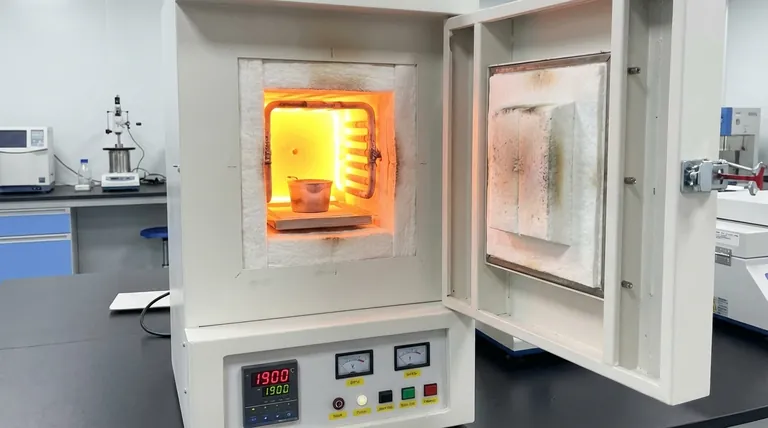
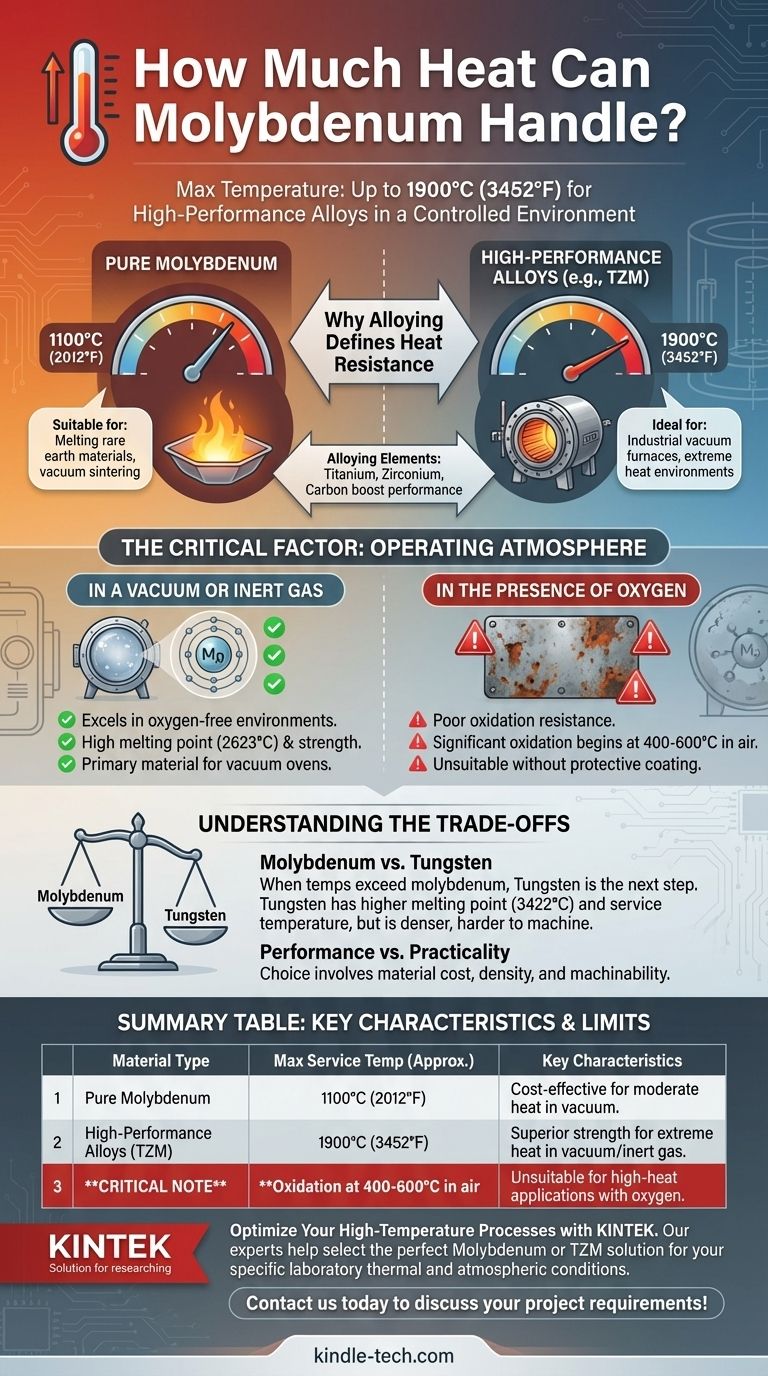
In a controlled, oxygen-free environment, high-performance molybdenum alloys can handle temperatures up to approximately 1900°C (3452°F). However, the heat resistance of pure, unalloyed molybdenum is significantly lower, and its performance in the presence of oxygen degrades rapidly at much lower temperatures.
Molybdenum is an exceptional refractory metal for high-heat applications, but its maximum service temperature is not a single number. It is critically dependent on two factors: the specific alloy being used and the surrounding atmosphere.

Why Alloying Defines Heat Resistance
The term "molybdenum" often refers to a family of materials. The performance difference between its pure form and its engineered alloys is substantial, especially at extreme temperatures.
Pure Molybdenum
Pure molybdenum components, such as evaporation boats, are typically suitable for service temperatures up to around 1100°C (2012°F).
This level of performance is sufficient for applications like melting certain rare earth materials or for specific sintering processes in a vacuum.
High-Performance Molybdenum Alloys
To push the temperature limits, molybdenum is alloyed with other elements. The most common is TZM, a molybdenum alloy containing small amounts of titanium, zirconium, and carbon.
Alloys like TZM and Lanthanum Molybdenum (Mo-La) can endure temperatures up to approximately 1900°C (3452°F). This makes them ideal for demanding components inside industrial vacuum furnaces and other high-temperature environments.
The Critical Factor: Operating Atmosphere
Temperature tolerance figures for molybdenum and its alloys almost always assume the material is being used in a vacuum or an inert gas environment. This is the single most important consideration for its practical application.
In a Vacuum or Inert Gas
Molybdenum excels in oxygen-free environments. Its high melting point (2623°C) and strength at elevated temperatures are why it is a primary material for constructing industrial vacuum ovens and their internal components.
In the Presence of Oxygen
Molybdenum has poor resistance to oxidation at high temperatures. In air, significant oxidation can begin at temperatures as low as 400-600°C. This makes it entirely unsuitable for high-heat applications exposed to the atmosphere without a protective coating.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a refractory metal involves balancing thermal performance against other factors. Molybdenum is often chosen for a specific combination of properties, but it is not always the superior choice.
Molybdenum vs. Tungsten
When temperatures exceed molybdenum's capabilities, tungsten is often the next logical step. As the reference material notes, tungsten is a better option for even more extreme heat requirements.
Tungsten has a significantly higher melting point (3422°C) and can be used at higher service temperatures than even the best molybdenum alloys.
Performance vs. Practicality
The choice between molybdenum and tungsten often comes down to more than just temperature. Factors like material cost, density, and ease of machining also play a critical role in the final engineering decision.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires a clear understanding of the environmental and thermal demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is moderate heat (up to 1100°C) in a vacuum: Pure molybdenum is a cost-effective and reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is extreme heat (up to 1900°C) in a vacuum or inert atmosphere: TZM and other high-performance molybdenum alloys are the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is operating in an oxygen-rich environment or at temperatures above 1900°C: You must consider alternative materials, such as tungsten or specialized ceramics.
Ultimately, matching the specific molybdenum alloy to your precise thermal and atmospheric conditions is the key to successful application.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Max Service Temperature (Approx.) | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Pure Molybdenum | 1100°C (2012°F) | Cost-effective for moderate heat in vacuum environments |
| High-Performance Alloys (e.g., TZM) | 1900°C (3452°F) | Superior strength for extreme heat in vacuum/inert gas |
| Critical Note | Oxidation begins at 400-600°C in air | Unsuitable for high-heat applications with oxygen exposure |
Optimize your high-temperature processes with the right materials.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including vacuum furnace components made from advanced molybdenum alloys like TZM. Whether your application requires moderate heat resistance or extreme temperature capabilities up to 1900°C, our experts can help you select the perfect solution for your laboratory's specific thermal and atmospheric conditions.
Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our materials can enhance your efficiency and results.
Get in touch with our specialists now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature for silicon carbide heating element? The Real Limit for Your High-Temp Furnace
- What is the best electric heating element? Match the Right Material to Your Application's Needs
- What is used for high temperature heating? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heating Elements
- What is the design and application of PTC surface heaters? Optimize Direct Contact Heating for Laboratory Precision
- What advantages do carbon/carbon (C/C) composite resistors offer? High-Resilience Heating for Si2N2O Synthesis
- What is the maximum operating temperature of molybdenum? It Depends on Your Atmosphere
- How effective is electrical resistance heating? It's 100% efficient at the point of use.
- What are the technical advantages of using graphite rods? Boost Precision in 1200°C High-Temperature Operations



















