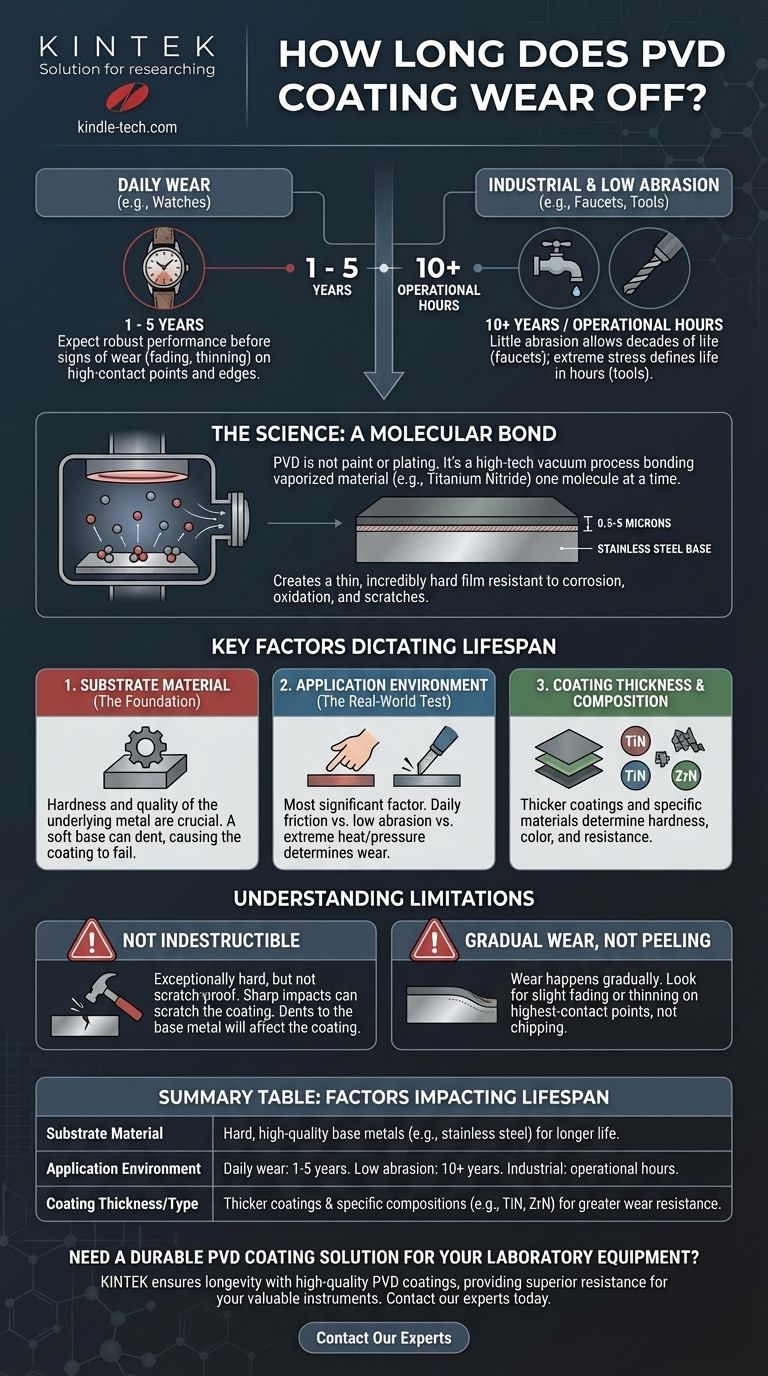
The lifespan of a PVD coating is not a single number but a wide spectrum, ranging from a few years to decades. For a daily-wear item like a watch, you can realistically expect 1 to 5 years of robust performance before signs of wear appear, while industrial applications can last for 10 years or more. This massive variance exists because the coating's longevity is less about the coating itself and more about the underlying material, its intended use, and the quality of the application process.
The durability of a Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) finish is not an isolated feature. It is a direct result of the entire system: the base metal it's bonded to, the coating's thickness and composition, and the specific abrasive or environmental stress it is designed to withstand.

What "PVD Coating" Truly Means
A Molecular Bonding Process
Physical Vapor Deposition is not paint or plating; it's a high-tech vacuum process that bonds a coating to a surface one molecule at a time.
A solid material, such as titanium nitride, is vaporized in a vacuum chamber at high temperatures (250°C to 750°C). This vapor then condenses and bonds with the target object—often stainless steel—on a molecular level.
The Result is a Thin, Hard Film
This process creates an incredibly thin—typically 0.5 to 5 microns—yet extremely hard and durable layer.
The resulting surface is highly resistant to corrosion, oxidation, and scratches, which is why it vastly outperforms traditional finishing methods.
The Key Factors That Dictate Lifespan
The reason one PVD coating lasts two years and another lasts twenty is due to a few critical variables.
The Substrate Material (The Foundation)
The performance of the PVD coating is fundamentally tied to the hardness and quality of the metal beneath it.
A super-hard coating on a soft base metal will fail if the base metal gets dented or deeply scratched. The coating is only as strong as its foundation.
The Application Environment (The Real-World Test)
This is the most significant factor. A PVD-coated watch bracelet faces constant friction against skin, desks, and cuffs, limiting its pristine appearance to a few years.
In contrast, a PVD-coated faucet or industrial cutting tool experiences a different kind of wear. The faucet sees little abrasion and can last for decades, while the tool endures extreme heat and pressure, with its lifespan measured in operational hours, not years.
Coating Thickness and Composition
Thicker PVD coatings generally offer greater wear resistance and a longer lifespan.
Furthermore, the specific material used for the coating (e.g., Titanium Nitride vs. Zirconium Nitride) determines its hardness, color, and resistance properties, directly impacting its durability for a given task.
Understanding the Limitations
PVD is Not Indestructible
While PVD is exceptionally hard and scratch-resistant, it is not scratch-proof. A sharp, forceful impact with an abrasive surface can still scratch the coating.
Crucially, because the coating is so thin, it does not protect the underlying object from dents. A significant impact will dent the base metal and the PVD coating along with it.
Wear is Gradual, Not Sudden
A quality PVD coating does not chip or peel like paint. Instead, wear happens gradually over a long period.
You will typically notice it first as a slight fading or thinning on the highest-contact points and sharpest edges of the object.
Color Influences Perceived Wear
The visibility of wear depends heavily on the color contrast between the coating and the substrate.
A black PVD coating on a silver-colored stainless steel watch will show scratches much more obviously than a gold-tone PVD coating, as the underlying steel color is more exposed.
How to Apply This to Your Product
Understanding the goal of the PVD coating on your specific item is key to setting realistic expectations for its longevity.
- If your primary focus is a daily-wear item (e.g., watch, ring): Expect several years of excellent durability, but know that high-wear areas like clasps and edges will eventually show signs of fading.
- If your primary focus is household fixtures (e.g., faucets, door handles): You can expect a very long lifespan, often 10 years or more, as these items do not face constant, abrasive friction.
- If your primary focus is high-performance tools: The coating's purpose is to enhance operational life under extreme stress, vastly outperforming uncoated alternatives but still being a consumable part of the tool.
Ultimately, PVD is the most durable coating commercially available today, and its lifespan is a direct function of the quality of its application and the demands of its environment.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on PVD Coating Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Substrate Material | Hard, high-quality base metals (e.g., stainless steel) provide a strong foundation for longer life. |
| Application Environment | Daily wear (watches): 1-5 years. Low abrasion (faucets): 10+ years. Industrial tools: lifespan in operational hours. |
| Coating Thickness/Type | Thicker coatings and specific compositions (e.g., TiN, ZrN) offer greater hardness and wear resistance. |
Need a Durable PVD Coating Solution for Your Laboratory Equipment?
At KINTEK, we understand that the longevity of your lab equipment's finish is critical for both performance and appearance. Our expertise in high-quality PVD coatings ensures a molecular bond that provides superior resistance to corrosion, oxidation, and scratches, extending the life of your valuable instruments.
Whether you are coating components for analytical instruments, sample handling tools, or other laboratory devices, KINTEK delivers durable, application-specific solutions. Contact our experts today to discuss how our PVD coating services can enhance the durability and value of your laboratory products.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















