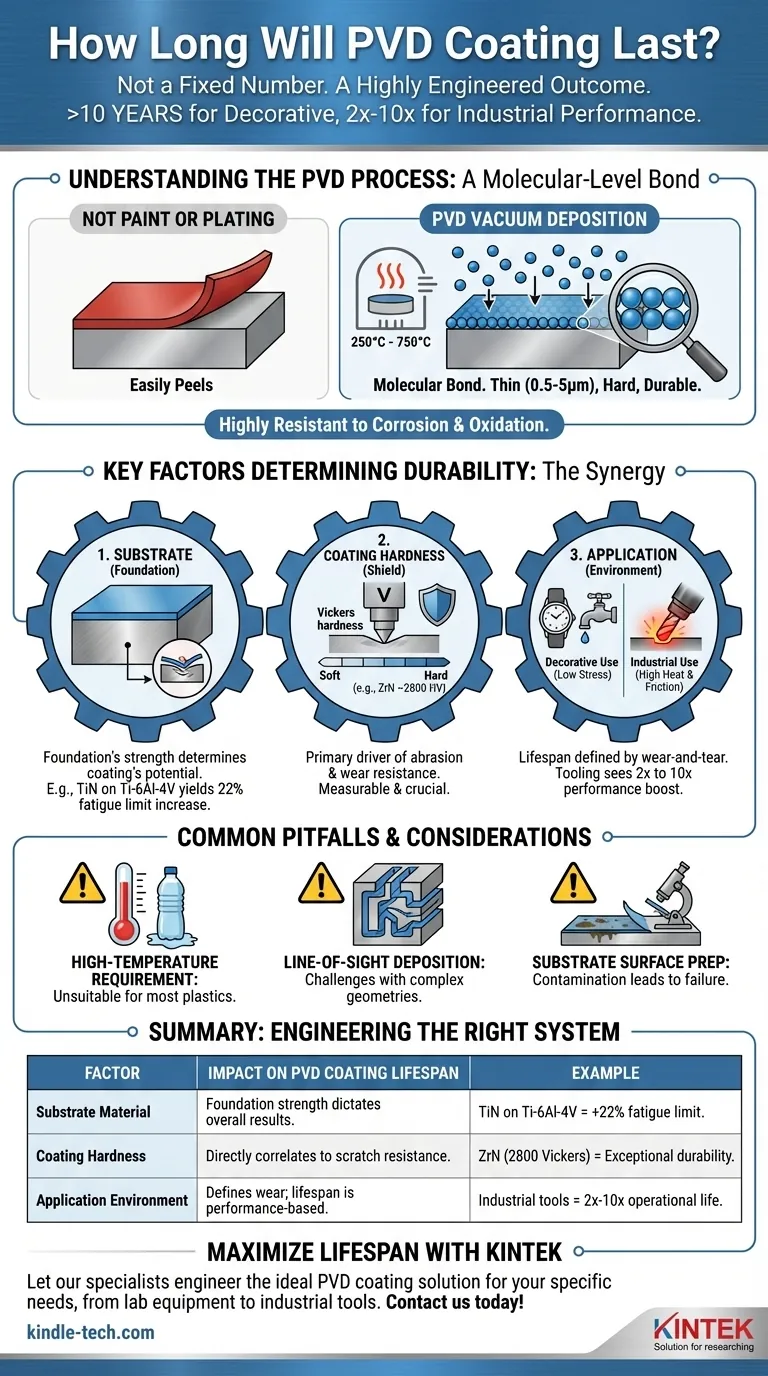
The lifespan of a PVD coating is not a fixed number. It is a highly engineered outcome that can range from over ten years for decorative finishes to a 10x performance increase for industrial tools. The longevity is determined less by time and more by the interaction between the coating itself, the material it's applied to, and the specific wear-and-tear it endures in its application.
The durability of a PVD coating is not an inherent property but a function of a complete system. Its lifespan depends entirely on the synergy between the substrate material, the coating's specific properties, its thickness, and the environment it operates in.

Understanding the PVD Process
A Molecular-Level Bond
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is not a paint or a simple plating. It is an advanced vacuum deposition process where a solid material is vaporized and then deposited atom by atom onto the surface of a part.
This process, conducted at high temperatures between 250°C and 750°C, creates a molecular bond with the substrate. The result is an extremely thin—typically 0.5 to 5 microns—yet exceptionally hard and durable surface layer.
More Than Just a Layer
Because it changes the properties of the metal on a molecular level, PVD coating is highly resistant to corrosion and oxidation. It is not something that can easily peel or flake away.
The Key Factors That Determine Durability
The vast range in PVD lifespan comes from the interplay of several critical variables. Understanding these factors is the key to achieving the desired performance.
The Foundation: Substrate Material
The properties of the PVD coating are directly influenced by the material underneath it. A PVD film can only be as strong as its foundation.
For example, a Titanium Nitride (TiN) coating applied to a robust Ti-6Al-4V alloy can increase its fatigue limit by 22%. The same coating on a softer metal would not yield the same performance benefits because the underlying material would fail first.
The Shield: Coating Hardness
The hardness of the specific coating material is a primary driver of its resistance to abrasion and wear. This is a measurable and crucial factor.
For instance, a Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) PVD finish, often used for "Lifetime Brass" fixtures, can have a hardness of 2800 Vickers. This extreme hardness is what provides its exceptional scratch resistance.
The Application: Environment and Use
How the coating is used is arguably the most important factor. A decorative PVD finish on a watch case sees vastly different stress than a PVD coating on an industrial cutting tool.
For tooling applications, "lifespan" is measured in operational performance. A PVD-coated tool can see its useful life increase by 2 to 3 times, with some applications showing improvements exceeding 10 times that of an uncoated tool. This is due to the coating's resistance to heat and friction during high-stress operations.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
To make an informed decision, you must understand the limitations of the process.
High-Temperature Requirement
The PVD process requires high temperatures. This means the substrate material must be able to withstand this heat without deforming or losing its essential properties. This makes PVD unsuitable for most plastics and some low-melting-point metals.
Line-of-Sight Deposition
PVD is a "line-of-sight" process. The vaporized material travels in a straight line to the substrate. This can make it challenging to achieve a perfectly uniform coating on parts with complex internal geometries or deep, narrow holes.
Substrate Surface Preparation
The bond strength of the PVD coating is highly dependent on the cleanliness and preparation of the substrate surface. Any contamination can lead to poor adhesion and premature failure, making meticulous preparation a non-negotiable step.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the lifespan of a PVD coating, you must align the coating system with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is decorative durability (e.g., fixtures, watches): Prioritize a hard coating material like Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) on a stable substrate like stainless steel for maximum scratch and corrosion resistance.
- If your primary focus is industrial performance (e.g., cutting tools, dies): Focus on the synergy between the tool's base metal, a coating like Titanium Nitride (TiN), and the specific heat and friction demands of the application.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance: Ensure the chosen coating is chemically inert for your specific environment and that the process provides complete, uniform coverage over the entire exposed surface.
Ultimately, the longevity of a PVD coating is a direct result of engineering the right material system for a specific purpose.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on PVD Coating Lifespan | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Substrate Material | Determines the foundation's strength; a stronger base yields better results. | TiN coating on Ti-6Al-4V alloy increases fatigue limit by 22%. |
| Coating Hardness | Directly correlates to abrasion and scratch resistance. | ZrN coating hardness of 2800 Vickers provides exceptional durability. |
| Application Environment | Defines the wear-and-tear; lifespan is measured by performance. | Industrial cutting tools see a 2x to 10x increase in operational life. |
Maximize the lifespan of your components with the right PVD coating solution.
At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables, including advanced PVD coating systems. We understand that the right coating is a synergy of substrate, material, and application. Our expertise can help you select the ideal PVD coating to achieve superior durability, whether for decades of decorative use or a 10x performance boost for your industrial tools.
Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and let our specialists engineer a solution that extends the life and enhances the performance of your laboratory equipment. Get in touch via our contact form for a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Tweezers
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why can graphite withstand heat? Unlocking Its Extreme Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What is the temperature resistance of graphite? Unlocking Its High-Temp Potential in Your Lab
- What is the graphite furnace used for? Achieve Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C in a Controlled Environment
- How is synthetic graphite manufactured? A Deep Dive into the High-Temperature Process
- What is the maximum working temperature of graphite? Unlock High-Temp Performance with the Right Atmosphere



















