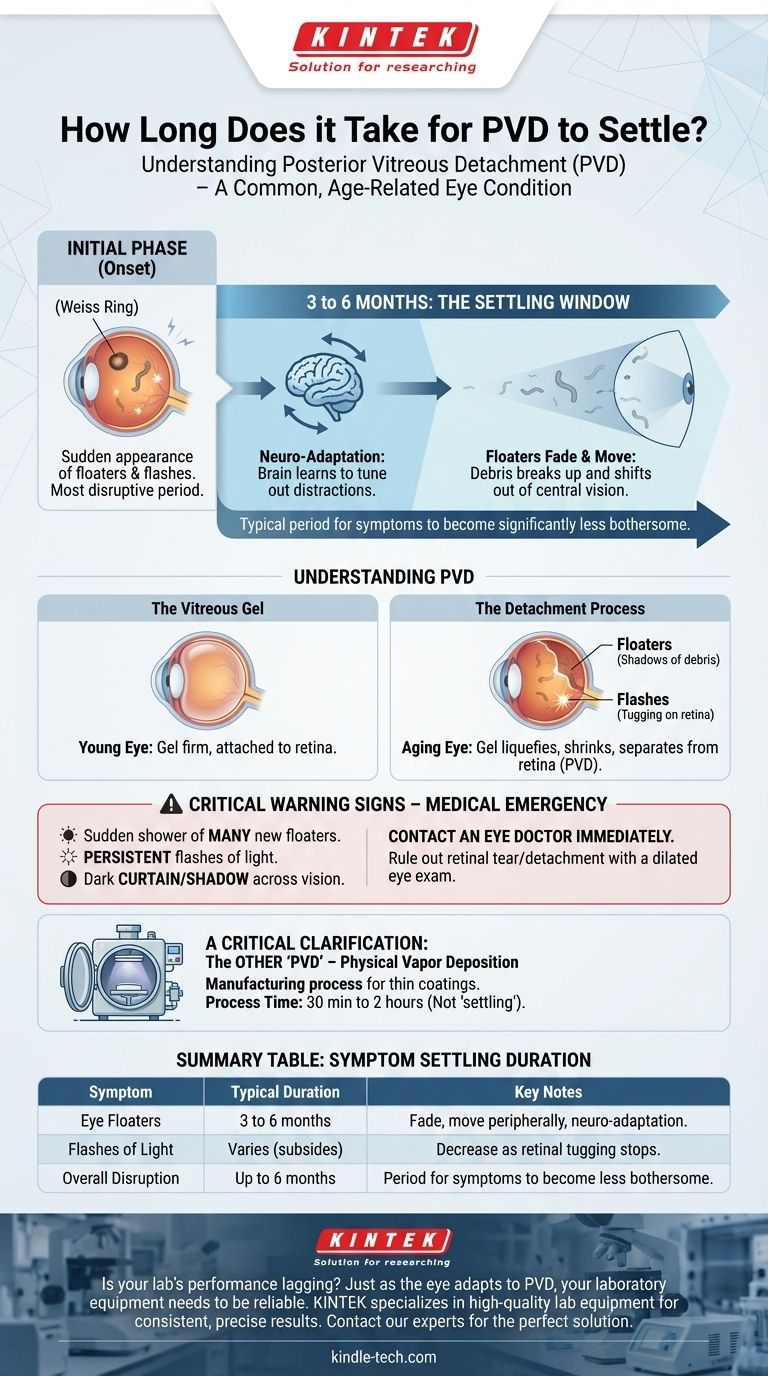
In the context of eye health, the term "PVD" refers to Posterior Vitreous Detachment, a common, age-related condition. The most noticeable symptoms, primarily eye floaters, typically take 3 to 6 months to settle or become significantly less bothersome. During this period, the floaters may fade, move out of your primary line of sight, and your brain learns to ignore them.
The core issue behind your question is likely concern over new and disruptive changes in your vision. While Posterior Vitreous Detachment (PVD) is a normal process, understanding its timeline and distinguishing it from more serious conditions is essential for your peace of mind and safety.

Understanding Posterior Vitreous Detachment (PVD)
A PVD is a natural event, not a disease. To understand why it happens and why symptoms occur, we need to look at the structure of the eye.
The Vitreous Gel
Your eye is filled with a clear, gel-like substance called the vitreous humor. In youth, this gel is firm and attached to the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye.
The Detachment Process
As you age, the vitreous gel naturally liquefies and shrinks. Eventually, it can pull away and separate from the retina. This separation is a Posterior Vitreous Detachment.
Why Floaters and Flashes Appear
The "settling" process you're asking about relates directly to the symptoms caused by this separation. Debris or condensed fibers in the shrinking gel cast shadows on the retina, which you perceive as floaters. Any tugging on the retina by the separating gel can stimulate it, causing you to see flashes of light.
The Timeline for Symptoms to Settle
The experience of a PVD evolves over several months. While the detachment itself may happen at a specific moment, the symptoms take time to resolve.
The Initial Phase
The onset of a PVD can be sudden and alarming, often marked by a new, large floater (sometimes called a Weiss Ring) and possibly flashes of light. This is the most disruptive phase.
The 3-6 Month Improvement Window
This is the typical period for symptoms to "settle." The floaters don't always vanish completely, but two things happen: the debris can break up and move out of your central vision, and your brain begins a process of neuro-adaptation, learning to tune out the visual distraction.
When Symptoms Persist
In some cases, floaters can remain bothersome for longer than six months. If they significantly impact your ability to perform important tasks like reading or driving, a surgical procedure to remove them may be considered.
A Critical Clarification: The Other "PVD"
It's important to note that "PVD" can also stand for Physical Vapor Deposition, a manufacturing process used to apply a thin, durable coating to materials to improve hardness or reduce friction.
Process Time, Not Settling Time
This coating process typically takes 30 minutes to 2 hours to complete in a vacuum chamber. It does not "settle" over time in the way a medical condition does. Given your use of the word "settle," you are almost certainly asking about the eye condition.
Important Considerations and When to See a Doctor
While a PVD is usually harmless, it carries a small but significant risk of causing a more serious problem.
PVD is Overwhelmingly Benign
For the vast majority of people, a PVD is a normal part of aging that resolves without causing permanent vision problems.
Critical Warning Signs
The separating vitreous gel can sometimes pull too hard on the retina, causing a retinal tear or detachment. This is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention to prevent vision loss.
Contact an eye doctor immediately if you experience:
- A sudden shower of many new floaters.
- Persistent flashes of light.
- A dark curtain or shadow moving across your field of vision.
The Need for a Professional Diagnosis
You should always have symptoms of a PVD evaluated by an optometrist or ophthalmologist. They can perform a dilated eye exam to confirm the diagnosis and, most importantly, rule out any damage to your retina.
Making the Right Choice for Your Health
Navigating a PVD is primarily about understanding the process and knowing the difference between normal symptoms and warning signs.
- If you have just been diagnosed: Your priority is to ensure you've had a thorough dilated eye exam to check for any retinal complications.
- If you are currently bothered by floaters: Understand that patience is key; your brain will very likely adapt over the next 3 to 6 months, making them far less noticeable.
- If you notice a sudden change or worsening of symptoms: Your only action should be to contact your eye doctor immediately for an evaluation.
Ultimately, being informed about the natural course of a PVD allows you to manage the experience calmly and confidently.
Summary Table:
| Symptom | Typical Duration to Settle | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Eye Floaters | 3 to 6 months | Floaters fade, move out of central vision, and your brain learns to ignore them (neuro-adaptation). |
| Flashes of Light | Varies, often subsides as the vitreous fully detaches | Usually decrease as the tugging on the retina stops. |
| Overall Disruption | Up to 6 months | This is the typical period for symptoms to become significantly less bothersome. |
Is your lab's performance lagging? Just as the eye adapts to PVD over time, your laboratory equipment needs to be reliable and efficient from the start. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, ensuring your research and analysis run smoothly without disruptive downtime. Let us help you achieve consistent, precise results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating



















