Determining the cost of a pyrolysis plant is not a matter of looking up a simple price tag; the final investment can range from tens of thousands of dollars for a small-scale batch unit to several million dollars for a large, fully automated industrial facility. The price is fundamentally tied to the plant's capacity, the type of waste it will process, the level of automation, and the quality of the final products you intend to produce.
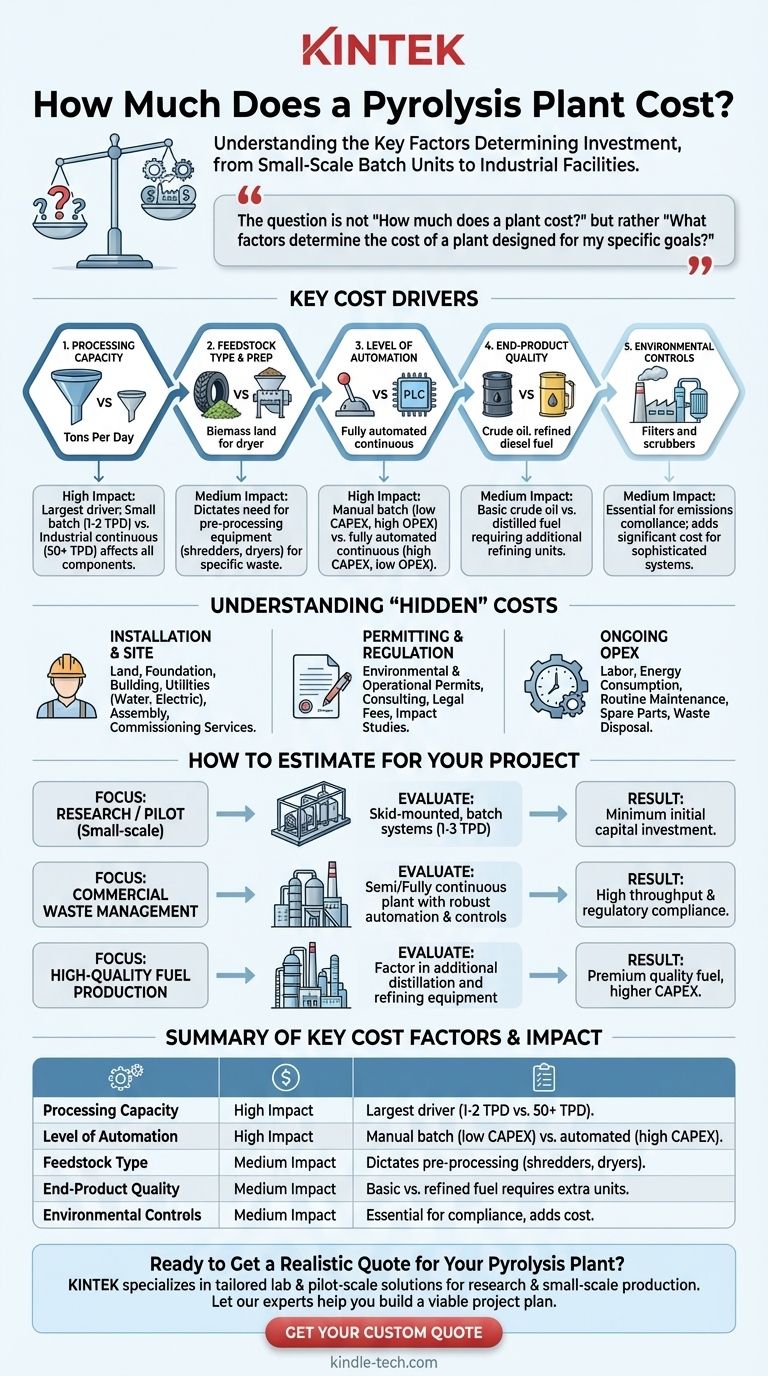
The question is not "How much does a plant cost?" but rather "What factors determine the cost of a plant designed for my specific goals?" Understanding these key cost drivers—from processing capacity to environmental controls—is the only way to develop a realistic budget for a pyrolysis project.

Why a Single Price Tag Doesn't Exist
A pyrolysis plant is not an off-the-shelf product. It's a complex industrial system tailored to a specific feedstock and desired output. The vast price range is a direct result of the significant differences in system design and operational scale.
Batch vs. Continuous Systems
A batch system is the simplest and least expensive type. Waste is loaded into a reactor, the process runs, and then the system is cooled and emptied before the next cycle can begin. This is suitable for very small operations or research.
In contrast, a fully continuous system operates 24/7 with automated feeding and discharge mechanisms. This design maximizes throughput and efficiency but involves far more complex machinery and control systems, leading to a much higher initial investment.
Small-Scale vs. Industrial-Scale
A small, skid-mounted plant might process 1-2 tons of waste per day. An industrial-scale facility could be designed to handle 50 tons or more per day. This difference in scale affects not just the size of the reactor but the entire infrastructure for material handling, storage, and processing.
Key Factors Driving Pyrolysis Plant Costs
To build an accurate financial model, you must evaluate how each of the following components contributes to the total capital expenditure.
1. Processing Capacity (Tons Per Day)
This is the single most significant cost driver. A plant designed to process 10 tons of plastic per day will be substantially more expensive than a 1-ton-per-day model because every component—from the reactor to the storage tanks—must be larger and more robust.
2. Feedstock Type and Preparation
The type of waste dictates the need for pre-processing equipment. Processing whole tires requires powerful shredders, while wet organic waste or biomass may need large industrial dryers. Each additional pre-processing step adds a significant capital cost.
3. Level of Automation
A manually operated batch plant requires constant human intervention, keeping equipment costs low but operational costs high. A fully automated continuous plant uses PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) systems to manage everything from feeding to temperature control, drastically increasing the initial price but reducing long-term labor needs.
4. End-Product Quality and Upgrading
A basic plant produces a crude pyrolysis oil, carbon black (char), and non-condensable gas. If you require higher-quality products, such as distilled fuel comparable to diesel, you will need to invest in additional post-processing equipment like distillation units and refining systems.
5. Environmental Control Systems
Modern plants must meet strict emissions standards. This requires sophisticated gas scrubbing and filtration systems to handle exhaust and treat syngas before it's used or flared. These environmental controls are non-negotiable and represent a major part of the budget.
Understanding the "Hidden" Costs
The price quoted for the core equipment is only one piece of the puzzle. Overlooking associated project costs can lead to significant budget overruns.
Installation and Site Preparation
The cost of the land, foundation work, building construction, and utility connections (water, electricity) are all major expenses. Assembling and commissioning the plant also requires specialized labor and engineering services.
Permitting and Regulatory Hurdles
Securing environmental and operational permits can be a lengthy and expensive process involving consultants, legal fees, and impact studies. This phase should be factored into the project timeline and budget from the very beginning.
Ongoing Operational Expenses (OPEX)
Your financial plan must account for long-term costs beyond the initial purchase. This includes labor, energy consumption (electricity and/or supplementary fuel), routine maintenance, spare parts, and waste disposal for any non-valuable byproducts.
How to Estimate the Cost for Your Project
The first step toward a realistic budget is to clearly define your project's primary objective.
- If your primary focus is research or a small-scale pilot project: Start by evaluating skid-mounted, batch-type systems with a capacity of 1-3 tons per day, as this will keep initial capital investment at a minimum.
- If your primary focus is commercial waste management: Your model must be based on a semi-continuous or fully continuous plant with robust automation and environmental controls to ensure high throughput and regulatory compliance.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality fuel: Factor in the significant additional cost of distillation and refining equipment alongside the core pyrolysis unit.
Understanding these variables is the essential first step in transforming a general inquiry into a viable project plan.
Summary Table:
| Key Cost Factor | Impact on Price | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Capacity | High | Largest driver; small batch (1-2 TPD) vs. industrial continuous (50+ TPD) |
| Level of Automation | High | Manual batch (low CAPEX) vs. fully automated continuous (high CAPEX, low OPEX) |
| Feedstock Type | Medium | Dictates need for pre-processing equipment (e.g., shredders, dryers) |
| End-Product Quality | Medium | Basic crude oil vs. distilled fuel requiring additional refining units |
| Environmental Controls | Medium | Essential for emissions compliance; adds significant cost |
Ready to Get a Realistic Quote for Your Pyrolysis Plant?
Understanding the variables is the first step. KINTEK specializes in providing tailored lab and pilot-scale pyrolysis solutions for research and small-scale production. We help you navigate the complexities of capacity, automation, and feedstock to find the right system for your budget and goals.
Contact us today for a detailed consultation and let our experts help you build a viable project plan.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time



















