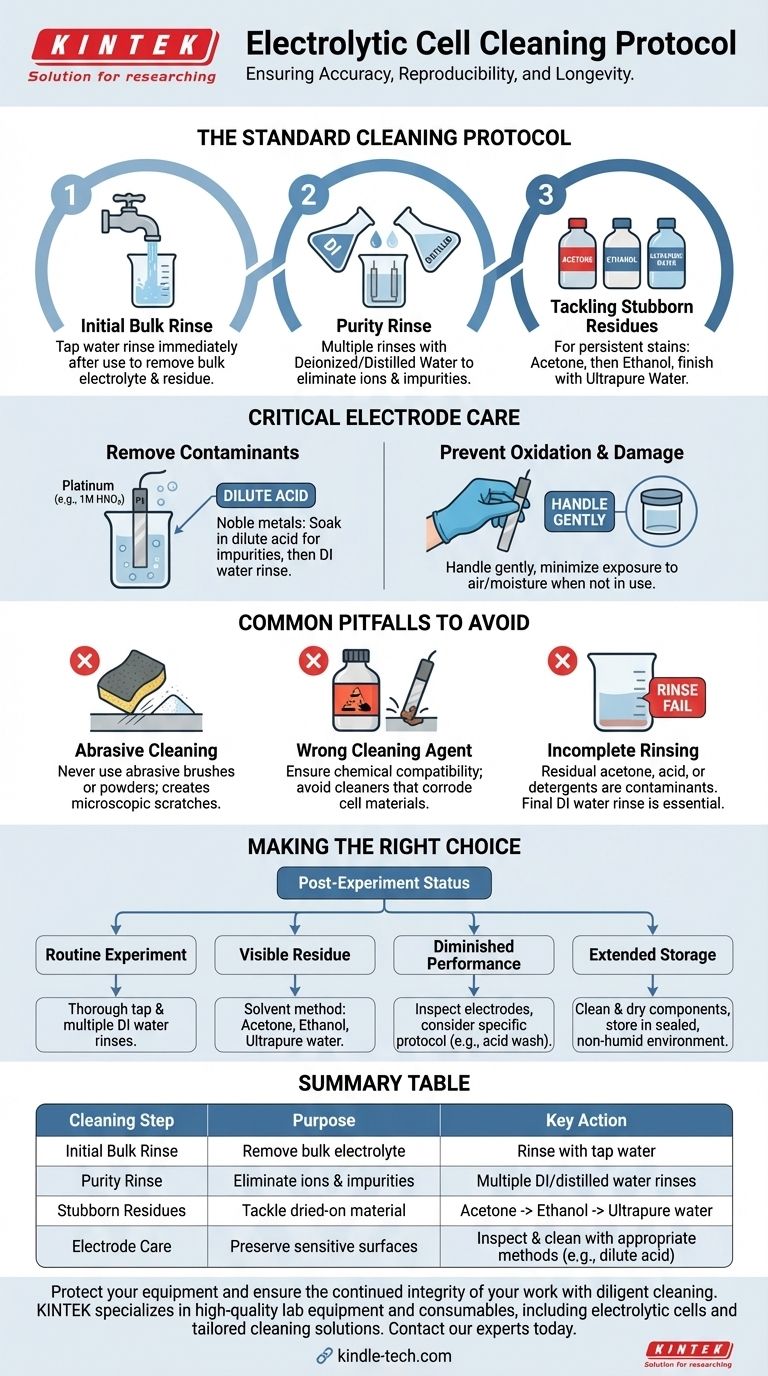
Properly cleaning an electrolytic cell after use is a critical step that goes far beyond simple washing. The standard procedure begins with a thorough rinse using tap water to remove the bulk of the residual electrolyte and reaction products. This is immediately followed by multiple rinses with deionized or distilled water to eliminate any remaining ions and impurities, ensuring the cell is chemically clean for the next experiment.
The goal of cleaning an electrolytic cell is not merely to make it look clean, but to prevent cross-contamination and preserve the sensitive surfaces of the electrodes. This meticulous process is fundamental to ensuring the accuracy, reproducibility, and integrity of your experimental results.

The Standard Cleaning Protocol
A consistent, multi-stage cleaning process is essential for maintaining your equipment. Each step serves a specific purpose, from removing bulk material to achieving chemical purity.
Step 1: The Initial Bulk Rinse
Immediately after your experiment, disassemble the cell and rinse all components with standard tap water. This first pass is designed to wash away the majority of the electrolyte solution and any loose product residue before they have a chance to dry and adhere to the surfaces.
Step 2: The Purity Rinse
After the tap water rinse, wash the cell and its components several times with deionized (DI) or distilled water. This is a critical step that removes the ions and minerals present in tap water, which could otherwise interfere with subsequent reactions. For highly sensitive work, a final rinse with ultrapure water (resistivity >18.2 MΩ・cm) is recommended.
Step 3: Tackling Stubborn Residues
For persistent stains or dried-on material, a more aggressive cleaning with solvents may be necessary. A common and effective sequence is to first scrub or sonicate the inner walls with acetone, followed by a rinse with ethanol, and concluding with the final ultrapure water rinse.
Beyond the Cell Body: Critical Electrode Care
The electrodes are the active heart of your cell and require special attention. Their surface condition directly impacts reaction efficiency and data quality. Cleaning them improperly can cause irreversible damage.
Why Electrode Cleaning is Different
Unlike the inert glass body, electrodes have catalytically active surfaces that can be easily contaminated or damaged. Cleaning must remove residue without altering the electrode's surface chemistry or morphology.
Removing Surface Contaminants
Regularly inspect electrodes for any visible contamination or discoloration. For noble metal electrodes, such as platinum, a common method is to soak them in a dilute acid (e.g., 1M nitric acid) to dissolve metallic impurities, followed by a thorough rinsing with deionized water.
Preventing Oxidation and Damage
Always handle electrodes gently to avoid scratching or deforming their surfaces. For metal electrodes prone to oxidation, minimize their exposure to air and moisture when not in use.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Mistakes during cleaning can be as detrimental as running a contaminated experiment. Being aware of these common errors is key to preserving your equipment.
The Risk of Abrasive Cleaning
Never use abrasive brushes or powders on the cell's interior surfaces, and especially not on the electrodes. Physical scouring can create microscopic scratches that alter electrode surface area and can become sites for contamination to accumulate.
Choosing the Wrong Cleaning Agent
The most critical rule is to use a cleaner that will not corrode or react with the cell materials or electrodes. A solvent that is safe for glass may be highly corrosive to a specific electrode material. Always verify chemical compatibility before use.
The Danger of Incomplete Rinsing
Failing to thoroughly rinse away a cleaning agent is a common source of contamination. Residual acetone, acid, or detergents can interfere with your next experiment just as much as leftover electrolyte. The final DI water rinse is non-negotiable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your post-experiment procedure should be tailored to the nature of the experiment you just completed and your plans for the equipment.
- If you just finished a routine experiment: A thorough tap water rinse followed by multiple deionized water rinses is sufficient.
- If you see visible residue or stubborn stains: Employ the solvent method, rinsing with acetone, then ethanol, and finishing with ultrapure water.
- If electrode performance seems diminished: Inspect the electrodes and consider a specific cleaning protocol, such as a dilute acid wash for noble metals.
- If storing the cell for an extended period: Ensure all components are perfectly clean and dry, and store them in a non-humid environment, sealing the cell container.
Adopting this diligent cleaning and maintenance routine is the best way to protect your equipment and ensure the continued integrity of your work.
Summary Table:
| Cleaning Step | Purpose | Key Action |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Bulk Rinse | Remove bulk electrolyte & residue | Rinse with tap water immediately after use |
| Purity Rinse | Eliminate ions & impurities | Wash multiple times with deionized/distilled water |
| Stubborn Residues | Tackle dried-on material | Use acetone, then ethanol, finish with ultrapure water |
| Electrode Care | Preserve sensitive surfaces | Inspect & clean with appropriate methods (e.g., dilute acid for Pt) |
Ensure the longevity of your lab equipment and the accuracy of your experiments. Proper cleaning is essential for reliable results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including electrolytic cells and cleaning solvents tailored to your laboratory's specific needs. Contact our experts today to find the right solutions for your maintenance protocols and ensure your equipment performs flawlessly, experiment after experiment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- Double Layer Five-Port Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- H Type Electrolytic Cell Triple Electrochemical Cell
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
People Also Ask
- How should the body of an electrolytic cell be maintained for longevity? Extend Your Equipment's Lifespan
- How should the five-port water bath electrolytic cell be operated during an experiment? Master Precise Control for Reliable Results
- What material is the five-port water bath electrolytic cell made of? High Borosilicate Glass & PTFE Explained
- How should the five-port water bath electrolytic cell be cleaned for maintenance? A Step-by-Step Guide to Reliable Results
- What are the proper storage procedures for the multifunctional electrolytic cell? Protect Your Investment and Ensure Data Accuracy



















