense stress of constant expansion and contraction, which can eventually cause cracks.
What Causes a Heating Component to Fail?
While these components are built to last, certain conditions will drastically shorten their lifespan. The primary cause of premature failure is almost always overheating.
Restricted Airflow
This is the number one killer of both electric heating elements and gas heat exchangers. A dirty, clogged air filter reduces the amount of air moving across the hot components. With less air to absorb the heat, the components get far hotter than they were designed for, leading to metal fatigue, cracks, and burnout.
Electrical Issues (Electric Furnaces)
For electric furnaces, external factors like power surges can damage the heating coils. Internal issues like loose wiring or a failing sequencer (the part that controls when elements turn on) can also cause an element to overheat and fail.
Age and Metal Fatigue
Over thousands of cycles of heating up and cooling down, the metal in both electric elements and gas heat exchangers becomes brittle. Eventually, it can simply crack and fail from cumulative stress. This is the natural end-of-life for the component.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Repair vs. Replace
When a heating component fails, the correct response depends entirely on the type of furnace and the age of the system.
The Case for Repair: Electric Furnaces
Replacing a single heating element in an electric furnace is a common and relatively inexpensive repair. Because the elements are modular, a technician can simply swap out the failed coil. If your electric furnace is otherwise in good shape, repairing a single element is almost always the right financial choice.
The Case for Replacement: Gas Furnaces
A cracked heat exchanger is a serious safety hazard. It can allow deadly carbon monoxide gas to leak into your home's air supply. For this reason, repair is almost never an option. The choice is between replacing the heat exchanger or replacing the entire furnace.
Given that a heat exchanger replacement is a very expensive, labor-intensive job, it rarely makes sense to put that much money into an older furnace (15+ years). In most cases, a failed heat exchanger means it is time for a new furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your System
Your maintenance strategy and repair decisions should be tailored to the technology heating your home.
- If you have an electric furnace: Your primary focus is airflow. Regularly changing your air filter is the single most effective action to prevent premature element failure.
- If you have a gas furnace: Your primary focus is safety. Prioritize annual professional inspections to check the heat exchanger for cracks, ensuring both system longevity and your family's safety.
- If you are facing a failure: Evaluate the component and system age. A failed electric element is a straightforward repair, but a cracked heat exchanger in a furnace over 15 years old signals that replacement is the wisest investment.
Ultimately, proactive maintenance is the key to a reliable and long-lasting heating system.
Summary Table:
| Component | Typical Lifespan | Failure Consequence | Key Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Furnace Heating Element | 20-30 years (often the furnace's lifespan) | Reduced heating capacity; a maintenance issue | Ensure proper airflow (clean filters) |
| Gas Furnace Heat Exchanger | 15-20 years | Critical safety hazard (risk of carbon monoxide leak) | Requires annual professional inspection |
Ensure Your Lab's Heating Equipment is Safe and Efficient
Just like your home's furnace, your laboratory's heating equipment—from ovens and furnaces to hot plates—requires expert knowledge to ensure longevity and safety. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables. Our team can help you select the right heating solutions for your specific applications and provide guidance on maintenance to prevent costly downtime and safety risks.
Let our experts help you maintain a safe and productive lab environment. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation on your laboratory heating needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- What are silicon carbide heating elements used for? Reliable High-Temp Heating for Industrial Processes
- What kind of metal is used in heating elements? A Guide to Materials for Every Temperature & Atmosphere
- What is SiC elements? The Ultimate High-Temperature Heating Solution
- What is silicon carbide rod heated to high temperature used as? A Premier Heating Element for Extreme Environments
- What is the maximum temperature for silicon carbide heating element? The Real Limit for Your High-Temp Furnace



















